
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2026-01-26 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● What Is Additive Manufacturing?
● Additive Manufacturing vs Rapid Prototyping
● How Rapid Prototyping Works in Practice
● Benefits of Rapid Prototyping with Additive Manufacturing
● Role of CNC Machining in Rapid Prototyping
● Rapid Prototyping with 3D Printing
● From Rapid Prototyping to Mass Production in China
● Applications of Rapid Prototyping and Additive Manufacturing
● How Shangchen Supports Rapid Prototyping and OEM Services
● Why Rapid Prototyping Matters for Global OEMs
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the main difference between additive manufacturing and Rapid Prototyping?
>> 2. Can Rapid Prototyping be done without additive manufacturing?
>> 3. Is additive manufacturing suitable for mass production?
>> 4. Why is Rapid Prototyping important for foreign OEM buyers?
>> 5. How does Shangchen integrate Rapid Prototyping with CNC and mass production?
Additive manufacturing and Rapid Prototyping are closely related technologies that are transforming how modern products are designed, tested, and brought into mass production. Both are essential tools for global OEM buyers looking for reliable Chinese manufacturing partners like Shangchen for CNC machining, rapid prototype development, and precision batch production.

Additive manufacturing is a production method where parts are created layer by layer directly from 3D digital data, rather than being cut from a solid block of material. It is often associated with industrial 3D printing and can be used for both prototypes and end-use parts.
Key characteristics of additive manufacturing include:
- Layer‑by‑layer building of parts from CAD models.
- Minimal material waste compared with traditional subtractive machining.
- Ability to produce highly complex internal features and lightweight structures.
- Compatibility with various materials such as plastics, resins, metals, and ceramics, depending on the specific process.
For international brands and wholesalers, additive manufacturing allows flexible production runs, quick design changes, and localized manufacturing without investing in hard tooling. This flexibility is particularly valuable when testing new product concepts, customizing parts for niche markets, or launching low-volume series.
Rapid Prototyping is a group of techniques used to quickly create physical models or prototypes directly from 3D CAD data to evaluate design, assembly, and function before committing to full-scale production. Rapid Prototyping does not refer to one single technology but to a workflow that can include 3D printing, CNC machining, vacuum casting, and other methods.
Essential features of Rapid Prototyping include:
- Fast production of physical parts for design verification and functional testing.
- Typical use during the design and development stage rather than the final production stage.
- Support for multiple technologies, including additive manufacturing, CNC machining, and sheet metal fabrication.
- Helping engineers iterate quickly, catch errors early, and optimize parts before investing in molds and tools.
For OEM clients working with Shangchen, Rapid Prototyping is the bridge between a digital idea and a manufacturable product ready for CNC machining, injection molding, and precision mass production. Well-planned Rapid Prototyping compresses the development cycle and gives decision‑makers real parts in hand instead of only digital simulations.
Although the two are often confused, additive manufacturing and Rapid Prototyping are not identical. Rapid Prototyping is a product development strategy, while additive manufacturing is one of the technologies used in that strategy.
- Purpose
- Rapid Prototyping focuses on prototypes, test parts, and design validation.
- Additive manufacturing focuses on creating both functional prototypes and final-use components for production.
- Scope
- Rapid Prototyping covers various technologies such as 3D printing, CNC machining, and sometimes laser cutting or sheet metal forming.
- Additive manufacturing is specifically about layer‑by‑layer additive processes like industrial 3D printing.
- Position in the product life cycle
- Rapid Prototyping is primarily used in concept, design, and pre‑production phases.
- Additive manufacturing can be used in both prototyping and final mass production.
For a Chinese manufacturing factory like Shangchen, the typical path is: Rapid Prototyping → design validation → tooling or direct additive manufacturing → CNC and batch production. In other words, Rapid Prototyping answers the question “Is this design correct?”, while additive manufacturing answers “How can we produce this part additively?”.
In a typical Rapid Prototyping project, a foreign brand or OEM sends 3D CAD files and basic requirements to a manufacturing partner. The partner then chooses the most suitable Rapid Prototyping technology based on material, geometry, and target timing.
A common workflow looks like this:
1. CAD design and DFM review
- The customer shares CAD models and key tolerances.
- The engineering team performs a design‑for‑manufacturing (DFM) analysis to ensure the design is feasible for Rapid Prototyping, CNC machining, injection molding, or sheet metal manufacturing.
2. Technology selection for Rapid Prototyping
- Additive manufacturing / 3D printing for complex internal channels, lightweight structures, and quick visual models.
- CNC machining Rapid Prototyping for precise metal and plastic parts requiring tight tolerances and similar materials to production.
- Sheet metal prototyping for enclosures, brackets, and structural components.
3. Prototype manufacturing
- Prototypes are produced within days to verify dimensions, assembly, and function.
- Multiple Rapid Prototyping iterations can be scheduled in short cycles, allowing quick design evolution.
4. Testing and iteration
- The customer tests the Rapid Prototyping parts in real or simulated operating conditions.
- Feedback is collected and design adjustments are applied to the CAD model.
5. Transition to production
- Once Rapid Prototyping is successful, the design is frozen and transferred to CNC machining, molding, or additive manufacturing for batch production.
- Documentation and quality standards used in Rapid Prototyping are refined for production control.
This is precisely where Shangchen provides value: integrating Rapid Prototyping with CNC machining, turning, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, and mold production for a complete OEM solution.
When Rapid Prototyping is combined with additive manufacturing, product development becomes faster, more flexible, and more cost‑effective.
Key benefits include:
- Faster development cycles
Rapid Prototyping lets teams validate ideas quickly, while additive manufacturing allows immediate creation of new iterations, reducing the time from concept to market. This speed is critical in competitive industries where product life cycles are short.
- Reduced risk and lower development cost
Rapid Prototyping helps discover design errors before expensive tooling is produced. Additive manufacturing provides low‑volume production without high upfront tooling costs, which is ideal for pilot runs and market testing.
- Greater design freedom
Additive manufacturing can create complex geometries that are impossible or extremely expensive with traditional machining. Combining CNC Rapid Prototyping with additive manufacturing gives engineers the freedom to choose the best method for each component depending on strength, surface finish, and cost.
- Easier customization
Rapid Prototyping with additive manufacturing makes it economical to customize parts for specific customers, local regulations, or small batches. This is especially useful for medical devices, consumer electronics accessories, and specialty industrial equipment.
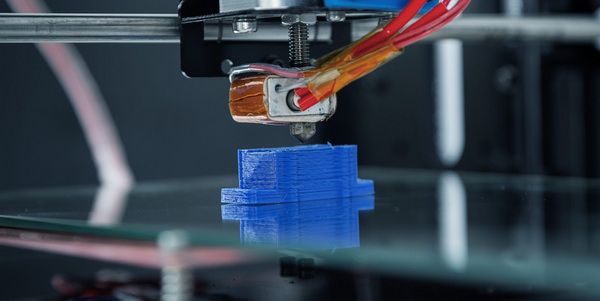
Despite the growth of additive manufacturing, CNC machining remains a core technology in professional Rapid Prototyping. For many functional prototypes, especially metal components, CNC machining is still the best way to simulate final production conditions.
Advantages of CNC‑based Rapid Prototyping:
- High dimensional accuracy and tight tolerances suitable for mechanical, automotive, and aerospace parts.
- Wide choice of engineering metals and plastics that match final production materials, such as aluminum alloys, stainless steels, and engineering plastics.
- Excellent surface finish, especially when combined with post‑processing such as anodizing, polishing, bead blasting, or coating.
Chinese factories like Shangchen often integrate CNC Rapid Prototyping with long‑term mass production, ensuring that the prototype and final product come from the same technical team and process knowledge base. This continuity makes it easier to control tolerances and repeatability when scaling up.
3D printing is one of the most popular additive manufacturing methods used in Rapid Prototyping because it can quickly transform CAD designs into physical parts with minimal setup.
Common use cases:
- Visual models for marketing, concept approval, and investor presentations.
- Fit‑check parts to verify assembly, clearances, and interface with other components.
- Functional Rapid Prototyping using advanced resins and engineering plastics for mechanical testing, snap‑fit testing, and ergonomic evaluation.
There are several typical 3D printing processes used in Rapid Prototyping:
- Fused filament fabrication (FFF/FDM) for basic plastic prototypes and housings.
- Stereolithography (SLA) for high‑detail, smooth prototypes suitable for cosmetic evaluation.
- Selective laser sintering (SLS) for robust functional parts with good mechanical strength.
- Metal additive manufacturing for high‑value components that must be tested under real load in Rapid Prototyping stages.
For international OEM clients, combining 3D printing Rapid Prototyping with CNC and sheet metal options allows each part of a product to use the most efficient manufacturing technique.
The real power of Rapid Prototyping appears when it is connected seamlessly to mass production. A typical journey for a foreign brand working with a Chinese factory like Shangchen looks like this:
- Rapid Prototyping stage
- Additive manufacturing and CNC machining are used to create initial prototypes.
- Multiple Rapid Prototyping rounds ensure that all design, performance, and quality targets are met.
- Pre‑production and tooling
- Once Rapid Prototyping is confirmed, molds for injection molding or die casting are designed and manufactured.
- CNC fixtures, inspection gauges, and jigs are prepared for stable mass production.
- Mass production
- Precision CNC machining, turning, sheet metal fabrication, and molding operations are launched under strict quality control.
- Rapid Prototyping facilities remain available for engineering changes, custom variants, and next‑generation product development.
Shangchen's integrated services—Rapid Prototyping, CNC machining, turning, sheet metal manufacturing, 3D printing, and mold production—are designed to support this complete development‑to‑production workflow for overseas OEM clients.
Companies across many sectors are using Rapid Prototyping and additive manufacturing together to shorten launch times and improve product performance.
Example applications include:
- Automotive
Rapid Prototyping of brackets, housings, trim parts, and interior components, followed by additive manufacturing or CNC production for end-use parts, small series, or motorsport components.
- Aerospace and aviation
Lightweight structural parts, complex ducting, and brackets created by additive manufacturing, validated first through Rapid Prototyping models for vibration, thermal, and fit tests.
- Consumer products and electronics
Fast Rapid Prototyping of housings, handles, and mechanisms to check ergonomics, button feel, and appearance before investing in high‑cost molds and tooling.
- Industrial equipment and machinery
CNC Rapid Prototyping of precision components to test performance under real‑world loads and to adjust design for maintainability and assembly efficiency.
- Medical and healthcare
Patient‑specific guides and components made possible by combining Rapid Prototyping with additive manufacturing based on scan data, while production tooling is still in development.
For foreign buyers, working with a Chinese supplier that understands both Rapid Prototyping and large‑scale CNC and molding production is critical to achieving shorter lead times and reliable quality.
As a Chinese factory focusing on Rapid Prototyping, CNC machining, precision batch production, lathe turning, sheet metal manufacturing, 3D printing services, and mold production, Shangchen is structured to support overseas brand owners, wholesalers, and manufacturers through OEM cooperation.
Core capabilities aligned with Rapid Prototyping and additive manufacturing include:
- Engineering support for CAD review and DFM to select the best Rapid Prototyping route, whether 3D printing, CNC machining, or sheet metal fabrication.
- Flexible production that moves from Rapid Prototyping batches to full mass production using the same engineering data and quality standards.
- Strict quality control with dimensional inspection, functional testing, and documentation suitable for international OEM projects.
Shangchen's engineering team can recommend when to use Rapid Prototyping via additive manufacturing for speed and when to switch to CNC or molding for cost and durability. This consultative approach helps clients choose the right balance between development cost, lead time, and part performance.
Global OEMs and brand owners face intense pressure to launch new products faster while maintaining high quality and competitive pricing. Rapid Prototyping, especially when combined with additive manufacturing and CNC machining in a single factory, directly supports these goals.
The strategic advantages for OEMs include:
- More design freedom at early stages, because Rapid Prototyping encourages experimentation and quick iteration.
- Better communication between design teams and manufacturing engineers, thanks to physical prototypes instead of only drawings.
- Improved decision‑making, since managers can hold and test real Rapid Prototyping parts before committing to tooling budgets.
- A smoother transition to mass production when the same supplier handles Rapid Prototyping and final manufacturing.
Shangchen, as a one‑stop Rapid Prototyping and OEM manufacturing partner in China, enables foreign customers to leverage these advantages with clear communication, stable quality, and competitive lead times.
Additive manufacturing and Rapid Prototyping are closely related but distinct concepts that together enable faster, more flexible, and more reliable product development. Rapid Prototyping focuses on quickly creating test parts to validate design and function, using technologies such as additive manufacturing, CNC machining, and sheet metal forming. Additive manufacturing, in turn, provides a layer‑by‑layer technology that supports both functional Rapid Prototyping and end‑use production parts.
For international brands, wholesalers, and OEMs working with a Chinese manufacturing partner like Shangchen, integrating Rapid Prototyping with CNC machining, turning, sheet metal manufacturing, 3D printing, and mold production creates a complete path from concept to mass production. This integration helps control development risk, reduce costs, shorten time‑to‑market, and maintain consistent quality from the first prototype to the final shipped product.
Contact us to get more information!
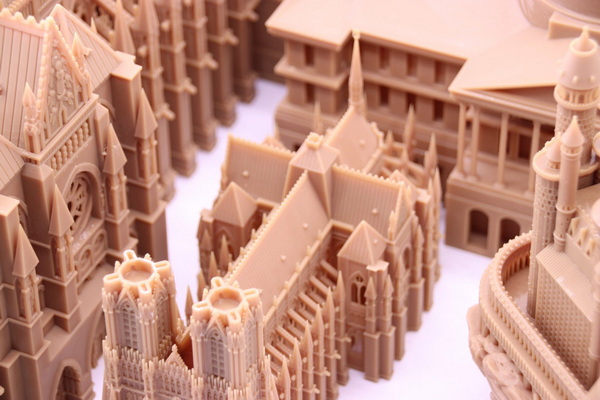

The main difference is that additive manufacturing is a specific production technology, while Rapid Prototyping is a development approach. Rapid Prototyping often uses additive manufacturing, but it also includes CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, and other quick‑turn methods. Additive manufacturing can be applied both to prototypes and to final-use parts, whereas Rapid Prototyping is focused on design validation and early‑stage testing.
Yes. Rapid Prototyping can be performed using CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, vacuum casting, or other fast manufacturing processes in addition to 3D printing. The choice depends on factors such as material requirements, desired accuracy, geometry complexity, and budget. Many metal and high‑precision prototypes are still produced through CNC Rapid Prototyping rather than purely additive methods.
In many cases, additive manufacturing is suitable for low‑ to medium‑volume mass production, especially when parts have complex geometries, frequent design updates, or customization requirements. However, for very high volumes and simpler geometries, traditional processes like injection molding, die casting, and conventional CNC machining often remain more economical. A common strategy is to use additive manufacturing for Rapid Prototyping and for early market launches, then transition to tooling‑based mass production once demand is stable.
Rapid Prototyping helps foreign OEM buyers verify design ideas, avoid costly mistakes in molds and tooling, and confirm performance before committing to mass production. It improves communication between overseas design teams and Chinese manufacturers by providing physical samples, making it easier to align expectations. Rapid Prototyping also shortens development cycles, supports design optimization, and reduces the risk of quality issues after launch.
Shangchen uses Rapid Prototyping methods such as 3D printing and CNC machining to create early prototypes, then transitions successful designs to precision CNC, turning, sheet metal fabrication, and molding for batch production. The same engineering team that supports Rapid Prototyping also defines process parameters and quality standards for production, ensuring consistency across all stages. This integrated approach shortens lead time, improves repeatability, and gives overseas customers a single, reliable partner from concept to final OEM delivery.
1. https://jp-murphy.com/blog/additive-manufacturing/
2. https://richconn.com/zh-CN/
3. https://www.rinapart.com/injection-molding/additive-manufacturing-vs-rapid-prototyping-whats-the-difference-.html
4. https://www.teamrapidtooling.com/zh-CN/cnc-machining-services-t-19.html
5. https://luxcreo.com/what-is-3d-printing-additive-manufacturing-and-rapid-prototyping-lc/
6. https://www.enggweb.com/rapid-prototyping-vs-additive-manufacturing/
7. https://www.makerverse.com/resources/insights-and-trends/the-guide-to-rapid-prototyping-with-additive-manufacturing/
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal