
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-12-08 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Shangchen: Your Rapid Prototyping Partner
● Rapid Prototyping UX: Core Definition
● How Rapid Prototyping UX Works
● Why Rapid Prototyping Matters in UX
● Types of Rapid Prototyping UX
>> Low-Fidelity Rapid Prototypes
>> Mid-Fidelity Rapid Prototypes
>> High-Fidelity Rapid Prototypes
● Digital vs Physical Rapid Prototyping in UX
● Role of Shangchen in Physical Rapid Prototyping for UX
● Benefits of Rapid Prototyping UX for Businesses
● Best Practices for Using Rapid Prototyping in UX
● When to Engage a Manufacturing Partner in UX Rapid Prototyping
● Rapid Prototyping UX and Agile Development
● FAQ
>> 1. What does Rapid Prototyping mean in UX?
>> 2. How does Rapid Prototyping improve the user experience?
>> 3. How is Rapid Prototyping different from traditional UX design?
>> 4. Why should UX teams involve a factory like Shangchen in Rapid Prototyping?
>> 5. Is Rapid Prototyping only relevant for software products?
Rapid Prototyping in UX is an iterative design approach where teams quickly create and test simplified versions of digital products to validate ideas, user flows, and usability before full-scale development. It reduces risk, accelerates time‑to‑market, and results in experiences that better match real user needs.

Shangchen (sc-rapidmanufacturing.com) is a China-based OEM factory specializing in Rapid Prototyping, CNC machining, precision batch production, CNC turning, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, and mold production for overseas brands, wholesalers, and manufacturers. By integrating multiple Rapid Prototyping processes in one facility, Shangchen helps UX and product teams move quickly from 3D CAD models to real parts that support both early experimentation and low-volume production.
Shangchen's Rapid Prototyping capability covers concept models, appearance samples, functional parts, pre-production batches, and tooling, which is particularly valuable when UX requirements must be validated on real hardware or physical interfaces. Global customers also benefit from engineering support, design-for-manufacturing feedback, and strict quality control, ensuring each Rapid Prototyping iteration is accurate and reproducible.
In UX, Rapid Prototyping is a fast, cyclical method of creating interactive models of products—such as mobile apps, websites, or embedded interfaces—to test usability, visual hierarchy, and interaction design. These prototypes can be low-fidelity sketches, mid-fidelity wireframes, or high-fidelity clickable simulations that behave almost like finished products.
The primary goal of Rapid Prototyping UX is learning. Teams quickly discover what users understand, where they get lost, and which features actually matter. Because each iteration is relatively inexpensive, UX designers can explore more options and make evidence-based decisions instead of relying on guesswork or internal assumptions.
Rapid Prototyping UX usually follows an iterative loop: ideate, prototype, test, and refine. This loop repeats until the design team gains enough confidence that the experience is usable, useful, and aligned with business goals. Each cycle may be short—sometimes just a few days—allowing teams to keep momentum and continuously improve.
In early cycles, Rapid Prototyping focuses on core concepts and main user paths using low-fidelity representations. Later cycles increase fidelity and detail, exploring visual design, micro-interactions, animations, and edge cases. For products involving hardware, UX Rapid Prototyping can integrate digital screens with physical models to test the complete user journey in a realistic context.
Rapid Prototyping in UX reduces the risk of building the wrong product by revealing usability issues early, while changes are still cheap and fast. This helps teams avoid costly rework that usually appears when problems are discovered just before launch or after development is finished.
It also accelerates time-to-market because short feedback loops allow teams to converge on a solid solution more quickly. Continuous iteration improves user satisfaction, as design decisions are grounded in observed behavior rather than personal preferences. For stakeholders, Rapid Prototyping produces tangible artifacts that make communication and alignment far easier than abstract documents alone.
Rapid Prototyping in UX spans several fidelity levels and formats. Each type is suited to a particular stage and goal, from rough idea exploration to near-final validation.
Low-fidelity Rapid Prototyping uses quick sketches, paper mockups, or simple digital wireframes to explore concepts. These prototypes are fast to create, easy to discard, and ideal for brainstorming, early workshops, and preliminary usability sessions.
Because low-fidelity Rapid Prototyping focuses on structure rather than detail, participants feel more comfortable giving critical feedback. The team can experiment freely with alternative flows, navigation schemes, and layouts before investing serious time in visuals or interaction details.
Mid-fidelity Rapid Prototyping introduces more structure and consistency, often using grayscale wireframes with defined grids, content blocks, and UI components. At this level, the team refines information architecture, screen hierarchy, and core interaction logic.
These prototypes are detailed enough to support more realistic tasks in usability tests, while remaining fast to change. Mid-fidelity Rapid Prototyping bridges the gap between early conceptual exploration and later visual design work, helping teams validate that the skeleton of the experience is sound.
High-fidelity Rapid Prototyping produces interactive prototypes that closely resemble the final product in look and feel. They often include brand colors, typography, icons, animations, and realistic data, making them suitable for in-depth usability tests and stakeholder demos.
At this stage, Rapid Prototyping helps verify fine details such as micro-interactions, transition timings, form behavior, accessibility, and responsiveness across devices. High-fidelity Rapid Prototyping also supports development teams by clarifying exact states and expected behavior, reducing ambiguity during implementation.
Many UX projects focus on purely digital experiences, but a growing number involve physical products with screens, buttons, sensors, or haptic feedback. In these cases, Rapid Prototyping must address both the digital interface and the physical form to ensure a coherent experience.
Digital Rapid Prototyping uses design tools to create on-screen simulations, while physical Rapid Prototyping uses technologies like CNC machining, 3D printing, and sheet metal fabrication to build actual objects. Integrating both types allows teams to test ergonomics, visibility, and interaction patterns in real-world conditions rather than only on a flat screen.
For example, the same Rapid Prototyping UX cycle might test a mobile app interface in a lab environment while simultaneously evaluating a handheld device shell that affects how users grip and interact with the product. This holistic approach reveals issues that cannot be seen through digital prototypes alone.
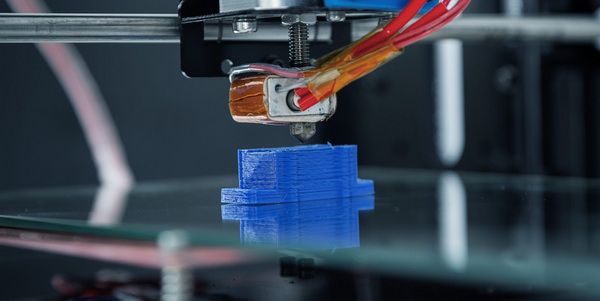
Shangchen plays a key role in physical Rapid Prototyping for UX by providing fast manufacturing of prototype components that align with digital designs. With capabilities in CNC machining, CNC turning, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, and mold production, Shangchen can produce housings, brackets, panels, and structural parts for a wide range of industries.
For UX teams working on hardware or mixed hardware–software products, this means they can:
- Validate ergonomics by testing real device shapes, sizes, and weights.
- Check how screens, buttons, and sensors align with human hands, eyes, and motion.
- Evaluate material choices, surface textures, and tolerances that influence perceived quality and comfort.
Once a Rapid Prototyping iteration has been tested, Shangchen can quickly adjust designs and produce the next version, supporting tight iteration cycles similar to digital Rapid Prototyping. When the design stabilizes, the same factory can transition from Rapid Prototyping to precision batch production and eventually to full OEM manufacturing.
For businesses, Rapid Prototyping UX is more than a design technique; it is a strategy for reducing uncertainty and driving innovation. Companies that embed Rapid Prototyping in their UX process typically see several advantages:
- Lower development costs, because flawed concepts are filtered out early.
- Faster decision-making, as stakeholders review realistic prototypes instead of abstract reports.
- Stronger alignment between product, design, development, and marketing teams.
- Improved customer satisfaction, thanks to experiences shaped by real user feedback.
When combined with physical Rapid Prototyping from a partner like Shangchen, businesses can also reduce the risk associated with tooling investments, as critical design decisions are validated on real parts before committing to expensive molds or large production runs.
To get the full value from Rapid Prototyping UX, teams should adopt a few key best practices that keep the process focused and efficient.
First, each Rapid Prototyping cycle should start with a clear learning objective. Instead of trying to test everything, choose a small set of questions, such as whether users understand the onboarding flow or can complete a specific task without help. This keeps prototypes lean and targeted.
Second, match fidelity to the question. Early on, low-fidelity Rapid Prototyping is usually enough to validate ideas and navigation. As the team gains confidence, mid- and high-fidelity Rapid Prototyping become appropriate to refine visual design and interaction details.
Third, involve real users early and often. Rapid Prototyping UX works best when actual target users interact with prototypes, complete realistic tasks, and speak freely about what feels confusing or delightful. Observing real behavior often reveals insights that internal discussions cannot.
Fourth, document insights after each round and intentionally feed them into the next iteration. Rapid Prototyping is not just about building; it is about learning and applying that learning systematically.
For purely digital products, design tools may be enough in the early stages. However, for any project that eventually becomes a physical product, involving a manufacturing partner like Shangchen early in the Rapid Prototyping UX process can prevent costly surprises.
Engaging Shangchen during concept development allows the team to receive feedback on feasibility, materials, and tolerances, while still having flexibility to change the design. This makes both digital and physical Rapid Prototyping more realistic, as prototypes can be built using processes and materials closer to the final product.
As the design matures, Shangchen can support higher-fidelity Rapid Prototyping with improved finishing, tighter tolerances, and more advanced materials. This is particularly important for UX evaluation of premium products, where surface quality, touch, and weight strongly influence user perception.
Rapid Prototyping UX aligns naturally with agile development methodologies, which emphasize short cycles, continuous feedback, and incremental delivery. In an agile context, Rapid Prototyping acts as a bridge between product discovery and implementation.
Before each sprint or release, UX teams can use Rapid Prototyping to test concepts, refine requirements, and validate user journeys. Developers then build features with greater clarity, reducing rework and increasing the chances of delivering value in each iteration.
For products including hardware, sprint planning can also incorporate physical Rapid Prototyping, where Shangchen delivers updated components or assemblies for evaluation. This synchronizes software and hardware progress and keeps the full experience aligned.
Rapid Prototyping UX is an iterative, user-centered approach that turns ideas into testable prototypes quickly, helping teams validate and refine experiences long before large investments in development or tooling. By cycling through ideation, prototyping, testing, and refinement, businesses reduce risk, accelerate time-to-market, and deliver solutions that align more closely with user expectations.
When digital Rapid Prototyping is combined with physical Rapid Prototyping from a capable OEM factory like Shangchen (sc-rapidmanufacturing.com), teams can evaluate the complete user experience across interfaces, ergonomics, and product performance. This integrated strategy allows overseas brands, wholesalers, and manufacturers to move from early concepts to reliable batch production with greater confidence and fewer surprises.

Rapid Prototyping in UX is a fast, cyclical process where designers build simplified versions of a product's interface to test ideas, user flows, and usability before full development. It focuses on learning from real user interactions and refining designs step by step based on feedback.
Rapid Prototyping improves user experience by exposing design issues early, such as confusing navigation or unclear content, while changes are still easy to make. Repeated testing and refinement ensure that the final product is intuitive, efficient, and aligned with how users actually think and behave.
Traditional UX design often relies on longer planning phases and fewer iterations, with user testing concentrated near the end of the project. Rapid Prototyping, in contrast, emphasizes short cycles with frequent user testing and incremental improvements, reducing the risk of major changes late in development.
UX teams should involve a factory such as Shangchen when their products include physical components, enclosures, or mechanical parts that affect the overall experience. Shangchen provides physical Rapid Prototyping through CNC machining, 3D printing, sheet metal fabrication, and mold production, allowing teams to test real parts alongside digital interfaces.
Rapid Prototyping is widely used for software UX, but it is also essential for products that involve physical interaction, such as medical devices, industrial equipment, consumer electronics, and smart home systems. Combining digital Rapid Prototyping with physical Rapid Prototyping ensures the complete system is comfortable, safe, and easy to use.
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal