
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-10-20 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Understanding Vacuum Mold Casting
● Key Design Considerations for Vacuum Mold Casting
>> Rounded Corners and Fillets
>> Avoid Undercuts or Use Inserts
● Material Selection and Preparation
>> Match Shore Hardness to Applications
>> Thorough Mixing and Degassing
● Optimizing Mold Design and Construction
>> Mold Thickness and Strength
>> Rapid Prototyping for Mold Patterns
● Enhancing Production Efficiency
>> Automation in Mixing and Casting
>> Automated Trimming and Finishing
● Quality Control and Troubleshooting
● Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
>> 1. What wall thickness is recommended for vacuum mold casting?
>> 2. How important are draft angles in vacuum mold casting?
>> 3. Can vacuum mold casting produce complex geometries?
>> 4. How do I reduce air bubbles in vacuum casting?
>> 5. What types of molds are best for vacuum casting?
Vacuum mold casting is a highly versatile manufacturing process widely used for producing precise, low-volume plastic parts and prototypes. By combining mold-making with vacuum casting, this technique ensures detailed and accurate reproductions of complex designs. Optimizing your product design specifically for Vacuum Mold Casting can greatly enhance casting efficiency, reduce production costs, and improve the final product quality.
This article offers a comprehensive guide to design optimization for vacuum mold casting. It covers essential considerations such as design guidelines, material selection, mold construction, cycle time reduction strategies, and automation, providing actionable insights for manufacturers and designers to maximize efficiency and product quality.
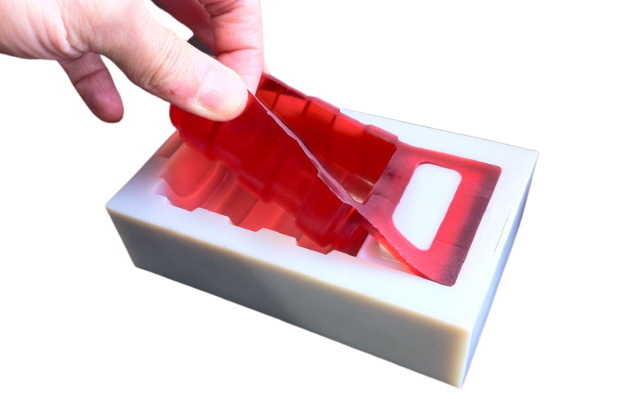
Vacuum mold casting involves creating parts by pouring liquid polyurethane or other castable resins into a mold placed inside a vacuum chamber. The vacuum environment removes trapped air bubbles during the casting process, which results in parts with smooth surfaces and excellent dimensional accuracy. This method is ideal for rapid prototyping, short runs, and parts that require intricate details and high surface finish quality.
The typical vacuum casting process involves several steps:
- Creating a master model using 3D printing or CNC machining.
- Making a silicone mold from the master model.
- Preparing and degassing the casting resin.
- Casting the resin into the mold under vacuum.
- Curing the part and post-processing it.
Each step plays a crucial role in determining the quality and efficiency of the final casting.
Designing your parts with vacuum mold casting in mind is essential for optimizing production efficiency and part quality. Here are critical design rules to follow:
Aim for uniform wall thickness throughout the part—typically between 2 to 5 mm. Consistent thickness avoids internal stresses, uneven cooling, warping, or sink marks. If variations are necessary, ensure transitions are gradual with proper fillets.
Incorporate draft angles of around 1 to 3 degrees on all vertical surfaces. Draft angles allow easy ejection of parts from flexible silicone molds without damaging the cast or mold.
Sharp corners can create stress concentrations and make resin flow difficult. Designing rounded corners or fillets improves resin flow, mold release, and mechanical integrity of the parts.
Undercuts complicate mold design and make demolding difficult. If undercuts are necessary, design them as removable mold inserts or consider alternative geometry to simplify the mold.
Proper venting in the mold design lets trapped air escape during casting, preventing air pockets and defects in the final part.
While vacuum casting can capture great detail, extremely thin or delicate features may be fragile or difficult to cast correctly. Design considering the mechanical strength and reproducibility of such features.
The material choice significantly impacts vacuum casting efficiency and final part properties.
Low-viscosity polyurethane resins flow more easily into molds under vacuum, ensuring complete cavity filling and reducing cycle times.
Choose resin shore hardness that meets your mechanical strength, flexibility, and durability requirements.
You can add pigments or other additives during resin mixing to achieve desired colors or enhanced properties.
Mix resin components thoroughly to avoid curing problems, and degas the mixture under vacuum to remove entrapped air for bubble-free parts.
The mold itself is the core of efficient vacuum casting.
Silicone is preferred for overmolding because of its flexibility, heat resistance, and ability to capture fine details.
Design the mold with enough thickness to resist deformation during casting but avoid unnecessary bulk to reduce material use and cost.
Multi-cavity molds enable producing several parts per cycle, boosting productivity for small batch production.
Incorporate removable inserts to handle complex geometries, undercuts, or interchangeable features without remaking the entire mold.
Use 3D printing or CNC machining for creating master models quickly, allowing faster iteration on mold design and part features.
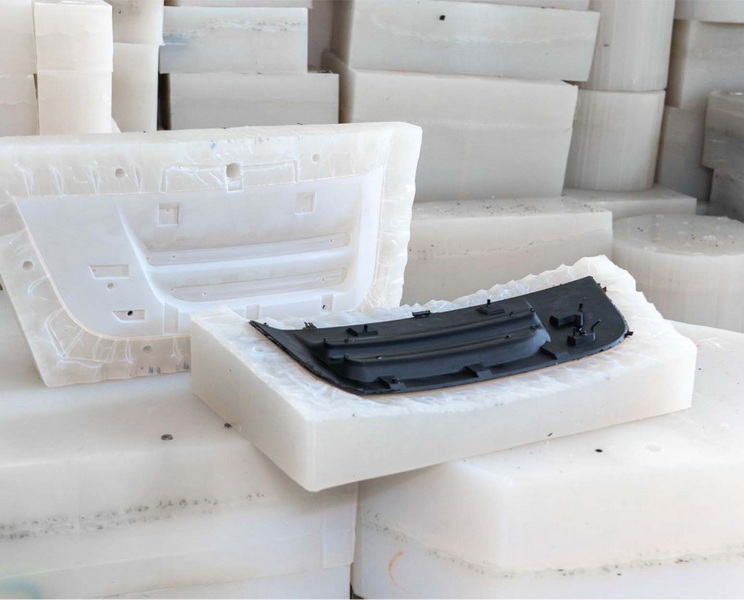

Optimizing your casting process beyond design can further reduce costs and improve output rates.
Select resins with shorter cure times compatible with your mold and part requirements to lower cycle duration.
Use controlled oven curing and maintain constant mold temperatures to promote uniform curing and minimize part warping.
Automate resin mixing, degassing, and pouring processes using vacuum casting machines to improve reproducibility and reduce human error.
CNC trimming and finishing can speed up post-processing and ensure consistent quality in cast parts.
Maintaining quality across batches prevents costly defects and production delays.
- Air Bubbles: Degas resin thoroughly and ensure proper mold venting.
- Shrinkage: Adjust resin formulation or mold design to compensate for volume shrinkage.
- Warping and Distortion: Maintain consistent wall thickness and control curing temperature.
- Mold Wear: Monitor mold usage and replace molds after their lifespan (typically 10-20 castings) to maintain dimensional accuracy.
Optimizing your design for vacuum mold casting efficiency requires a comprehensive approach. By applying best practices in part design, material selection, mold construction, and process automation, you can achieve faster production cycles, reduce defects, and enhance part quality. Paying attention to draft angles, wall thickness, venting, and mold modularity enables smooth casting and demolding operations. With continuous improvements and quality control, vacuum mold casting becomes a powerful method for rapid prototyping and low-volume manufacturing, providing a cost-effective alternative to traditional molding techniques.

Consistent wall thickness of about 2 to 5 mm is optimal to ensure even resin flow and reduce warping or sink marks in vacuum cast parts.
Draft angles of 1 to 3 degrees help in the smooth release of the part from the silicone mold, minimizing damage and reducing cycle time.
Yes, but complex features with undercuts require removable mold inserts or design modifications to simplify mold manufacturing and demolding.
Use low-viscosity resins, thoroughly degas resin mixtures under vacuum, and ensure molds have proper venting to let trapped air escape.
Silicone molds are preferred for their flexibility and ability to capture fine details. For larger runs, aluminum molds may be used but are less common.
[1](https://formlabs.com/blog/vacuum-casting-urethane-casting-polyurethane-casting/)
[2](https://www.immould.com/vacuum-casting/)
[3](https://an-prototype.com/ultimate-guide-to-vacuum-casting/)
[4](https://objectify.co.in/a-comprehensive-guide-to-vacuum-casting-everything-you-need-to-know/uncategorized/)
[5](https://xdmining.in/2024/10/02/elementor-11005/)
[6](https://ame-3d.co.uk/news/a-complete-guide-to-vacuum-casting-polyurethane-casting)
[7](https://blog.isa.org/what-are-vacuum-casting-factories-a-comprehensive-guide-to-the-manufacturing-process)
[8](https://leadrp.net/blog/overview-of-vacuum-casting/)
[9](https://www.kemalmfg.com/complete-guide-to-vacuum-casting/)
[10](https://www.zintilon.com/blog/vacuum-casting/)
content is empty!
How Vacuum Mold Casting Compares to Silicone Mold Casting for Precision Parts
Vacuum Mold Casting vs. Resin Casting: Key Differences You Should Know
Vacuum Mold Casting vs. 3D Printing: Choosing the Best Rapid Prototyping Method
Best Vacuum Mold Casting Services for Precision Manufacturing in 2025
Top Vacuum Mold Casting Manufacturers Delivering High-Quality Prototypes
Best Practices from Leading Vacuum Mold Casting Companies Worldwide
Top Vacuum Mold Casting Providers for Custom Batch Production
How to Choose the Right Vacuum Mold Casting Service for Your Product