
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-12-01 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Shangchen: One-Stop Rapid Prototyping Partner
● Understanding Rapid Prototyping
● What Is a Rapid Prototyping Machine?
● Main Types of Rapid Prototyping Machines
>> Additive Manufacturing Systems
>> Sheet Metal Fabrication Equipment
>> Mold-Making and Tooling Machines
● How Rapid Prototyping Machines Work
● Common Rapid Prototyping Processes
● Benefits of Rapid Prototyping Machines
● Rapid Prototyping Machines at Shangchen
● Choosing the Right Rapid Prototyping Machine
● Industries Using Rapid Prototyping Machines
● Trends in Rapid Prototyping Machines
● FAQs
>> 1. What is the main purpose of a rapid prototyping machine?
>> 2. How is a rapid prototyping machine different from traditional manufacturing equipment?
>> 3. Which materials can rapid prototyping machines handle?
>> 4. Why should overseas OEM brands choose Shangchen for rapid prototyping?
>> 5. How do I start a rapid prototyping project with Shangchen?
A rapid prototyping machine is any digitally controlled manufacturing system that quickly turns 3D CAD data into physical prototypes so engineers can validate design, fit, and function before mass production. In modern product development, rapid prototyping machines include 3D printers, CNC machining centers, sheet metal equipment, and tooling machines working together in an integrated workflow.[11][12][13][14]
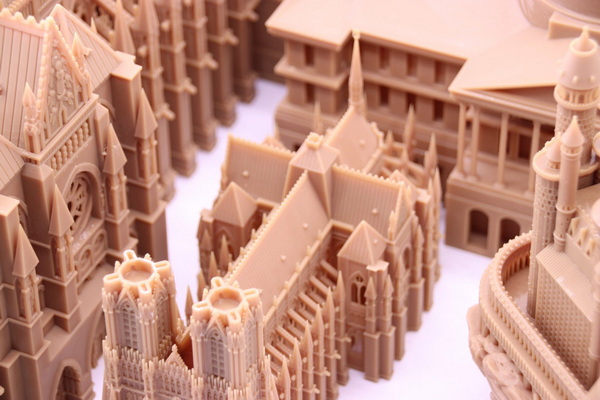

Shangchen (sc-rapidmanufacturing.com) is a China-based OEM factory specializing in rapid prototyping, CNC machining services, precision batch production, turning, sheet metal manufacturing, 3D printing services, and mold production for overseas brands, wholesalers, and manufacturers. By combining a wide range of rapid prototyping machines under one roof, Shangchen supports customers from early design validation to small-batch production and tooling for full-scale manufacturing.[15][16][17][18]
Shangchen operates multi-axis CNC machining centers, turning lathes, industrial 3D printers, sheet metal fabrication lines, and mold-making equipment to deliver fast and accurate rapid prototyping solutions. Overseas OEM clients can order engineering prototypes, cosmetic mock-ups, and functional low-volume parts without coordinating multiple suppliers, reducing risk and saving time.[16][17][18][19][15]
- CNC rapid prototyping for tight-tolerance metal and plastic parts.
- Sheet metal rapid prototyping for enclosures, brackets, and frames.
- 3D printing rapid prototyping for complex geometries and quick iteration.
- Mold production and rapid tooling for bridge and mass production.[17][15][16]
Rapid prototyping is a group of techniques used to quickly fabricate a physical part, model, or assembly directly from three-dimensional CAD data. It enables design teams to move from virtual models to tangible parts in days instead of the weeks or months required by traditional prototyping methods.[12][13][14][20][11]
Most rapid prototyping workflows rely on digital manufacturing technologies such as additive manufacturing (3D printing), CNC machining, and hybrid processes that shorten lead times and reduce development risk. With rapid prototyping, companies can test more design iterations, identify problems earlier, and refine products with real-world feedback before committing to expensive tooling.[9][13][20][11]
A rapid prototyping machine is any automated system that converts CAD models into physical parts quickly and with minimal manual intervention. Common examples include industrial 3D printers, CNC machining centers, CNC turning lathes, laser cutting machines, and equipment used for prototype tooling.[14][21][22][11]
These machines interpret CAD data, generate toolpaths or sliced layers, and then shape materials such as plastics, resins, aluminum, and steels into accurate prototypes. In OEM environments, multiple rapid prototyping machines often run in parallel to produce different components of a product, accelerating iteration cycles and shortening time-to-market.[13][21][23][11]
Additive manufacturing machines—commonly called 3D printers—build parts layer by layer from materials such as thermoplastic filaments, photopolymer resins, or powders. Key technologies include FDM, SLA, SLS, and Multi Jet Fusion, each offering different balances of speed, accuracy, and material performance.[8][24][9][11][13][14]
3D printing rapid prototyping is ideal for concept models, ergonomic studies, and early functional prototypes where design changes happen frequently and turnaround time is critical. Because no hard tooling is required, additive rapid prototyping offers low entry cost for single parts or very small batches, making it attractive for startups and custom products.[24][25][13]
CNC milling and turning machines are subtractive rapid prototyping tools that remove material from solid blocks or bars using programmed cutting paths. Modern 3‑, 4‑, and 5‑axis CNC rapid prototyping machines can achieve tight tolerances, high dimensional accuracy, and excellent surface finishes in metals and engineering plastics.[3][21][22]
CNC rapid prototyping is preferred when prototypes must closely match the strength, tolerance, and finish of final production parts, such as in aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and industrial machinery. For Shangchen's OEM customers, the same CNC rapid prototyping machines used for one-off parts can be scaled to precision batch production, ensuring consistent quality from prototype to volume.[19][22][23][26][15][16]
Sheet metal rapid prototyping relies on digital equipment such as fiber laser cutters, turret punches, bending machines, and welding systems to convert flat metal sheets into functional components. These machines use CAD data to generate nesting and bending programs, significantly reducing setup time for low- and medium‑volume runs.[25][14][15]
Sheet metal rapid prototyping is widely used for control boxes, electronics housings, chassis, mounting brackets, and structural frames that must be tested under real conditions before tooling is finalized. By combining sheet metal rapid prototyping with CNC and 3D printing, Shangchen can supply complete mechanical assemblies for overseas OEMs.[15][17]
High-speed machining centers, EDM systems, and polishing lines become rapid prototyping machines when they are applied to prototype mold and die production. Prototype tooling enables manufacturers to test real production materials and injection molding or die-casting processes while still leaving room for design changes.[21][27]
Using rapid prototyping for tooling—sometimes called bridge tooling or soft tooling—supports economical low- to mid‑volume production and design validation before committing to fully hardened, high-volume tools. Shangchen's mold production capabilities allow overseas brands to move smoothly from rapid prototyping to full-scale manufacturing using validated tooling.[27][9][16][15]
Rapid prototyping machines always begin with 3D CAD models created in software and exported as STEP, IGES, STL, or similar formats. This digital data is then processed by CAM or slicing software to generate machine instructions, such as toolpaths for CNC rapid prototyping machines or layer patterns for 3D printers.[20][9][11][21][25]
In a typical rapid prototyping workflow:
1. Designers upload CAD files, specify tolerances, materials, and surface requirements.
2. The appropriate rapid prototyping machine is selected based on geometry, performance needs, and budget.
3. The machine manufactures the part, often followed by post‑processing such as support removal, deburring, painting, or coating.[26][11][13]
Rapid prototyping rarely relies on a single process; most projects combine multiple technologies to balance cost, speed, and performance. For example, 3D printing may be used for fast early concepts, while CNC rapid prototyping machines handle structural or precision-critical components.[22][23][9][13]
Typical rapid prototyping stages include:
- Concept and styling models with 3D printing rapid prototyping for look-and-feel.
- Functional and mechanical prototypes using CNC rapid prototyping machines for strength and accuracy.
