
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2026-01-28 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● 1. Why CNC Machining Still Matters in the Future
● 2. Industry 4.0, Smart Factories, and CNC Machining
● 3. Automation, Robots, and Lights‑Out CNC Machining
● 4. Artificial Intelligence and CNC Machining Optimization
● 5. CNC Machining and Additive Manufacturing: Competition or Cooperation?
● 6. Customization, Small Batches, and On‑Demand CNC Machining
● 7. Sustainability and Green CNC Machining
● 8. Workforce, Skills, and Human–Machine Collaboration
● 9. What the Future of CNC Machining Means for Global OEM Customers
● 10. Example CNC Machining Workflow with Future‑Ready Technology
● 11. Digital Content and CNC Machining Demonstrations
● FAQ About the Future of CNC Machining
>> 1. Will CNC machining be replaced by 3D printing?
>> 2. How will AI change CNC machining?
>> 3. What does “lights‑out” CNC machining mean?
>> 4. How will CNC machining support small‑batch and customized production?
>> 5. Why is sustainability important for CNC machining?
In global manufacturing, CNC machining is entering a new era driven by digitalization, automation, and flexible, small‑batch production demands. For factories like Shangchen that provide CNC machining, rapid prototyping, and OEM services, the future means smarter, more connected, and more sustainable production.
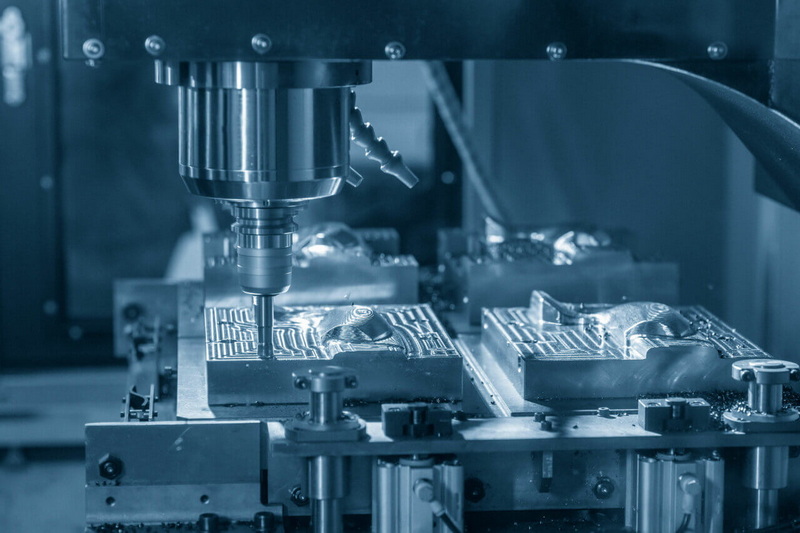

CNC machining will remain a core manufacturing process because it delivers high precision, repeatability, and tight tolerances for metals and engineering plastics. Even with the rise of additive manufacturing, CNC machining continues to excel in dimensional accuracy and surface finish, especially for functional components and end‑use parts.
Key reasons CNC machining stays essential:
- High accuracy for aerospace, medical, and automotive parts.
- Excellent surface finish, often better than additive manufacturing.
- Compatibility with a wide range of metals and plastics.
- Strong scalability from prototypes to precision batch production.
- Capability to integrate into automated cells and smart factories.
As global supply chains demand faster response and higher quality, CNC machining will continue to be the backbone process that turns digital designs into reliable physical components.
One of the most important future trends for CNC machining is the integration with Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing. CNC machining centers are increasingly connected to IoT platforms, MES systems, and cloud dashboards that collect real‑time production data, tool wear information, and machine health status.
Core elements of smart CNC machining include:
- IoT sensors on CNC machining equipment monitoring vibration, temperature, spindle loads, and cycle times.
- Data analytics dashboards optimizing CNC machining utilization, changeovers, and OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness).
- Centralized scheduling that dynamically allocates CNC machining jobs based on machine status and delivery priorities.
- Digital twins that simulate CNC machining processes before actual cutting to prevent errors and collisions.
These technologies allow CNC machining factories to run more efficiently, reduce downtime, and respond faster to OEM customer orders. In a smart factory, CNC machining is no longer an isolated process but a connected, transparent, and data‑driven system.
Automation is reshaping CNC machining by enabling higher productivity with fewer manual interventions. Robotic arms, automated guided vehicles, and pallet systems now work together with CNC machining centers to ensure continuous output.
Typical automation trends in CNC machining:
- Robotic arms loading and unloading parts from CNC machining centers for lights‑out production.
- Pallet systems and automatic tool changers to switch CNC machining jobs with minimal setup.
- Integrated inspection stations feeding measurement data back into CNC machining programs for closed‑loop adjustments.
- Automated storage systems that manage tools, fixtures, and workpieces for CNC machining cells.
For a factory like Shangchen, building semi‑ or fully automated CNC machining cells will be critical to meet 24/7 OEM demand with stable quality. Lights‑out CNC machining allows machines to continue running during nights and weekends, increasing capacity without proportionally increasing labor costs.
Artificial intelligence is rapidly becoming one of the most powerful tools to optimize CNC machining processes. Machine learning algorithms can analyze historical and real‑time sensor data from CNC machining operations to adjust feeds, speeds, and toolpaths automatically.
Important AI applications in CNC machining include:
- AI‑driven process optimization: real‑time adjustment of cutting parameters in CNC machining to reduce cycle time and extend tool life.
- Predictive maintenance: models that detect abnormal patterns in CNC machining equipment, preventing unplanned breakdowns and costly stoppages.
- AI‑enhanced CAD/CAM: software that automatically generates and optimizes CNC machining toolpaths, reducing programming time and improving manufacturability.
- Intelligent scheduling: AI engines that assign CNC machining jobs to specific machines based on capacity, skills, and due dates.
As AI becomes more mature, CNC machining will shift from static programming to self‑optimizing systems that continuously learn from production data. This evolution will help CNC machining service providers offer shorter lead times, more competitive pricing, and more consistent quality.
Additive manufacturing (3D printing) is often seen as a competitor to CNC machining, but the future is more about hybrid workflows that combine both technologies. Additive processes are excellent for complex, lightweight geometries, while CNC machining is superior for final precision surfaces and tolerances.
Key differences and synergies:
- Additive manufacturing creates complex internal channels and organic shapes, but CNC machining refines critical surfaces and tolerances.
- Hybrid manufacturing builds near‑net‑shape parts additively, then uses CNC machining to achieve final dimensions and surface finish.
- Combining 3D printing and CNC machining can reduce material waste and shorten total production time for complex parts.
- CNC machining often finishes metal or plastic parts that were initially produced through additive processes, casting, or forging.
For Shangchen, offering both 3D printing services and CNC machining allows flexible solutions for rapid prototyping and precision batch production in one integrated workflow. Customers can test designs quickly using additive methods, then shift to CNC machining for stable, repeatable production.
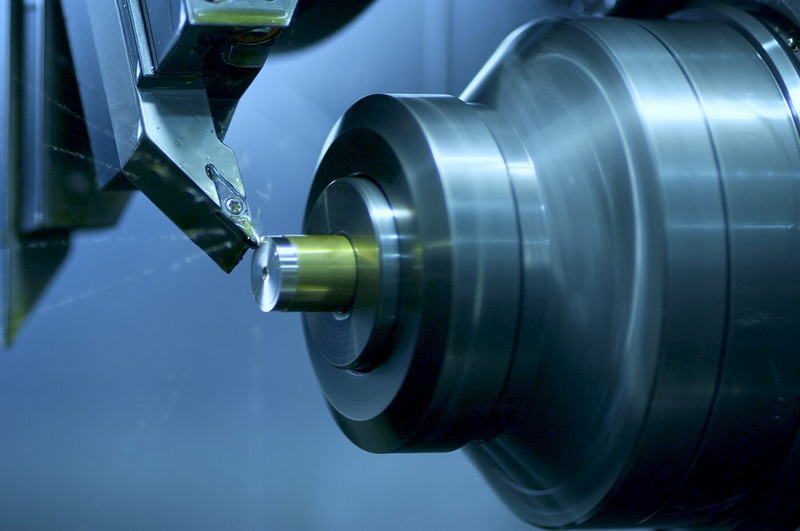
Global markets increasingly demand customized products, small batches, and frequent design updates, which favors flexible CNC machining. High‑mix, low‑volume production requires CNC machining lines that can change programs quickly and maintain quality with minimal setup losses.
Future‑ready CNC machining factories will focus on:
- Fast programming and setup for new designs, supported by AI‑enhanced CAM tools.
- Modular fixturing and tooling that support multiple part families on the same CNC machining cell.
- Digital order management and online quotation systems for rapid, on‑demand CNC machining services.
- Short lead times for CNC machining prototypes that can later scale to mass production.
This model matches OEM needs for flexible supply chains and allows providers like Shangchen to serve brands, wholesalers, and manufacturers worldwide with short delivery times. On‑demand CNC machining supported by digital platforms will become a standard service in the global manufacturing ecosystem.
Sustainability is another major driver shaping the future of CNC machining. Customers and regulators are pushing for lower energy consumption, reduced waste, and more efficient use of raw materials throughout CNC machining operations.
Sustainable CNC machining practices include:
- Optimizing toolpaths to shorten cycle time and reduce energy use.
- Using hybrid additive–subtractive workflows to minimize material removal and scrap.
- Recycling chips and coolant from CNC machining processes, and selecting eco‑friendly cutting fluids where possible.
- Monitoring energy consumption of individual CNC machining centers and using data to guide process improvements.
Factories that invest in greener CNC machining can enhance their brand image and meet the environmental expectations of leading overseas OEMs. For Shangchen, demonstrating sustainable CNC machining practices can also be a key marketing advantage when working with European and North American clients.
Even in a highly automated future, skilled people remain crucial for CNC machining. The role of operators is shifting from manual control to monitoring, process optimization, and collaboration with robots and AI systems in CNC machining cells.
Emerging skill needs around CNC machining include:
- Ability to program and fine‑tune CNC machining processes using advanced CAM and simulation tools.
- Understanding of data analytics and AI‑assisted decision‑making in CNC machining production.
- Cross‑disciplinary knowledge across CNC machining, additive manufacturing, and digital quality control.
- Strong problem‑solving capabilities for process optimization and complex part development.
Companies like Shangchen that invest in training machinists and engineers to work with smart CNC machining systems will be better positioned to support complex OEM projects. Human–machine collaboration will ensure that CNC machining remains both technically advanced and responsive to specific customer requirements.
For overseas brands, wholesalers, and manufacturers, the evolution of CNC machining translates into faster development cycles, higher quality, and more flexible supply chains. Smart, automated CNC machining factories can quickly turn 3D models into finished components while maintaining cost control and traceability.
Benefits OEM customers can expect from advanced CNC machining partners:
- Shorter lead times from rapid prototyping to precision batch production.
- Better consistency as CNC machining processes become more data‑driven and self‑correcting.
- More design freedom through hybrid CNC machining and 3D printing workflows.
- Transparent communication with digital tracking of CNC machining orders, quality reports, and production status.
Shangchen, with its mix of CNC machining, turning, sheet metal, 3D printing, and mold manufacturing capabilities, is aligned with these future expectations of international OEM buyers. By adopting modern CNC machining technologies, Shangchen can support customers across multiple industries and regions.
A typical future‑oriented CNC machining project for an OEM customer might look like this:
1. The customer uploads CAD data to an online portal, where AI‑enabled software evaluates manufacturability and suggests optimal CNC machining strategies.
2. The system automatically generates a quote, selects appropriate CNC machining centers, and schedules production based on live machine status.
3. CNC machining programs are created by AI‑assisted CAM, with toolpaths optimized for minimum cycle time and tool wear.
4. Robots load raw material into CNC machining cells, and IoT devices stream performance data to a central dashboard.
5. In‑process measurement systems verify dimensions and feed corrections back to CNC machining controls in real time.
6. Finished components undergo final inspection, are packed, and shipped with full digital traceability records for the entire CNC machining process.
Such a workflow shows how deeply digitalization, automation, and CNC machining will be integrated in the factories of the future. It also illustrates the level of responsiveness and transparency that OEM customers can expect.
To help customers understand complex processes, more CNC machining providers are using digital content and videos in marketing and technical communication. High‑quality process videos can show the entire CNC machining workflow, from rough stock to finished part, including hybrid additive–subtractive steps.
Typical CNC machining video content in the future might include:
- Time‑lapse clips of lights‑out CNC machining cells running with robots and automated inspection.
- Side‑by‑side comparisons of conventional vs. AI‑optimized CNC machining toolpaths.
- Demonstrations of hybrid 3D printing plus CNC machining for complex components.
- Educational clips explaining how CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, and mold making work together in product development.
For Shangchen, using professional CNC machining videos and digital demonstrations can help overseas buyers quickly evaluate capabilities, build trust, and reduce communication barriers.
The future of CNC machining will be defined by smart technologies, automation, AI‑driven optimization, and deep integration with additive manufacturing. These developments will improve the speed, quality, and cost‑effectiveness of CNC machining while making production more flexible and sustainable. For global OEM customers, partnering with advanced CNC machining factories means faster innovation cycles, more reliable supply, and broader design freedom. Factories like Shangchen, which combine CNC machining, rapid prototyping, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, turning, and mold production, are well positioned to serve this new generation of high‑mix, high‑quality OEM projects.
Conntact us to get more information!
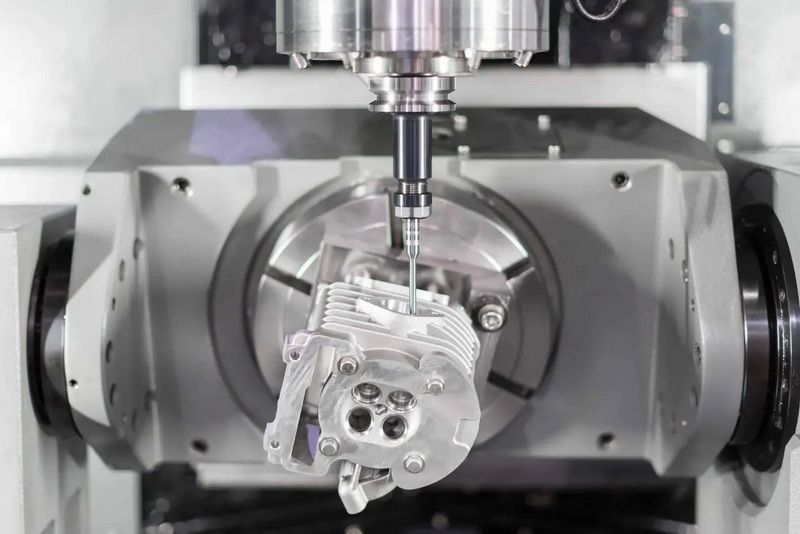

No, CNC machining will not be fully replaced by 3D printing because CNC machining still offers superior dimensional accuracy and surface finish for many critical parts. In the future, additive manufacturing and CNC machining will increasingly work together in hybrid workflows that combine the strengths of both technologies, especially for complex and high‑value components.
AI will make CNC machining more intelligent by optimizing toolpaths, predicting tool wear, and preventing machine breakdowns through predictive maintenance. This will lead to shorter cycle times, better quality, and higher machine utilization in CNC machining factories, allowing service providers to offer shorter lead times and more competitive prices.
“Lights‑out” CNC machining refers to production that can run with minimal or no human supervision, often overnight or 24/7, using automation and remote monitoring. Robots, automated loading systems, and smart sensors allow CNC machining cells to operate safely and efficiently without constant operator presence, significantly increasing available machine hours.
Future CNC machining systems will support high‑mix, low‑volume production through faster programming, modular fixturing, and digital scheduling tools. This enables CNC machining providers to deliver customized components and small batches quickly while preserving precision and cost control, which is essential for brands that frequently update designs or launch limited‑edition products.
Sustainability is important because customers and regulators expect lower energy use, less scrap, and more efficient material utilization across CNC machining operations. By optimizing toolpaths, using hybrid additive–subtractive processes, and recycling materials, CNC machining factories can reduce environmental impact, meet certification requirements, and stay competitive in international markets.
1. https://www.3erp.com/blog/future-of-cnc-machining/
2. https://www.americanmicroinc.com/resources/future-cnc-machining-trends-predictions/
3. https://kerfdevelopments.com/future-of-cnc-cutting-trends-in-manufacturing/
4. https://hotean.com/blogs/hotean-blog/additive-manufacturing-vs-cnc-machining
5. https://www.stratasys.com/en/resources/blog/cnc-vs-additive-manufacturing-am-3-scenarios-where-am-wins/
6. https://www.additivemanufacturing.media/articles/additive-manufacturing-is-subtractive-too-how-cnc-machining-integrates-with-am-
7. https://blog.hurco.com/how-ai-is-revolutionizing-the-cnc-machining-industry
8. https://www.makera.com/blogs/article/exploring-ai-future-role-in-cnc-machining
9. https://www.sahilcnc.com/technical-press-news/cnc-machining-in-2025-what-s-changing-in-the-industry/
content is empty!