
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-10-20 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● What Is Vacuum Mold Casting?
● The Vacuum Mold Casting Process Explained
● How Vacuum Mold Casting Improves Product Quality
>> Elimination of Air Bubbles and Voids
>> Superior Dimensional Accuracy and Detail Reproduction
>> Maintenance of Material Integrity
>> Enhanced Mechanical Properties
● Advantages Over Traditional Casting
● Applications of Vacuum Mold Casting
● Factors Influencing Vacuum Mold Casting Quality
● Environmental and Economic Considerations
● Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
>> 1. What materials can be used in vacuum mold casting?
>> 2. How does vacuum mold casting compare to pressure casting?
>> 3. Can vacuum mold casting be scaled for large production volumes?
>> 4. Does vacuum mold casting speed up the curing process?
>> 5. Is vacuum mold casting environmentally sustainable?
Vacuum mold casting is a highly precise manufacturing process widely adopted in industries that demand superior product quality and consistency. This article delves into the technical aspects of Vacuum Mold Casting, highlighting how it improves production outcomes, its benefits, applications, and the key factors that influence its effectiveness.

Vacuum mold casting is a fabrication technique where liquid material—typically silicone, polyurethane, or other polymers—is poured into a mold within a vacuum chamber. The vacuum environment removes air pockets and trapped gases during the casting process, helping to achieve flawless and dense products.
This method is particularly effective in producing parts that require detailed finishes, durable mechanical properties, and dimensional accuracy. By minimizing defects caused by trapped air, vacuum mold casting delivers superior parts that meet exacting specifications.
The process follows a series of carefully controlled steps to maximize product quality:
1. Preparation of the Mold: A master pattern is first created, usually by 3D printing or CNC machining. This master is then used to make a silicone mold that captures intricate surface details.
2. Material Mixing: Liquid casting material is mixed in precise ratios to ensure chemical integrity. Careful hand or mechanical mixing helps to prevent early air entrapment.
3. Vacuum Degassing: The liquid material is placed into a vacuum chamber, where negative pressure draws out entrapped air and gases, reducing bubble formation.
4. Pouring: Still within the vacuum environment, the degassed liquid is poured slowly into the mold. This ensures the material flows properly into every corner without gas entrapment.
5. Curing: The filled mold is removed from the vacuum chamber and allowed to cure. Curing time and temperature depend on the specific polymer used.
6. Demolding: Once solidified, the casting is carefully removed from the mold, revealing a highly detailed, bubble-free part.
Each step is critical to achieving the high-quality results vacuum mold casting is known for.
One of the biggest problems in conventional casting is the presence of air bubbles trapped inside the mold. Air pockets cause structural weak points and surface imperfections. Vacuum mold casting removes these bubbles by subjecting the casting material to a pressure lower than atmospheric, effectively drawing air out before curing.
This results in products with smooth surfaces free from pinholes and imperfections, ideal for applications where appearance and airtightness are critical.
The silicone molds used in vacuum casting capture fine details from master patterns with exact precision. Since the casting material is introduced under vacuum, it fully penetrates all cavities without bubbles or shrinkage, resulting in highly accurate reproductions of the original design.
This dimensional accuracy makes vacuum mold casting suitable for prototypes and parts used for verification before mass production.
Vacuum degassing not only eliminates air but prevents oxygen exposure during curing, reducing oxidation or bubbles formed by gases released inside materials. This means the cured parts maintain their intended mechanical and chemical properties fully.
Materials cured in vacuum environments show enhanced strength, flexibility, and resistance to wear compared to those produced by traditional methods.
The absence of voids inside the casting improves the overall structural strength. This makes vacuum cast parts more durable under mechanical stress and less prone to cracking or failure.
Industries demanding reliability and safety, such as automotive or aerospace, benefit from these improved mechanical characteristics.
Compared with gravity or pressure casting, vacuum mold casting excels in producing parts with minimal defects, superior surface finish, and dimensional precision, making it the preferred choice for critical applications. It also reduces material waste caused by rejected parts containing defects, improving overall manufacturing efficiency.
Vacuum mold casting finds use in a diverse range of applications:
- Prototyping: It allows rapid creation of physical models with tight tolerances for design validation.
- Small-Scale Production: Economical for producing limited series customized parts.
- Automotive Industry: For manufacturing prototype components, dashboards, and housings requiring fine details.
- Electronics: For producing insulating cases and functional parts.
- Medical Devices: To create biocompatible, high-precision parts such as surgical tools and device housings.
- Consumer Products: For cosmetics containers, art replicas, and more.
Its versatility makes vacuum mold casting an essential technique across sectors.
- Mold Quality: High-grade silicone molds with proper curing produce better products.
- Vacuum Pressure: Achieving and maintaining a deep vacuum level is crucial for air removal.
- Material Selection: Different polymers have specific curing needs and properties; choosing the right material impacts final quality.
- Mixing Techniques: Uniform and careful mixing avoids premature bubble formation.
- Curing Conditions: Proper temperature and time ensure optimal polymerization without defects.
Vacuum mold casting generally produces less scrap and waste due to higher yield and fewer rejected parts. Though initial mold creation can be costly, the reduced waste and repeatability make it cost-effective for short to medium runs.
Most casting materials are thermosetting polymers, which can have environmental impacts depending on disposal methods. However, advances in biodegradable polymers are starting to integrate with vacuum casting technology.
- High initial mold fabrication cost limits suitability for mass production.
- Cycle times can be longer than some injection molding processes.
- Some materials are incompatible with vacuum conditions or require specialized handling.
- Specialized equipment needed adds to setup costs.
Despite these, vacuum mold casting remains a top choice when quality cannot be compromised.
Vacuum mold casting significantly enhances product quality and consistency by eliminating air bubbles, ensuring dimensional accuracy, and preserving the material's mechanical properties. It is especially beneficial for prototyping and small-to-medium batch production where superior surface finish and structural integrity are paramount.
The controlled vacuum environment ensures reliable replication of intricate details and improved durability for a wide array of applications, from automotive parts to medical devices. While it carries some limitations related to cost and volume, the advantages make it indispensable in modern manufacturing.
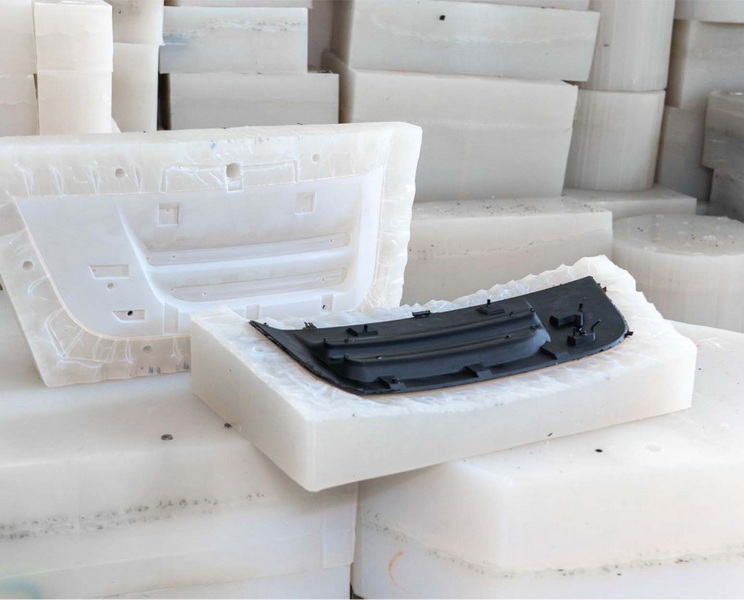

Most liquid polymers such as silicones, polyurethanes, and epoxy resins are suitable. Material choice depends on the end-use requirements like flexibility, hardness, or temperature resistance.
Vacuum casting uses suction to remove air bubbles before pouring, while pressure casting forces material into molds at high pressure. Vacuum casting excels at removing internal voids, pressure casting improves flow into complex shapes.
It is primarily optimized for prototyping and small to medium batch production. For large-scale runs, processes like injection molding might be more cost-effective.
The vacuum environment doesn't accelerate curing but helps produce parts with fewer defects, ensuring full mechanical properties post-curing.
It reduces waste by lowering rejected parts. However, sustainability depends on the materials used. Emerging biodegradable polymers are making vacuum casting greener.
content is empty!
How Vacuum Mold Casting Compares to Silicone Mold Casting for Precision Parts
Vacuum Mold Casting vs. Resin Casting: Key Differences You Should Know
Vacuum Mold Casting vs. 3D Printing: Choosing the Best Rapid Prototyping Method
Best Vacuum Mold Casting Services for Precision Manufacturing in 2025
Top Vacuum Mold Casting Manufacturers Delivering High-Quality Prototypes
Best Practices from Leading Vacuum Mold Casting Companies Worldwide
Top Vacuum Mold Casting Providers for Custom Batch Production
How to Choose the Right Vacuum Mold Casting Service for Your Product