- Pilot runs using sheet metal fabrication and prototype molds to validate assembly, reliability, and manufacturability.[13][22][25]
Rapid prototyping machines dramatically reduce time-to-market by compressing development and testing cycles from months to days or weeks. Faster iterations allow engineers to explore more design options, detect issues earlier, and refine ergonomics and aesthetics using real physical models.[4][14][20][13]
Rapid prototyping also lowers risk by catching manufacturing problems, performance weaknesses, and usability issues before final tooling is committed. For OEMs, partnering with a provider like Shangchen that operates multiple rapid prototyping machines enables cost-effective low-volume production with production-grade materials and processes.[18][4][17][21][13][15]
Key advantages of rapid prototyping:
- Shorter development cycles and quicker decision-making.
- Better communication among design, engineering, and marketing teams.
- More accurate cost and manufacturability assessments before scaling up.[9][20][13]
Shangchen integrates several rapid prototyping technologies into a single OEM service platform designed for overseas customers. Clients can share CAD models and project details and receive expert advice on whether to use 3D printing, CNC rapid prototyping, sheet metal fabrication, or prototype tooling for each stage.[16][17][18][15]
Shangchen's rapid prototyping strengths include:
- CNC rapid prototyping: multi-axis milling and turning for precision parts in metals and plastics.[19][22]
- 3D printing rapid prototyping: fast iteration with complex geometries, internal channels, and lightweight structures.[24][13]
- Sheet metal rapid prototyping: laser cutting, bending, and welding of steel, aluminum, and other alloys for structural components.[17][15]
- Rapid tooling and mold manufacturing: prototype and bridge molds that enable low- to mid‑volume production with real production materials.[15][16]
By coordinating these rapid prototyping machines and processes, Shangchen helps OEM customers move from concept to production with fewer handoffs and stronger process control.[18][17][15]
Selecting the most suitable rapid prototyping machine depends on part geometry, material, tolerance, surface quality, mechanical performance, and budget. As a general guideline, 3D printing rapid prototyping is ideal for complex shapes and early-stage concepts, while CNC rapid prototyping machines excel in high-precision, load-bearing parts.[2][23][13][24]
Sheet metal rapid prototyping is the best fit for enclosures and structural frameworks, and rapid tooling is appropriate once the design is close to final and realistic production materials are required. In many projects, a hybrid strategy that combines additive and subtractive rapid prototyping offers the best balance between speed, cost, and functionality.[23][4][14][25][13][15]
Practical selection tips:
- Use 3D printing rapid prototyping for complex, organic, or lattice geometries and visual models.
- Choose CNC rapid prototyping machines when tolerances, strength, or surface finish are critical.
- Select sheet metal rapid prototyping for boxes, frames, and mounting structures likely to remain metal in production.
- Move to rapid tooling when design risk is low and realistic production parts are needed.[2][14][13]
Rapid prototyping machines are widely adopted in industries such as automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, medical devices, industrial equipment, and robotics. These sectors rely on rapid prototyping to shorten innovation cycles, improve product quality, and respond quickly to technology and market changes.[4][20][27][9][13]
For overseas OEM brands and wholesalers, working with a specialized partner like Shangchen eliminates the need to invest heavily in equipment and in-house manufacturing capacity. By combining rapid prototyping machines with quality systems and engineering support, Shangchen helps customers transform ideas into reliable, manufacturable products that are ready for global markets.[16][17][18][15]
Rapid prototyping machines are evolving with better automation, higher accuracy, and smarter software integration. Multi-axis CNC rapid prototyping machines, higher-resolution 3D printers, and more versatile materials are expanding the range of parts that can be prototyped and even produced in end-use quality.[6][8][20][9][13]
Digital connectivity and cloud-based collaboration tools also make it easier for overseas OEM teams to work with manufacturing partners like Shangchen. Engineers can share CAD models, track rapid prototyping progress, and review feedback in real time, even if they are located in different countries.[20][4][9][13]
A rapid prototyping machine is any digitally driven manufacturing system—such as a 3D printer, CNC machining center, sheet metal line, or tooling machine—that transforms CAD models into physical prototypes at high speed. By deploying these rapid prototyping machines in a coordinated workflow, companies can validate designs more quickly, reduce technical and commercial risks, and bring better products to market in less time.[11][12][14][21][13][20]
Shangchen (sc-rapidmanufacturing.com) combines rapid prototyping, CNC machining services, precision batch production, turning, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, and mold production to support overseas OEM brands from early concept through long-term manufacturing. For teams that want to leverage rapid prototyping without building their own factories, partnering with Shangchen provides a flexible and scalable path to high-quality, production-ready parts.[17][18][15][16]

The main purpose of a rapid prototyping machine is to turn digital CAD designs into physical prototypes quickly so engineers can test form, fit, and function before investing in mass production. This rapid prototyping approach helps prevent costly late-stage design changes and accelerates the overall product development cycle.[21][11][13][20]
Rapid prototyping machines are optimized for flexibility, low setup time, and short lead times, making them ideal for small batches and frequent design changes. Traditional manufacturing equipment is usually configured for high-volume, repeat production, where changeovers are slower and design changes are more expensive.[14][25][11][20]
Rapid prototyping machines can process thermoplastics, photopolymer resins, aluminum, steels, and various engineering plastics, depending on the technology. Additive rapid prototyping machines often use polymer and powder materials, while CNC rapid prototyping machines work with a broad range of metals and engineering-grade plastics for functional testing.[23][26][11][13][24]
Overseas OEM brands benefit from Shangchen's combination of rapid prototyping, CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, and mold production paired with strong OEM experience. This one-stop rapid prototyping service simplifies communication, improves consistency, and offers a clear route from early prototypes to precision batch production and long-term manufacturing.[18][15][16][17]
To start a rapid prototyping project with Shangchen, OEM customers share CAD files, material choices, target quantities, and functional requirements. Shangchen's engineering team then recommends suitable rapid prototyping machines and processes—such as 3D printing, CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, or rapid tooling—and provides quotations and realistic lead times.[15][16][17]
[1](https://jiga.io/articles/rapid-prototyping-process-how-to-choose/)
[2](https://www.protolabs.com/resources/guides-and-trend-reports/rapid-prototyping-processes/)
[3](https://www.3erp.com/manufacturing-technology/rapid-prototyping/)
[4](https://www.fictiv.com/articles/rapid-prototyping-guide)
[5](https://prototal.co.uk/blog/rapid-prototyping-processes/)
[6](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0890695597001375)
[7](https://www.lsrpf.com/en/blog/what-are-the-types-of-rapid-prototyping)
[8](https://formlabs.com/blog/fdm-vs-sla-vs-sls-how-to-choose-the-right-3d-printing-technology/)
[9](https://bigrep.com/posts/rapid-prototyping-3d-printing/)
[10](https://www.naun.org/main/NAUN/mcs/16-591.pdf)
[11](https://www.twi-global.com/technical-knowledge/faqs/faq-manufacturing-what-is-rapid-prototyping)
[12](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rapid_prototyping)
[13](https://formlabs.com/blog/ultimate-guide-to-rapid-prototyping/)
[14](https://www.weerg.com/guides/what-is-rapid-prototyping)
[15](https://www.sc-rapidmanufacturing.com/how-to-do-rapid-prototyping.html)
[16](https://www.sc-rapidmanufacturing.com/products.html)
[17](https://www.sc-rapidmanufacturing.com)
[18](https://www.sc-rapidmanufacturing.com/news/Machining-Productivity-Differences.html)
[19](https://www.sc-rapidmanufacturing.com/cnc-machining.html)
[20](https://www.autodesk.com/solutions/rapid-prototyping)
[21](https://www.datron.com/resources/blog/what-is-rapid-prototyping/)
[22](https://www.fictiv.com/articles/cnc-machining-for-prototyping)
[23](https://jlccnc.com/blog/cnc-machining-vs-3d-printing)
[24](https://www.roboze.com/en/resources/blog/rapid-prototyping-types-services-definition)
[25](https://www.cnc24.com/our-services/prototyping/)
[26](https://rapidmade.com/rapid-prototyping/)
[27](https://www.protolabs.com)
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal