
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-10-20 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Introduction to Vacuum Mold Casting
● Step 1: Designing the 3D Model
● Step 2: Creating the Master Pattern
● Step 3: Fabrication of the Silicone Mold
● Step 4: Vacuum Casting Process
● Step 5: Demolding and Post-Processing
● Applications of Vacuum Mold Casting
● Advantages of Vacuum Mold Casting
>> 1. How many parts can a silicone mold produce in vacuum casting?
>> 2. Can vacuum casting be used for large parts?
>> 3. What materials are commonly used in vacuum casting?
>> 4. How does vacuum casting differ from injection molding?
>> 5. Is post-processing always necessary after vacuum casting?
Vacuum mold casting is a high-precision, cost-effective manufacturing technology widely used in rapid prototyping and small-batch production. It combines silicone mold-making with vacuum-assisted resin casting to produce parts with excellent detail, smooth surfaces, and minimal defects. This process is ideal for prototypes, functional testing models, and limited production runs, especially when traditional injection molding is too costly or slow for small quantities.
This guide presents a detailed, step-by-step explanation of Vacuum Mold Casting, from initial design to final finishing. It is structured to help product designers, engineers, and manufacturers maximize the benefits of this versatile technique.
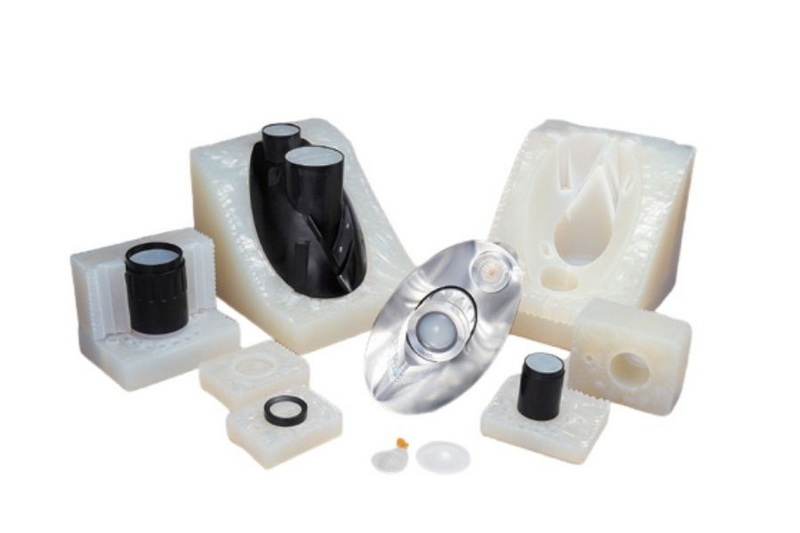

Vacuum mold casting replicates parts by pouring liquid resin into silicone molds inside a vacuum chamber. The vacuum removes air bubbles from the liquid resin, preventing common casting defects like voids and bubbles that compromise mechanical strength and surface quality. Silicone molds, made from master patterns, enable fast, low-cost creation of molds compared to metal tooling.
Such molds suit manufacturing up to 20 parts per mold, making this technology perfect for rapid prototyping cycles and lower-volume production where flexibility, accuracy, and surface finish are crucial.
The process begins with creating a precise 3D model in CAD software such as SolidWorks, AutoCAD, or CATIA. Attention to detail in wall thickness, draft angles, and mold release features ensures mold durability and easy demolding.
- Ensure uniform wall thickness to prevent sink marks and warping.
- Incorporate draft angles (typically 1-2 degrees) to facilitate mold removal.
- Avoid undercuts unless using flexible molds or inserts.
- Use 3D scanning to capture dimensions of existing physical objects for reverse engineering.
Final surface finishes and textures should be defined in the CAD model because these details transfer directly to the mold and final cast parts.
The master pattern is the physical replica of the 3D model used to create the silicone mold. It needs to be high quality with smooth surfaces for the best mold fidelity.
Master patterns are made by:
- CNC machining from metal, resin, or plastic blocks.
- 3D printing via SLA (stereolithography) or SLS (selective laser sintering) techniques.
Post-processing includes sanding, polishing, and painting to achieve the desired finish and protect the model during mold making. Master patterns should withstand the silicone curing temperature (about 40°C) without deformation.
With the master pattern ready, the mold is built by enclosing the pattern in a casting box or frame. Liquid silicone rubber is mixed and poured over the master pattern. This setup is then placed in an oven at around 40°C to cure for 8-16 hours.
After curing, the silicone mold is carefully cut and the master pattern removed, leaving a cavity that replicates the master model precisely. Mold release agents are often applied to the master to ease mold removal and prolong mold life—generally 15 to 20 casting cycles.
The flexibility of silicone molds allows demolding of complex geometries, including certain undercuts, without damaging the mold or the part.
The heart of vacuum mold casting is the vacuum-assisted resin filling stage:
1. Prepare the polyurethane or other casting resin by mixing two components and adding pigments or additives as needed.
2. Preheat the resin to approximately 40°C for better flowability.
3. Place the silicone mold inside a vacuum chamber.
4. Pour the resin into the mold cavity.
5. Apply vacuum to degas the resin, removing trapped air bubbles.
6. Maintain the vacuum while the resin cures in the mold.
The vacuum environment ensures the resin penetrates every detail of the mold without bubbles or voids, producing parts with a smooth finish and excellent mechanical properties. After curing, the vacuum is released and the mold opened.
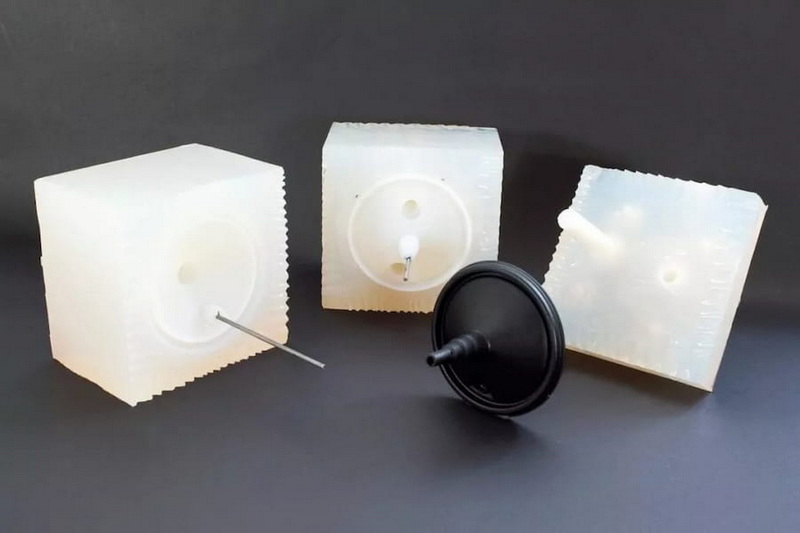
Once cured, the part is removed from the mold by flexing the silicone or cutting the mold along predetermined parting lines. Excess material and sprues are trimmed.
Parts may undergo secondary finishing processes for specific applications, including:
- Sanding and polishing for enhanced surface quality.
- Painting or coating for aesthetic or protective purposes.
- Assembly with inserts or fittings.
Final quality control verifies dimensional accuracy and surface integrity.
Vacuum casting excels in producing:
- Functional prototypes for design validation and testing.
- Low-volume production runs for market testing.
- Components for automotive, aerospace, electronics, consumer goods, and medical fields.
- Visual models for presentations and marketing.
It is particularly valuable when tight deadlines and cost constraints prohibit expensive tooling.
- High Detail Accuracy: Silicone molds capture intricate features and textures.
- Bubble-Free Results: Vacuum removes air, avoiding defects common in gravity casting.
- Versatile Material Use: Polyurethane and other resins can mimic various material properties such as flexibility or hardness.
- Short Lead Times: Parts can be ready within days to a week.
- Cost Efficiency: Ideal for runs from 1 to 20-30 parts without the expense of metal molds.
- Flexibility: Multiple iterations with minimal setup changes.
Vacuum mold casting offers a fast, economical, and precise route from prototype to small-batch production. The process leverages silicone molds and vacuum technology to produce bubble-free, highly detailed parts suitable for functional use or market introduction. By mastering each step—design, master pattern creation, mold making, vacuum casting, and finishing—businesses can greatly enhance their rapid prototyping capabilities and respond swiftly to product development needs.

Typically, a silicone mold lasts for about 15 to 20 casting cycles before degradation impacts the dimensional accuracy and surface finish of the parts.
Yes, vacuum casting can accommodate relatively large parts, though the size is limited by the mold box and vacuum chamber dimensions.
Polyurethane resins are most common, offering a variety of hardness levels and colors. Other materials include silicone and epoxy resins depending on application requirements.
Vacuum casting uses flexible silicone molds and operates under vacuum to remove air bubbles, suitable for low-volume production. Injection molding uses metal molds and high pressure, ideal for mass production with higher upfront tooling costs.
While vacuum casting parts have smooth surfaces, additional processes like sanding, painting, or machining may be performed to meet specific aesthetic or functional requirements.
[1](https://formlabs.com/blog/vacuum-casting-urethane-casting-polyurethane-casting/)
[2](https://www.immould.com/vacuum-casting/)
[3](https://an-prototype.com/ultimate-guide-to-vacuum-casting/)
[4](https://objectify.co.in/a-comprehensive-guide-to-vacuum-casting-everything-you-need-to-know/uncategorized/)
[5](https://xdmining.in/2024/10/02/elementor-11005/)
[6](https://ame-3d.co.uk/news/a-complete-guide-to-vacuum-casting-polyurethane-casting)
[7](https://blog.isa.org/what-are-vacuum-casting-factories-a-comprehensive-guide-to-the-manufacturing-process)
[8](https://leadrp.net/blog/overview-of-vacuum-casting/)
[9](https://www.kemalmfg.com/complete-guide-to-vacuum-casting/)
[10](https://www.zintilon.com/blog/vacuum-casting/)
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal