
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-10-20 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Understanding Vacuum Mold Casting
● Key Benefits of Vacuum Mold Casting
>> Cost-Efficiency for Short Runs
>> Exceptional Surface Finish and Detail
>> Variety in Material Properties
● Considerations and Limitations
● Factors to Consider When Choosing a Vacuum Mold Casting Service
>> Experience and Industry Know-How
>> Advanced Equipment and Technology
>> Quality Assurance Protocols
>> Communication and Customer Service
>> Turnaround Time and Production Capacity
>> Pricing and Cost Transparency
● How to Assess Vacuum Mold Casting Providers
● Design Guidelines for Vacuum Mold Casting
● Practical Applications of Vacuum Mold Casting
● Enhancing Understanding Through Visual Content
● FAQ
>> 1. What materials are commonly used in vacuum mold casting?
>> 2. How long does the vacuum mold casting process take?
>> 3. Can vacuum mold casting produce parts with fine details?
>> 4. Is vacuum mold casting suitable for mass production?
>> 5. How can defects be minimized in vacuum mold casting?
Vacuum mold casting has transformed the way manufacturers create high-quality prototypes, precision parts, and small batch productions. This advanced manufacturing process provides excellent detail and surface finish, making it a favored choice for companies aiming for quick turnaround and high customization without the high cost of traditional injection molding. Selecting the right vacuum mold casting service is essential to ensuring your product meets stringent quality standards, gets delivered on time, and stays within budget.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the Vacuum Mold Casting process, highlight its advantages and limitations, and help you identify the crucial factors when choosing a service provider. Whether you are a brand owner, wholesaler, or manufacturer, this article will equip you with all the knowledge necessary for successful vacuum mold casting collaboration.
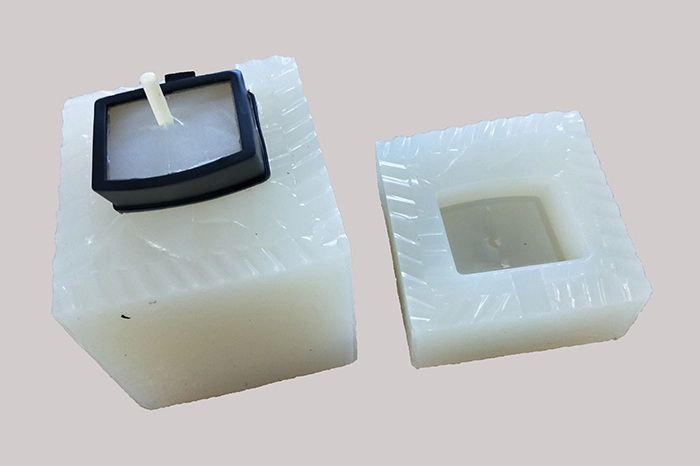
Vacuum mold casting is a process whereby liquid polyurethane or silicone is introduced into a silicone mold using vacuum pressure to eliminate air bubbles. The vacuum environment ensures the resin fills the mold cavities completely, resulting in detailed parts with smooth surfaces that closely mimic those made by injection molding—but with significantly lower tooling costs and faster production times.
It is primarily used for producing highly detailed prototypes, low-volume production runs, and parts requiring specialized material properties. Common sectors relying on vacuum mold casting include consumer electronics, automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and customized consumer products.
Unlike traditional injection molding, which involves costly steel molds, vacuum mold casting uses flexible silicone molds. The lower tooling cost significantly reduces upfront expenses, making it ideal for producing dozens to a few thousand parts economically.
Silicone molds can be fabricated in a matter of days, allowing fast transition from design to parts. This speeds up product development cycles and allows rapid iterations based on testing or market feedback.
The silicone molds capture fine textures and intricate features, producing parts with high fidelity and excellent surface quality. This makes vacuum casting perfect for visual prototypes and functional parts requiring cosmetic appeal.
Polyurethane resins used in vacuum casting come in numerous formulations that simulate the physical properties of many production plastics — from rigid, glass-filled compounds to flexible elastomers, transparent materials, and colored resins.
Despite its many benefits, vacuum mold casting has limitations. Silicone molds have a limited lifespan—typically producing a few dozen to a few hundred parts before degradation. This makes vacuum casting unsuitable for high-volume mass production.
Also, part sizes are limited by mold design and casting equipment capacity. Deep undercuts and certain complex geometries may pose challenges due to demolding constraints.

Select a provider with significant experience in vacuum mold casting and familiarity with your industry. Experienced vendors can predict challenges, optimize mold design, and recommend suitable materials, improving end product quality.
Verify that the supplier offers the specific polyurethane or silicone resins that match your product requirements. Discuss hardness, transparency, color, and mechanical properties needed for your parts.
Cutting-edge vacuum casting machines and mold-making technology ensure dimensionally accurate molds and defect-free parts. Confirm what type of molds the provider uses and the size limitations of their machines.
Look for companies adhering to recognized quality management standards such as ISO certifications. Inquire about inspection procedures, like coordinate measuring machine (CMM) verification, to maintain part tolerances and consistency.
Transparent communication through every stage is crucial. Choose suppliers who proactively engage in design consultation, promptly respond to queries, and provide detailed progress reports.
Make sure the provider has adequate capacity to handle your required volumes and can meet your deadlines without compromising quality.
Request detailed quotes that outline mold development costs, per-part pricing, and any additional fees. Avoid extremely low bids that may indicate compromises in quality or service.
- Inspect Sample Parts: Review samples of previously cast components to assess surface finish, detail, and mechanical properties.
- Demand References: Speak to past clients to verify reliability and service quality.
- Onsite Visits: If possible, perform a factory visit to evaluate equipment, cleanliness, and professional standards.
- Start with Pilot Runs: Initiate with a small order or prototype batch to test the provider's capabilities.
Designing your product in accordance with vacuum mold casting best practices improves manufacturability and part quality:
- Include sufficient draft angles (typically 1–3°) to facilitate part removal from the silicone mold without damage.
- Minimize deep undercuts and complex internal geometries that complicate demolding or require multi-part molds.
- Define critical dimensional tolerances clearly and early to avoid ambiguities.
- Account for slight shrinkage or dimensional variances inherent in the casting process.
Due to its versatility and cost benefits, vacuum mold casting is widely used across industries for:
- Functional prototypes for testing form, fit, and function.
- Replacement parts or spares for limited quantities.
- Custom components with specific material needs like translucency or flexibility.
- Short-run products for market testing or limited editions.
For those new to vacuum mold casting or seeking deeper insights, supplementing articles with visual media is valuable. Ideal visuals include:
- Step-by-step guides illustrating the vacuum casting workflow.
- Comparative diagrams showing vacuum casting vs. injection molding.
- Video demonstrations of mold preparation, casting, and part removal.
- Case study footage showcasing client projects from start to finish.
These help clarify the nuances and advantages of the technology beyond text alone.
Choosing the right vacuum mold casting service requires carefully balancing quality, cost, lead time, and communication. By prioritizing providers with proven experience, broad material offerings, advanced equipment, and quality assurance, you safeguard your product's success from prototype through production. Remember to engage in detailed discussions, request samples, and run pilot projects to mitigate risks. Attentive collaboration with your chosen casting partner will unlock the full potential of vacuum mold casting for your product development needs.

Vacuum mold casting commonly utilizes polyurethane resins available in a variety of hardness levels, colors, and transparency options. These materials can replicate many production plastics and elastomers.
From mold fabrication to part delivery, the process typically spans one to three weeks depending on part complexity and order size.
Yes, silicone molds create highly detailed parts with smooth surfaces, making vacuum casting excellent for prototypes requiring precision and aesthetic quality.
Generally, vacuum mold casting is better suited for low to medium volume production runs due to the limited lifespan of silicone molds.
Maintaining proper vacuum levels during casting, regular mold inspection, and choosing compatible materials reduce issues like air bubbles and incomplete filling.
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal