
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2026-01-28 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● How Is CNC Machining Changing?
● From 3‑Axis to Multi‑Axis CNC Machining
● Automation, Robotics and Lights‑Out CNC Machining
● AI, IoT and Smart CNC Machining
● Hybrid Manufacturing – CNC Machining Meets 3D Printing
● CNC Machining, Rapid Prototyping and Precision Batch Production
● CNC Machining Quality, Materials and Global OEM Expectations
● What This Means for OEM Buyers Working With Shangchen
● FAQ About Changing CNC Machining
>> 1. How is CNC Machining different today compared with ten years ago?
>> 2. Why is multi‑axis CNC Machining important for OEM projects?
>> 3. How do AI and IoT make CNC Machining more reliable?
>> 4. What is hybrid manufacturing in CNC Machining?
>> 5. How can Shangchen support my CNC Machining and OEM needs?
CNC machining is evolving from a traditional subtractive process into a smart, automated, and highly connected manufacturing backbone for global supply chains. For international OEM buyers, this means faster lead times, tighter tolerances, greater flexibility, and more options to integrate rapid prototyping with precision batch production in one streamlined CNC Machining workflow.

CNC Machining is no longer just “cutting metal”; it is becoming a digital, data‑driven ecosystem combining multi‑axis capability, robotics, AI, IoT, and even 3D printing in hybrid setups. For factories like Shangchen offering CNC Machining, rapid prototyping, turning, sheet metal, 3D printing and mold production, these shifts open up new ways to deliver higher‑value OEM services to global customers in automotive, aerospace, medical, consumer electronics and more.
As CNC Machining becomes more integrated with digital design and simulation tools, engineering teams can now move from CAD models to machine‑ready toolpaths with fewer manual steps. CAM software automatically generates optimized CNC Machining strategies for complex surfaces, undercuts and pockets, which helps shorten programming time and reduce the risk of human error. This digital thread—from design to CNC Machining and inspection—supports traceability and makes it easier for OEM customers to manage engineering changes.
Another key change is that CNC Machining is increasingly used as a flexible platform in multi‑process manufacturing cells. Instead of standing alone, CNC Machining centers are combined with turning, grinding, EDM, sheet metal and assembly to form compact production lines. This allows factories like Shangchen to handle complete parts or assemblies, not just single operations, which is attractive to overseas buyers seeking consolidated supply chains and fewer vendor interfaces.
Multi‑axis CNC Machining is one of the most visible changes in the industry. Traditional 3‑axis setups are being replaced by 4‑axis, 5‑axis and even 6‑axis CNC Machining centers that can machine complex geometries in a single clamping with far fewer setups.
Multi‑axis CNC Machining reduces repositioning, which directly improves accuracy and surface finish for complex parts such as turbine blades, orthopedic implants, and intricate housings. By machining more faces of the workpiece in one cycle, CNC Machining shops cut total machining time, reduce fixture costs, and improve throughput for both prototypes and precision batch production. For OEM buyers, multi‑axis CNC Machining means better repeatability across global orders, simpler drawings, and more freedom in design because more complex 3D forms are now practical to manufacture.
Multi‑axis technology also changes how CNC Machining projects are quoted and planned. Because more work is done in a single setup, many small fixtures and manual operations disappear, which simplifies cost structures and makes lead times more predictable. For example, a once‑complex assembly that required separate milled and drilled components can sometimes be redesigned as a single multi‑axis CNC Machining part, reducing logistics, stock‑keeping complexity and potential failure points in the field.
In addition, multi‑axis CNC Machining plays a vital role in lightweighting strategies. Engineers can remove more material from non‑critical areas, machine deep pockets with excellent rigidity, and create organic, topology‑optimized forms that still meet structural requirements. This is particularly valuable in aerospace and high‑performance automotive applications where every gram matters and CNC Machining must follow sophisticated 3D contours.
Another major shift is the spread of automation and lights‑out CNC Machining, where production continues with minimal human intervention. Robots, pallet systems, bar feeders, and integrated conveyors are increasingly paired with CNC Machining centers to keep spindles cutting 24/7.
Automated CNC Machining cells use robotic arms to load and unload parts, measure components, and even change pallets, allowing continuous production through nights and weekends. Lights‑out CNC Machining is supported by advanced monitoring; sensors measure temperature, vibration, spindle load and tool wear so that machines can stop safely or call for help before scrap is produced. For OEM clients, automated CNC Machining translates into shorter lead times, more consistent delivery schedules, and often lower unit prices on repeat orders due to higher machine utilization.
Automation in CNC Machining is also reshaping the role of skilled machinists. Instead of standing at a single machine for manual loading and unloading, technicians now oversee multiple CNC Machining cells, manage process optimization, and focus on setup, programming and troubleshooting. This makes better use of human expertise and helps factories cope with labor shortages while still scaling capacity for international orders.
Furthermore, automated pallet and tooling systems let CNC Machining shops react more quickly to changing priorities. High‑mix, low‑volume batches can be loaded in queue; the system automatically selects the right fixtures, tools and CNC Machining programs in sequence. For OEM buyers with multiple part numbers and frequent schedule changes, this flexible automation is a clear competitive advantage.
CNC Machining is being transformed by AI and IoT into a smart manufacturing platform that can sense, analyze, and optimize cutting operations in real time. Smart CNC Machining systems use machine‑learning algorithms and connected sensors to improve uptime, quality and cost efficiency.
AI‑driven CNC Machining can predict tool wear and spindle faults by analyzing vibration, torque, and temperature trends, scheduling maintenance before failures and reducing unexpected downtime. IoT connectivity in CNC Machining allows real‑time data collection across multiple machines; dashboards show feed rates, cycle counts, alarms and OEE so engineers can adjust processes quickly. Combining AI and IoT gives CNC Machining shops closed‑loop control: cutting parameters are adjusted automatically based on feedback, improving dimensional stability and lowering scrap rates.
Smart CNC Machining also supports better collaboration between suppliers and OEM buyers. Process data, quality records and performance trends can be shared securely so engineering teams at both sides can diagnose issues and optimize designs together. For example, if a particular feature consistently pushes the limits of CNC Machining tool life, the design team may adjust fillet radii, wall thickness or tolerances to achieve a better balance between functionality and manufacturability.
Over time, AI models learn from every CNC Machining job, building a knowledge base of what works best for different materials, cutter types, and geometries. This enables automatic recommendation of feeds, speeds and strategies for new parts, shortening the trial‑and‑error phase. For a factory like Shangchen that handles a broad range of OEM applications, this means more stable quality and shorter industrialization cycles for new CNC Machining projects.

CNC Machining is also changing by merging with additive manufacturing into hybrid manufacturing, where both processes run in a single workflow or even a single machine. This approach combines the design freedom of 3D printing with the precision and material versatility of CNC Machining.
In a hybrid workflow, a near‑net‑shape part is 3D printed and then finished by CNC Machining, reducing material waste and machining time while achieving tight tolerances. Hybrid CNC Machining can create complex internal channels, lattice structures or overhangs that would be impossible or very costly with subtractive processes alone. OEM buyers benefit because hybrid CNC Machining supports rapid prototyping, fast design iteration, and optimized lightweight designs, especially in aerospace, medical and high‑performance industrial applications.
Hybrid setups also expand the range of materials and surface properties that can be delivered. For example, a core section may be produced through 3D printing, while critical sealing faces, threads, and bearing seats are finished via CNC Machining to guarantee dimensional accuracy and surface integrity. This targeted use of CNC Machining ensures the final component meets demanding functional requirements without over‑machining non‑critical areas.
Another advantage is that hybrid manufacturing can simplify supply chains. Instead of outsourcing additive work to one supplier and CNC Machining to another, OEMs can rely on a single partner who manages both processes and the transition between them. Shangchen's combination of CNC Machining, 3D printing, sheet metal and mold production positions it well to support such integrated hybrid projects for international brands and wholesalers.
For OEM customers, one of the most valuable changes is how CNC Machining integrates rapid prototyping and precision batch production under one roof. Factories like Shangchen can now move from CAD model to first article and then to stable batch CNC Machining much faster than before.
Rapid prototyping with CNC Machining allows engineers to validate form, fit and function in real production materials, often within days, before committing to tooling or mass production. Once the design is frozen, the same CNC Machining setup, fixtures and programs can be scaled to precision batch production, ensuring consistent quality from prototype to pilot run to volume orders. When combined with sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing and mold making, CNC Machining becomes a central hub that coordinates different processes into one coherent OEM supply solution.
CNC Machining is particularly valuable during design changes and product refresh cycles. When an OEM brand updates a feature, port, logo or mounting interface, prototypes can be CNC machined quickly to confirm the update, and then production programs can be adjusted with minimal downtime. This agility helps brands shorten time‑to‑market and react to competitive pressures without waiting for long tooling lead times.
For precision batch production, CNC Machining also enables flexible order quantities. Overseas buyers can start with smaller runs to test the market, then gradually increase their order size as demand grows, all while keeping process conditions stable. Shangchen's CNC Machining capabilities, together with turning and sheet metal, support this step‑by‑step scaling strategy for OEM and wholesale projects.
Global buyers are raising expectations for quality, traceability, and material performance, and CNC Machining is adapting accordingly. Modern CNC Machining uses advanced materials, tighter process control and better inspection to meet standards in aerospace, medical, automotive, and industrial sectors.
CNC Machining now routinely handles high‑strength alloys, stainless steels, titanium, engineering plastics and composites, supported by optimized tooling, coolant strategies and multi‑axis strategies. Integrated inspection—CMMs, in‑machine probing, and optical measurement—ensures CNC Machining processes hit critical tolerances and provide data for PPAP, FAI and other qualification documents. OEMs also want sustainability; CNC Machining trends include energy‑efficient drives, coolant recycling, and hybrid additive‑subtractive processes that reduce scrap and resource usage.
Documentation and compliance are becoming a standard part of CNC Machining deliveries. Dimensional reports, material certifications, surface roughness records and process capability data are often required, especially in regulated industries. Suppliers like Shangchen must integrate measurement and quality management into their CNC Machining workflow so that such documents can be generated reliably for every batch.
Moreover, long‑term partnership expectations are evolving. OEM buyers are not only looking for CNC Machining capacity but also for engineering support and manufacturability feedback. By engaging early in the design process, a CNC Machining supplier can propose changes that reduce machining time, improve tool life, and enhance performance of the final part. This kind of co‑engineering relationship adds strategic value beyond basic part production.
For international OEM, brand and wholesale customers, these changes in CNC Machining translate into more flexible, reliable and scalable supply partnerships. A factory like Shangchen that offers CNC Machining together with rapid prototyping, turning, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing and mold production can act as a one‑stop engineering and manufacturing partner.
By combining multi‑axis CNC Machining, automation, and hybrid workflows, Shangchen can support complex part geometries, smaller batch sizes, and faster design changes without sacrificing quality. Smart CNC Machining, with AI‑ and IoT‑supported monitoring, helps keep uptime high and quality stable, which is critical for overseas buyers depending on consistent deliveries. Integrated services let OEM customers move from idea to market faster: CNC Machining prototypes, validation samples, and scaled production runs can all be coordinated through a single technical interface.
Shangchen's CNC Machining team can assist with material selection, tolerance negotiation, and surface finishing choices according to the end‑use environment and regulatory requirements. Whether an OEM buyer needs high‑precision aluminum housings, stainless steel fittings, brass turned parts, or complex plastic components, CNC Machining can be combined with other processes to create a robust and economical solution. With clear communication channels and professional project management, such a partnership reduces risk and simplifies global sourcing for demanding applications.
For brands and wholesalers who want to differentiate their products, advanced CNC Machining also enables more distinctive design features and higher perceived quality. Fine surface finishes, tight assembly fits, and precisely machined details contribute to better user experience and stronger brand image. By leveraging modern CNC Machining at Shangchen, international customers can transform their concepts into tangible, market‑ready products with strong competitive advantages.
CNC Machining is changing from a conventional subtractive process into a multi‑axis, automated, AI‑enabled, and hybrid manufacturing platform that supports the entire product lifecycle from prototype to global batch production. Multi‑axis capability, robotics, smart data, and integration with 3D printing are reshaping how parts are designed, manufactured, inspected and delivered across industries.
For OEM buyers partnering with factories such as Shangchen, these new CNC Machining capabilities deliver tighter tolerances, shorter lead times, smarter quality control, and more freedom to innovate across materials and designs in highly competitive international markets. As expectations for flexibility, traceability and technical support continue to rise, working with a CNC Machining supplier that embraces these changes will be a key factor in building resilient, high‑performance global supply chains.
Conntact us to get more information!
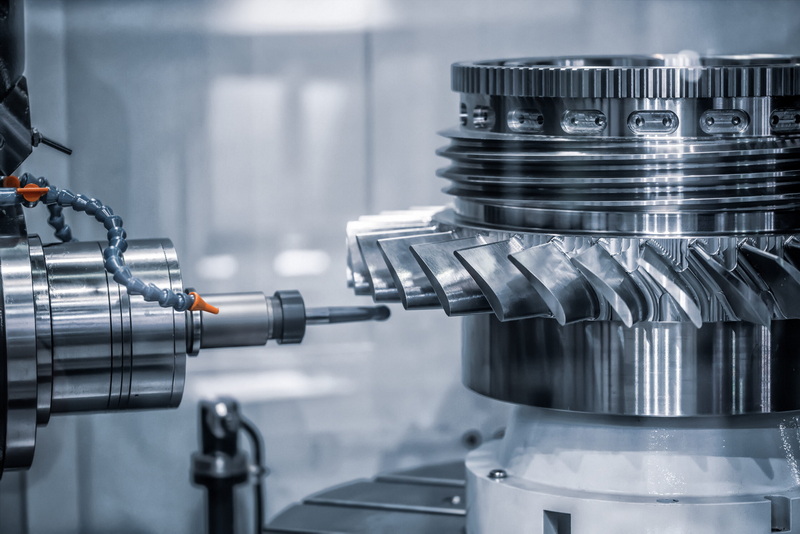
CNC Machining today uses multi‑axis machines, robotics, AI monitoring and hybrid additive‑subtractive workflows rather than relying mainly on standalone 3‑axis equipment and manual setups. The result is that modern CNC Machining achieves higher precision, faster cycle times, more complex geometries, and far better process transparency for OEM customers worldwide.
Multi‑axis CNC Machining allows complex parts to be produced in fewer setups, which improves accuracy and reduces cumulative error from repositioning. For OEM projects, this means more reliable tolerances, better surface finish, and often lower total cost, especially when dealing with intricate 3D shapes or high‑value materials.
AI analyzes CNC Machining sensor data to predict tool wear, detect anomalies and optimize cutting parameters, while IoT connects machines so data flows in real time. Together, they reduce unplanned downtime, minimize scrap, and give OEM buyers consistent quality backed up by clear digital records of the CNC Machining process.
Hybrid manufacturing combines 3D printing with CNC Machining in one integrated workflow or machine. Parts can be printed near net shape and then finished via CNC Machining, which cuts waste, speeds up prototyping, and still delivers the tight tolerances required in aerospace, medical, and other demanding industries.
Shangchen offers CNC Machining along with rapid prototyping, CNC turning, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing and mold production to serve OEM brands, wholesalers and manufacturers worldwide. By leveraging modern CNC Machining technologies, Shangchen can deliver prototypes, precision batch production and complex custom components with stable quality and competitive lead times for international projects.
1. https://www.sahilcnc.com/technical-press-news/cnc-machining-in-2025-what-s-changing-in-the-industry/
2. https://i-mas.com/en/trends-in-cnc-machining-for-2025-multi-axis-advanced-automation-and-hybrid-manufacturing/
3. https://mdcplus.fi/blog/top-5-cncs-for-2025/
4. https://www.accio.com/business/trend-of-new-special-cnc
5. https://cnctech.com.vn/content/integrating-ai-and-iot-in-modern-automation-machinery.html
6. https://www.kmlaerospacemfg.com/post/revolutionizing-manufacturing-the-role-of-ai-integration-and-iot-in-cnc-robotics-and-5-axis
7. https://www.automationwithinreach.com/blog/smart-manufacturing-with-cnc-automation
8. https://www.harveyperformance.com/in-the-loupe/cnc-machining-3d-printing-hybrid-manufacturing/
9. https://raven3dtech.com.au/exploring-hybrid-manufacturing-integrating-3d-printing-and-cnc-systems/
10. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1155/2016/8609108
content is empty!