
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-09-20 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Top 5 Vacuum Casting Materials
>> 1. ABS-like Polyurethane Resins
>> 2. Polycarbonate (PC)-like Resins
>> 3. Acrylic / PMMA-like Resins
>> 4. Polypropylene (PP)-like Resins
>> 5. Rubber-like Polyurethane Elastomers
● Applications of Vacuum Casting
● Extended Process Insights and Technical Considerations
● Advantages of Vacuum Casting Over Other Methods
● FAQ
>> 1. What is vacuum casting used for?
>> 2. How many parts can one vacuum casting mold produce?
>> 3. Can vacuum casting create transparent parts?
>> 4. How durable are parts made by vacuum casting compared to injection molding?
>> 5. Which vacuum casting materials are flexible or soft?
Vacuum casting is a highly effective manufacturing method used extensively for producing detailed prototypes and small batch production parts. It is particularly favored by OEM service providers like Shangchen, offering rapid prototyping, CNC machining, precision batch production, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, and mold production services to international brands, wholesalers, and manufacturers. This article delves into the top five vacuum casting materials, their unique properties, and wide-ranging applications, integrating the keyword "Vacuum Casting" throughout to ensure smooth readability and SEO effectiveness.
Vacuum casting, also known as urethane casting or polyurethane casting, is a process where a master model is used to create a silicone mold. Two-part polyurethane resin is then cast under vacuum into this mold to replicate the master form with high detail and surface finish. Employing vacuum during resin pouring helps remove air bubbles, ensuring precise replication of features and excellent mechanical properties. This makes vacuum casting an ideal choice for low-volume manufacturing and rapid prototyping when compared to injection molding, which uses metal molds and is cost-prohibitive for small runs.
The vacuum casting process involves the following key steps:
1. Master Model Creation: The process starts with designing and producing a master model, typically made with CNC machining or 3D printing technologies. This model must be designed to injection molding standards, considering wall thickness and draft angles.
2. Silicone Mold Making: The master model is suspended in a casting frame, and liquid silicone rubber is poured around it in a vacuum chamber to avoid air entrapment. The silicone cures in an oven for 8-16 hours, forming a flexible mold.
3. Casting the Parts: Two-part polyurethane resin is preheated, mixed, degassed under vacuum, and poured into the silicone mold placed inside a vacuum chamber. The vacuum helps fill intricate features by removing air pockets. The resin cures, typically in about an hour, at elevated temperature.
4. Demolding and Finishing: After curing, the flexible silicone mold is carefully opened, and the cast parts are removed. Excess material, gates, and runners are trimmed, and the parts are polished or painted as needed.
This process can be repeated multiple times before silicone molds wear, enabling short production runs with excellent repeatability, making vacuum casting a popular choice among manufacturers contracting with OEMs globally.
These resins best mimic acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), a common thermoplastic, in their hardness, impact resistance, and surface finish.
- Properties: Good toughness, rigidity, and impact resistance with excellent dimensional stability.
- Applications: Ideal for consumer electronics housings, automotive interior components such as dashboard panels, and robust prototype models.
- Benefits: Easily paintable, smooth finished surfaces, resistant to oil and chemicals, making them versatile for different functional requirements in prototypes and low-volume production parts.
PC-like resins in vacuum casting provide extra toughness, heat resistance, and clarity.
- Properties: Excellent impact strength, heat resistance, and UV stability.
- Applications: Suitable for transparent parts like automotive light lenses, electronic device housings, and structural prototypes requiring durability.
- Benefits: Ability to produce both opaque and transparent durable parts, with good thermal stability suitable for use in functional prototypes.
Acrylic resins replicate the transparency and weather resistance of plexiglass (PMMA).
- Properties: High clarity, UV resistance, and good impact strength.
- Applications: Used in optical components, display cases, aquariums, light covers, and automotive windows.
- Benefits: Mimics glass clarity but with higher impact resistance. Suitable for aesthetically critical parts needing a flawless transparent finish.
PP-like vacuum casting materials offer flexibility and chemical resistance.
- Properties: Lightweight, flexible, good chemical and heat resistance.
- Applications: Automotive interior parts, flexible hinges, large containers, and industrial prototypes requiring fatigue resistance.
- Benefits: Ability to produce parts that require repetitive bending or stretching with good endurance.
Rubber-like elastomers simulate soft, flexible materials.
- Properties: High elongation at break, various hardness levels, and excellent resilience.
- Applications: Ideal for seals, gaskets, grips, wearable devices, and other soft-touch parts.
- Benefits: Durable for functional and flexible prototype parts needing elasticity while maintaining mechanical robustness.

Vacuum casting serves a broad spectrum of industries due to its ability to produce functional and visually appealing parts efficiently:
- Automotive: Dashboard components, knobs, lighting housings, interior trims, and prototypes.
- Consumer Electronics: Housings, bezels, and button assemblies that require aesthetic quality and durability.
- Medical Devices: Custom-fitted prosthetics, hearing aid shells, and surgical instrument parts.
- Industrial Components: Small machinery parts, enclosures, functional prototypes.
- Art and Collectibles: Figurines, decorative objects, and limited-edition collectibles with fine detail.
- Packaging: Food-grade packaging and containers made using specialized resins.
Optimizing a vacuum casting project requires careful design and process control. Key technical details include:
- Design for Manufacture: Designing parts with draft angles and avoiding undercuts facilitates mold release and enhances mold longevity.
- Master Model Accuracy: High-quality master patterns, often made by CNC machining or SLA 3D printing, ensure that the vacuum cast parts replicate fine details.
- Silicone Mold Quality: Using platinum-cured or high-temperature vulcanizing (HTV) silicone molds improves mold durability and surface finish.
- Resin Mixing and Degassing: Precise mixing ratios coupled with thorough degassing under vacuum eliminate bubbles and ensure uniform part quality.
- Curing Parameters: Maintaining consistent temperature and time during curing optimizes resin mechanical properties and surface finish.
- Post-Processing: Polishing, painting, and coating can enhance both appearance and performance to meet client requirements.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Silicone molds cost less than metal molds, ideal for short runs and prototypes.
- Quick Turnaround: Faster mold and part production compared to injection molding.
- Versatility: Wide array of polyurethane materials replicates diverse mechanical and visual properties.
- Detail and Surface Finish: High fidelity to master patterns with smooth surface finishes.
- Flexibility: Ability to produce both rigid and flexible parts with different resin types.
Vacuum casting is a precise, flexible, and cost-effective manufacturing technology that serves as a critical bridge between prototyping and mass production. The top five vacuum casting materials—ABS-like, PC-like, PMMA-like, PP-like, and rubber-like polyurethane resins—each offer unique properties tailored for industrial applications ranging from automotive parts to medical devices, consumer electronics, and artistic collectibles. By selecting the appropriate material and carefully controlling the vacuum casting process, OEM service providers like Shangchen can deliver superior quality, highly detailed parts that fulfill both aesthetic and functional requirements for global customers efficiently.
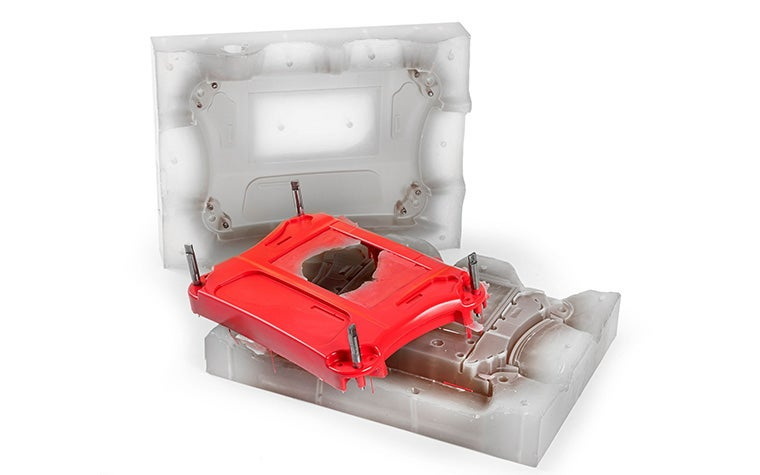

Vacuum casting is mainly used for producing high-quality prototypes and small batch production parts with detailed features and excellent surface finish. It is prevalent in automotive, medical, electronics, and consumer goods industries.
A standard silicone mold can produce approximately 30 to 50 parts, whereas high-temperature vulcanized silicone molds can extend the life to 300 to 500 parts, depending on the resin and mold handling.
Yes, vacuum casting can produce clear parts using acrylic or PMMA-like resins, suitable for optical and decorative applications requiring transparency and UV resistance.
Vacuum cast parts approximate many of the mechanical properties of injection molded parts but typically have lower heat and UV resistance. They are best suited for prototyping and low-volume production where short runs and quick delivery are priorities.
Rubber-like polyurethane elastomers are best for flexible or soft parts such as gaskets, grips, seals, and wearable devices, providing high elasticity and mechanical resilience.
[1](https://www.immould.com/vacuum-casting/)
[2](https://millennitek.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/H-5800-0660-01-A-EN-Vacuum-Casting-Techniques-User-Guide-Screen.pdf)
[3](https://xometry.eu/en/vacuum-casting-technology-overview/)
[4](https://formlabs.com/blog/vacuum-casting-urethane-casting-polyurethane-casting/)
[5](https://leadrp.net/blog/overview-of-vacuum-casting/)
[6](https://www.rapiddirect.com/blog/vacuum-casting-design-guide/)
[7](https://www.renishaw.com/media/pdf/en/9a351e67784c4e27992e5e3632434b1f.pdf)
[8](https://blog.isa.org/what-are-vacuum-casting-factories-a-comprehensive-guide-to-the-manufacturing-process)
[9](https://www.kemalmfg.com/complete-guide-to-vacuum-casting/)
[10](https://www.rocheindustry.com/guide-to-vacuum-casting/)
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal