








Content Menu
● Shangchen: One‑Stop Rapid Prototyping Partner
● Who Uses Rapid Prototyping? Key Sectors
>> Automotive and Transportation
>> Medical Devices and Healthcare
>> Consumer Electronics and Industrial Equipment
>> Startups, Innovators, and R&D Teams
>> Education, Labs, and Makers
● Why These Users Rely on Rapid Prototyping
>> Faster Development and Lower Risk
>> Design Freedom and Complexity
>> Cost Control and Better Communication
● How OEMs Use Shangchen for Rapid Prototyping
● Techniques Used in Rapid Prototyping
>> 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
>> Mold Making and Bridge Tooling
● Typical Workflow: From Idea to Production with Rapid Prototyping
● Why Overseas OEMs Choose Shangchen for Rapid Prototyping
● FAQs
>> (1) What types of companies use Rapid Prototyping?
>> (2) Why do OEMs prefer Rapid Prototyping before mass production?
>> (3) How does Shangchen support Rapid Prototyping projects?
>> (4) Which materials are commonly used in Rapid Prototyping?
>> (5) When should a company start using Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid Prototyping is now a core strategy for global brands, wholesalers, and manufacturers that want to bring better products to market faster, with less risk and lower total cost. It is used across many industries, from automotive and aerospace to medical devices, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment, and it is strongly supported by integrated suppliers such as Shangchen (sc-rapidmanufacturing.com).[1][2][3]

Shangchen (sc-rapidmanufacturing.com) is a specialized Chinese factory focused on Rapid Prototyping, CNC machining, precision batch production, lathe turning, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, and mold manufacturing for overseas OEM brands, wholesalers, and manufacturers. By combining engineering support with in‑house production, Shangchen helps foreign customers transform 3D concepts into real, testable Rapid Prototyping parts in very short lead times.[4][5][6]
Shangchen delivers one‑stop OEM support from early Rapid Prototyping through small‑batch bridge production and then into stable mass manufacturing. This integrated model reduces supplier hand‑offs, cuts communication delays, and ensures consistent quality across rapid CNC machining, 3D printing, sheet metal, and tooling programs.[3][5][6]
- Rapid Prototyping and functional prototypes for fit, assembly, and performance validation.[5][3]
- CNC milling and turning for tight‑tolerance metal and plastic components during Rapid Prototyping and early production.[6][7][8]
- Sheet metal fabrication for enclosures, brackets, and structural components in prototype and low‑volume runs.[3][4]
- 3D printing for complex geometries, lightweight structures, and quick design iterations within the Rapid Prototyping cycle.[9][1]
- Mold design and manufacturing to smoothly transfer from Rapid Prototyping to injection‑molded mass production.[10][3]
Shangchen is particularly suited to foreign OEM customers that need flexible Rapid Prototyping capacity, clear technical communication, and reliable lead times without building their own in‑house prototype shops. With a broad portfolio of materials, finishes, and quality‑control options, the company can support Rapid Prototyping projects from simple appearance models to demanding functional assemblies.[6][3]
Rapid Prototyping is a group of technologies and processes that quickly turn digital CAD designs into physical parts or assemblies for evaluation, testing, and validation. It often uses methods such as CNC machining, 3D printing, and sheet metal fabrication to produce prototype components within days instead of weeks or months.[2][1][10]
The goal of Rapid Prototyping is to shorten development cycles, reduce engineering changes during mass production, and improve product performance and user experience. Companies use Rapid Prototyping repeatedly throughout development: early appearance models, functional prototypes, engineering validation units, and pilot‑production parts.[11][1][2]
Rapid Prototyping is not limited to small startups; it is standard practice in large automotive, aerospace, and medical companies that operate global development programs. In each case, Rapid Prototyping provides physical feedback much earlier than traditional tooling, helping design and manufacturing teams make better decisions.[12][13][14]
Automotive OEMs and tier suppliers rely on Rapid Prototyping for design reviews, aerodynamic testing, and functional validation of structural and interior components. Rapid Prototyping supports fast iterations on brackets, housings, dashboards, lighting components, and under‑hood parts before hard tooling is frozen.[13][15][12]
Rapid Prototyping is also widely used to create fixtures, jigs, and test gauges for assembly lines and quality control. By applying Rapid Prototyping, manufacturers can adjust assembly concepts, ergonomics, and serviceability quickly when building new models or updating existing platforms.[7][16][12]
Aerospace manufacturers use Rapid Prototyping to develop lightweight, highly optimized parts for aircraft, satellites, UAVs, and rocket systems. Rapid Prototyping enables aerodynamic models, complex ducting, brackets, and interior components that must satisfy strict weight and safety requirements.[17][13]
Rapid Prototyping also plays a vital role in experimental programs and short‑run defense projects where traditional tooling would be too slow or expensive. Engineers can validate thermal behavior, assembly clearances, and maintainability using Rapid Prototyping components before committing to certified production hardware.[11][13][17]
Medical device companies use Rapid Prototyping for surgical tools, diagnostic equipment housings, implant concepts, and patient‑specific models generated from CT or MRI data. Rapid Prototyping supports early usability studies with doctors, nurses, and patients to optimize ergonomics, cleaning procedures, and user interfaces.[2][12][13]
Rapid Prototyping also accelerates regulatory documentation because design iterations and test results are generated much faster than with traditional machining alone. Hospitals and research centers apply Rapid Prototyping to create anatomical models for surgical planning, training, and communication with patients.[14][13][11]
Consumer electronics brands use Rapid Prototyping to refine product appearance, user interaction, and internal packaging of boards, batteries, and antennas. Rapid Prototyping of housings, buttons, and mounting features helps ensure reliability and a premium user feel before mass tooling.[9][12][2]
Industrial equipment manufacturers use Rapid Prototyping for machine covers, brackets, manifolds, and custom fixtures that must survive harsh operating conditions. Rapid Prototyping through CNC machining and sheet metal fabrication allows them to test real materials and full mechanical loads in the field, then feed improvements back into final designs.[8][18][7]
Startups and innovation labs depend heavily on Rapid Prototyping because they must prove concepts quickly while conserving capital. Rapid Prototyping makes it possible to build functional samples for investor demos, crowdfunding campaigns, and pilot customers without committing to large tooling investments.[1][14]
Corporate R&D departments also use Rapid Prototyping to explore new product lines and incremental upgrades in parallel, reducing the time between idea and market launch. By outsourcing Rapid Prototyping to experienced partners, internal teams can focus their resources on design and market strategy instead of managing complex shop floors.[10][2][11]
Universities, vocational schools, and research labs incorporate Rapid Prototyping into engineering, design, and innovation programs. Students and researchers use Rapid Prototyping to build experimental rigs, proof‑of‑concept devices, and competition robots that validate theoretical knowledge.[1][11]
Makerspaces and small workshops also adopt Rapid Prototyping to support hobbyists and independent developers who want to turn ideas into tangible parts. This culture of hands‑on Rapid Prototyping helps drive innovation and familiarizes the next generation of engineers with industrial processes.[14][9]
Across industries, Rapid Prototyping drastically shortens the time required to move from CAD model to physical part, often from months to days. This speed allows teams to test more ideas, identify design flaws early, and prevent expensive changes once mass production is underway.[2][11][1]
Rapid Prototyping also reduces risk by enabling real‑world testing under realistic loads, temperatures, and usage cycles before committing to high‑volume tooling. Engineers can iterate multiple Rapid Prototyping rounds to fine‑tune performance, manufacturability, and cost without interrupting existing production lines.[18][10][1]
Technologies used in Rapid Prototyping—such as multi‑axis CNC machining and advanced 3D printing—support complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible with conventional methods alone. Designers can experiment with internal channels, lattice structures, and topology‑optimized shapes during Rapid Prototyping without high tooling costs.[8][9][1]
This design freedom leads to lighter, stronger, and more efficient parts in fields like aerospace, motorsport, and high‑end industrial machinery, where performance margins are critical. Rapid Prototyping also makes customization practical, especially for medical and consumer products that require personalization or short production runs.[13][17][14]
Although each Rapid Prototyping part can be more expensive than a mass‑produced part, the overall project cost is usually lower because expensive design mistakes are avoided. Rapid Prototyping lets teams confirm functionality, assembly, and aesthetics before ordering expensive tools or committing to large purchase orders.[11][1][2]
Rapid Prototyping also improves communication among design, engineering, marketing, and end customers because a physical sample is easier to understand than drawings alone. Stakeholders can hold, test, and review Rapid Prototyping parts, which reduces misinterpretation and speeds up final approvals.[15][12][11]
Global brands, wholesalers, and manufacturers connect with Shangchen to manage complete Rapid Prototyping and pre‑production phases from a single source. By integrating CNC machining, lathe turning, sheet metal, 3D printing, and mold production, Shangchen maintains consistent tolerances and appearance across all Rapid Prototyping stages.[4][3][6]
Typical collaboration models for Rapid Prototyping with Shangchen include:[5][3][6]
- Concept and feasibility Rapid Prototyping: quick 3D printed mock‑ups and simple CNC parts for early feedback on form, size, and basic function.[9][1]
- Functional Rapid Prototyping: metal and engineering‑plastic CNC parts that are tested under real loads and environmental conditions in lab or field trials.[7][8]
- Pre‑production and bridge manufacturing: precision batch production using the same or similar processes and materials planned for mass manufacturing.[18][3]
Shangchen's OEM customers generally send 2D drawings or 3D CAD data together with material, finishing, and tolerance requirements for Rapid Prototyping. The engineering team then provides DFM (Design for Manufacturability) feedback, optimized Rapid Prototyping process selection, and clear lead‑time and cost estimates.[5][6]
For long‑term programs, Shangchen can maintain detailed production records so that Rapid Prototyping settings and inspection data evolve smoothly into mass‑production documentation. This continuity is valuable for industries that must follow strict quality and traceability standards such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices.[3][6]
CNC machining and turning are widely used Rapid Prototyping methods for parts requiring high precision, excellent mechanical properties, and real production materials. Metals such as aluminum, stainless steel, and tool steel, as well as plastics like ABS, nylon, and PEEK, are commonly used in Rapid Prototyping CNC processes.[7][8][18]
CNC Rapid Prototyping supports tight tolerances, smooth surface finishes, and high repeatability, making it ideal for functional testing and small‑batch production. It is especially valuable for automotive, aerospace, and industrial components where geometry and material performance must match final production parts.[17][8][7]
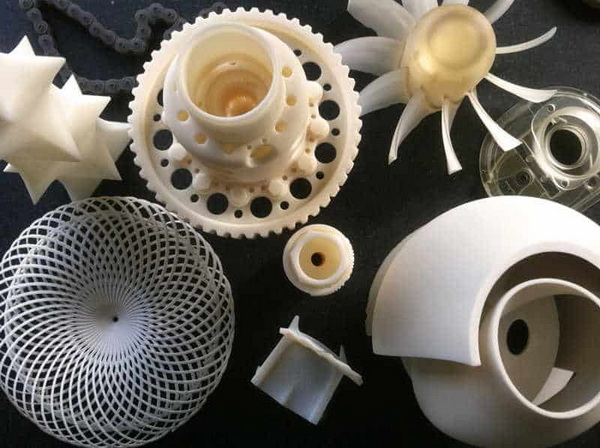
3D printing is a central technology in Rapid Prototyping because it can build complex shapes layer by layer directly from CAD data. It is frequently used for housings, brackets, internal airflow channels, lightweight structures, and aesthetic prototypes during Rapid Prototyping.[1][9][11]
Additive manufacturing in Rapid Prototyping is not limited to plastics; metal 3D printing is increasingly used for high‑performance aerospace and medical applications. These Rapid Prototyping methods reduce tooling cost and enable fast design changes without reworking molds or fixtures, especially during early design phases.[13][17][11]
Sheet metal fabrication is another important Rapid Prototyping approach for enclosures, frames, mounting plates, and support structures. Laser cutting, bending, welding, and surface finishing can all be combined in a Rapid Prototyping workflow to deliver robust parts quickly.[12][18][3]
Sheet metal Rapid Prototyping is used in industries such as electronics, telecom, and industrial automation, where cabinets, panels, and brackets must be tested in real installations. Shangchen includes sheet metal processes as part of its integrated Rapid Prototyping and OEM service offering so that customers can validate mechanical strength and assembly at early stages.[4][3]
For products that will ultimately be made by injection molding or die casting, Rapid Prototyping often includes soft tooling or bridge molds. These Rapid Prototyping tools are cheaper and faster to build than full production tools, allowing limited runs to validate design and market demand.[10][14][11]
Shangchen supports this stage by designing and manufacturing molds that connect Rapid Prototyping with scalable, repeatable mass production. This continuity ensures that learnings from Rapid Prototyping directly improve final tooling and production yields, reducing scrap and shortening ramp‑up time.[3][5][10]
A common product development flow using Rapid Prototyping looks like this:[2][11][1]
1. Concept design and CAD modeling for the initial idea.
2. Early Rapid Prototyping with 3D printing or simple CNC parts for appearance and basic functional review.
3. Iterative Rapid Prototyping rounds to refine ergonomics, tolerances, and materials using CNC, sheet metal, and higher‑performance 3D printing.
4. Validation and testing with Rapid Prototyping parts under real operating conditions, including mechanical, thermal, and environmental tests.
5. Bridge tooling and small‑batch production based on Rapid Prototyping learnings to check production stability and market feedback.
6. Transfer to full‑scale mass production once performance, reliability, and manufacturability are confirmed and all stakeholders approve the design.
Shangchen is designed to support customers through each of these Rapid Prototyping phases inside one organization, minimizing delays and miscommunication. Overseas OEM customers benefit from dealing with a single engineering and supply chain interface from first Rapid Prototyping sample to long‑term production, which simplifies project management.[6][5][3]
Overseas brands, wholesalers, and manufacturers select Shangchen as a Rapid Prototyping partner because it provides both flexibility and industrial‑grade quality. The combination of Rapid Prototyping with CNC machining, sheet metal, 3D printing, and mold production ensures that projects do not need to be transferred between multiple factories.[4][6][3]
Shangchen's Rapid Prototyping services are supported by experienced engineers who understand Western OEM requirements for tolerances, documentation, and long‑term reliability. With competitive pricing and efficient communication, Shangchen helps customers reduce development cost and compress product launch schedules through effective Rapid Prototyping.[18][5][3]
For customers who require long‑term cooperation, Shangchen can scale from one‑off Rapid Prototyping jobs to continuous production, serving as a strategic manufacturing partner. This combination of speed, flexibility, and scalability makes Shangchen a strong choice for companies that want to build global product portfolios using Rapid Prototyping as a core capability.[6][3]
Rapid Prototyping has become a standard tool for automotive, aerospace, medical, consumer, industrial, and startup teams that must innovate faster and reduce project risk. By combining CNC machining, 3D printing, sheet metal, and tooling into one integrated Rapid Prototyping workflow, companies can validate designs, test performance, and move to production with confidence.[17][11][1][2]
Shangchen (sc-rapidmanufacturing.com) stands out as a one‑stop Rapid Prototyping and OEM manufacturing partner for overseas brands, wholesalers, and manufacturers. Its combination of Rapid Prototyping expertise, CNC capabilities, precision batch production, lathe turning, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, and mold making gives global customers a reliable path from first idea to stable mass production.[5][3][4][6]

Rapid Prototyping is used by automotive, aerospace, medical device, consumer electronics, industrial equipment, telecom companies, startups, universities, and research institutions. Any organization that designs physical products and needs to test form, fit, function, or manufacturability can benefit from Rapid Prototyping across multiple stages of development.[15][12][14][13][17][1][2]
OEMs use Rapid Prototyping to detect design issues early, validate performance, and optimize manufacturability before investing in expensive production tooling. This approach reduces change orders, shortens time‑to‑market, and improves final product quality and customer satisfaction by basing decisions on tested hardware rather than only digital models.[14][11][1][2]
Shangchen supports Rapid Prototyping by offering CNC machining, turning, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, and mold manufacturing under one roof for overseas OEM customers. Its engineering team provides DFM advice, process selection, and optimized Rapid Prototyping solutions from concept samples through precision batch production, ensuring a smooth transition to mass manufacturing.[3][4][5][6]
Rapid Prototyping typically uses plastics such as ABS, nylon, polycarbonate, and PEEK, along with metals like aluminum, stainless steel, tool steel, and titanium. These materials allow prototypes to closely match final parts in strength, temperature resistance, and durability, particularly when produced by CNC Rapid Prototyping or advanced 3D printing technologies.[8][7][10][18]
A company should introduce Rapid Prototyping from the earliest concept stage and continue through all design and validation phases, updating prototypes as the design matures. Integrating Rapid Prototyping early with partners such as Shangchen enables faster learning cycles, better design decisions, and smoother transitions into large‑scale manufacturing programs.[1][2][5][3]
[1](https://formlabs.com/blog/ultimate-guide-to-rapid-prototyping/)
[2](https://www.autodesk.com/solutions/rapid-prototyping)
[3](https://www.sc-rapidmanufacturing.com)
[4](https://www.sc-rapidmanufacturing.com/news/Machining-Productivity-Differences.html)
[5](https://www.sc-rapidmanufacturing.com/what-is-rapid-prototyping-technology.html)
[6](https://www.sc-rapidmanufacturing.com/aboutus.html)
[7](https://www.bdeinc.com/capabilities/rapid-prototype-machining-services/)
[8](https://fastradius.com/capabilities/cnc-machining/prototyping/)
[9](https://www.phas.io/post/rapid-prototyping)
[10](https://www.xometry.com/rapid-prototyping-service/)
[11](https://xometry.pro/en/articles/rapid-prototyping-manufacturing/)
[12](https://manufactur3dmag.com/5-industries-benefit-from-rapid-prototyping/)
[13](https://www.ltc-proto.com/blog/the-role-of-rapid-prototyping-in-various-industries/)
[14](https://jiga.io/rapid-prototyping-definition/)
[15](https://www.sitech-corp.com/blog/6-industries-can-benefit-rapid-prototyping/)
[16](https://www.rcoeng.com/blog/rapid-prototyping-the-future-of-manufacturing)
[17](https://compositesuniversal.com/what-is-the-application-of-rapid-prototyping-in-aerospace-industry/)
[18](https://www.pcbway.com/rapid-prototyping/cnc-machining/)
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal