
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-10-09 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Introduction to Injection Molding
● The Rise of Automation in Injection Molding
● Automation Technologies Shaping the Industry
>> Robotics and Automated Handling
>> AI, Machine Learning and Smart Sensors
>> Automated Quality Assurance
● Innovations in Design and Prototyping
● How Automation Reduces Lead Times in Injection Molding
● How Automation Improves Product Quality
● Key Benefits of Injection Molding Automation
● Sustainability and Smart Manufacturing
● Emerging Trends and Future Directions
>> Industry 4.0 and the Connected Factory
>> Electric Servo-Hydraulic Machines
>> Micro-Molding and Multi-Material Molding
>> On-Demand Manufacturing and Customization
● Overcoming Implementation Challenges
● FAQs
>> 1. How does automation reduce injection molding lead times?
>> 2. What major quality improvements does automation bring?
>> 3. Is automation practical for low-volume, high-mix production?
>> 4. Which automation technologies are most impactful in injection molding?
>> 5. What are the top challenges when adopting automation in injection molding?
Injection molding remains a fundamental technique for producing plastic components that power global industries. Over the past decade, the integration of automation has revolutionized injection molding, streamlining lead times and enabling manufacturers to achieve unprecedented levels of quality, consistency, and productivity. As demand for high-precision plastics accelerates and competition in global markets tightens, manufacturers leveraging automation in injection molding are positioned to outperform competitors in both speed and performance.

Injection molding is a manufacturing process where molten plastic is injected into pre-designed molds, shaping the material into specific components. This process yields highly repeatable results, making it ideal for producing high volumes of identical parts. Traditionally, injection molding involved manual intervention at several stages, from material feeding and mold setup to part removal and inspection. However, with the advent of automation, these steps are increasingly handled by machines that work more efficiently and accurately than human operators.[1][2][3]
Automation in injection molding refers to the use of technologies such as robotics, artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT), and smart sensors to control and optimize the production process. Automated solutions may include robotic arms for material handling, machine vision systems for quality assurance, and centralized software for real-time monitoring. The benefits are clear: higher productivity, lower operational costs, and dramatically reduced risk of human error.[2][4][5]
Robotic automation is central to modern injection molding factories. Robots are built to remove finished parts from molds, handle secondary operations, stack components, and package products. With programmable accuracy, robots reliably perform repetitive tasks at high speeds, reducing cycle times and improving safety. Collaborative robots (“cobots”) are further enhancing efficiency by working alongside human operators on complex tasks such as assembly, insert molding, and inspection.[3][4][1]
Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms analyze sensor data to identify process anomalies, adjust machine parameters, and optimize workflow. Predictive maintenance powered by AI can detect machine wear and prevent unplanned downtime, keeping production lines running. IoT sensors enable remote monitoring and control through a centralized system, ensuring continuous quality and process refinement.
Real-time inspection, made possible by machine vision and advanced sensors, is eliminating much of the uncertainty in part quality. Automated systems continuously scan for defects, check dimensional accuracy, and verify product consistency. This technology allows manufacturers to detect and address problems instantly, reducing scrap rates and ensuring every part meets required specifications.[4][1][2][3]
Modern automation goes beyond direct production, extending to design and prototyping phases. Advanced CAD systems, 3D printing, and simulation software allow engineers to quickly iterate mold designs before mass production. Rapid prototyping makes it possible to create and test concepts on the fly, significantly shortening the timeline between product ideation and market launch.[1][3]
Simulation software predicts material flow, pressure points, and cooling dynamics, helping designers avoid costly mold modifications and delay. This digital-first approach to design ensures greater precision, reduces development risk, and supports a culture of continuous innovation among manufacturers.[3][1]
Lead times—the period between order placement and delivery—are critical in today's fast-paced markets. Automation compresses lead times by:
- Minimizing Setup Time: Automated mold changeover systems swiftly reconfigure machines for new product runs, ensuring minimal downtime between cycles.
- Continuous Production: Automated machinery can operate 24/7, unburdened by labor shifts or breaks, supporting rapid fulfillment of bulk orders.
- Just-In-Time Manufacturing: Automated inventory management and real-time monitoring allow injection molding operations to run lean, only producing what is needed when it is needed.
- Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing speeds up the creation of prototype molds for design validation, enabling manufacturers to quickly iterate and launch new products.
- Instant Quality Feedback: Automated inspection systems provide immediate feedback on the production line, allowing for real-time adjustments and avoidance of batch-wide defects.[5][2][3]
Product quality in injection molding is determined by part accuracy, consistency, material properties, and defect rates. Automation directly impacts each factor:
- Precision and Repeatability: Robots and advanced control systems guarantee the precise execution of every production cycle, maintaining tight tolerances and eliminating variations.
- Real-Time Quality Control: Automated vision systems scrutinize each part for defects, ensuring only flawless products are shipped.
- Optimized Processing Conditions: Advanced algorithms and sensors continually adjust molding parameters for ideal conditions, eliminating guesswork and variability.
- Material Traceability and Consistency: Automated systems deliver controlled mixtures and blends, ensuring consistent material quality throughout production runs.
- Defect Prevention: By monitoring critical variables — like temperature, pressure, and cooling rates — automation detects deviations early and prevents the creation of off-spec parts.[2][4][5][1]
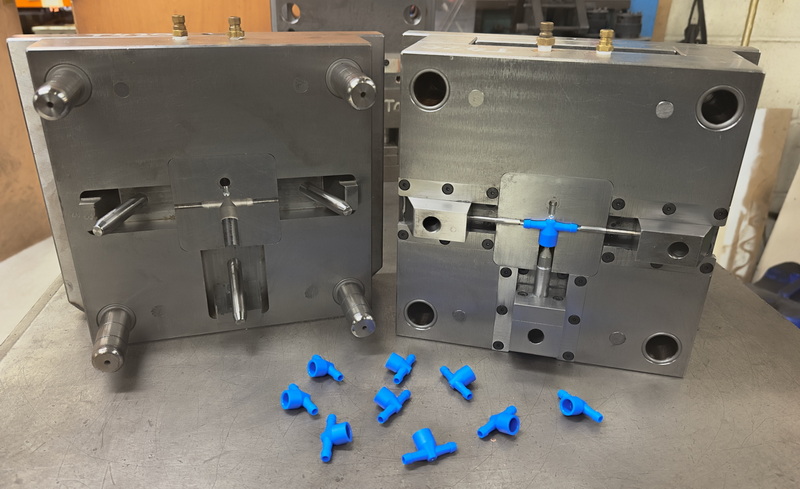
Manufacturers embracing automation enjoy clear advantages:
- Increased Throughput: Automated lines can complete cycles faster and operate continuously, boosting output and facilitating large-scale orders.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Fewer manual operators are needed, and highly skilled workers can focus on design, programming, and process optimization.
- Higher Product Quality: Automated inspection and control reduce scrap rates and rework costs.
- Safety Improvements: Automation reduces exposure to heat, chemicals, and repetitive motion injuries by shifting hazardous tasks to robots.[5][3]
- Scalability: Automated factories can scale up or shift production quickly to meet fluctuating demands.
- Sustainability: Modern machines use less energy and minimize waste, supporting corporate sustainability goals.[4][2][3]
The injection molding industry increasingly prioritizes sustainability. Automation supports eco-friendly manufacturing by:
- Reducing Material Waste: Precision controls optimize material usage and minimize excess scrap.
- Energy Efficiency: Electric and hybrid machines require less energy, contributing to lower carbon footprints.
- Circular Economy: Automation assists manufacturers in recycling plastics and integrating bio-based or recycled polymers into product lines.
- Predictive Maintenance: Monitoring and analytics help extend the life of machines, avoiding waste from breakdowns and emergency repairs.[7][8][4]
The rise of Industry 4.0 is creating “smart factories” where digitally-connected machines share data in real time. This enables predictive maintenance, streamlined logistics, flexible scheduling, and immediate troubleshooting. Manufacturers deploying these technologies lead in operational agility and process reliability.[6][2][4]
Next-generation servo-hydraulic and all-electric injection molding machines offer unparalleled control over speed, pressure, and timing. This results in lower energy consumption, improved part accuracy, and efficient processing of advanced materials.
Emerging techniques such as micro-molding for tiny part production, multi-material molding for complex assemblies, and gas-assisted molding for lightweight, strong products are rapidly gaining market share. These innovations offer manufacturers new capabilities to address customer needs in automotive, medical, consumer electronics, and aerospace sectors.[3][5]
Automation enables manufacturers to offer customized products, small batch runs, and rapid design modifications at scale. As consumer demand for personalized items increases, injection molding factories equipped with flexible automation are uniquely positioned to capture new segments.[5][3]
While the benefits of automation are pronounced, manufacturers face hurdles including:
- High Upfront Investment: Advanced automation systems and smart technologies require significant initial capital.
- Workforce Training: Skilled technicians are needed to operate, maintain, and program robotic systems and smart controls.
- Process Integration: Retrofitting existing equipment or integrating new automation solutions demands careful planning and system compatibility.
- Continuous Optimization: Automation introduces new data streams that require constant monitoring and adjustment for peak performance.[2][4][5]
Despite these challenges, industry trends indicate that automation's long-term advantages — in productivity, quality, and sustainability — far outweigh the short-term barriers.[4][2][3]
Automation stands as a transformative force in the injection molding sector. By leveraging robotics, AI, IoT, and other advanced technologies, manufacturers are slashing lead times, achieving unmatched precision and repeatability, and raising the bar for product quality. With sustainability and smart manufacturing principles guiding the next wave of progress, companies that invest in automation will remain at the forefront of modern industry, able to satisfy the ever-evolving needs of global markets.
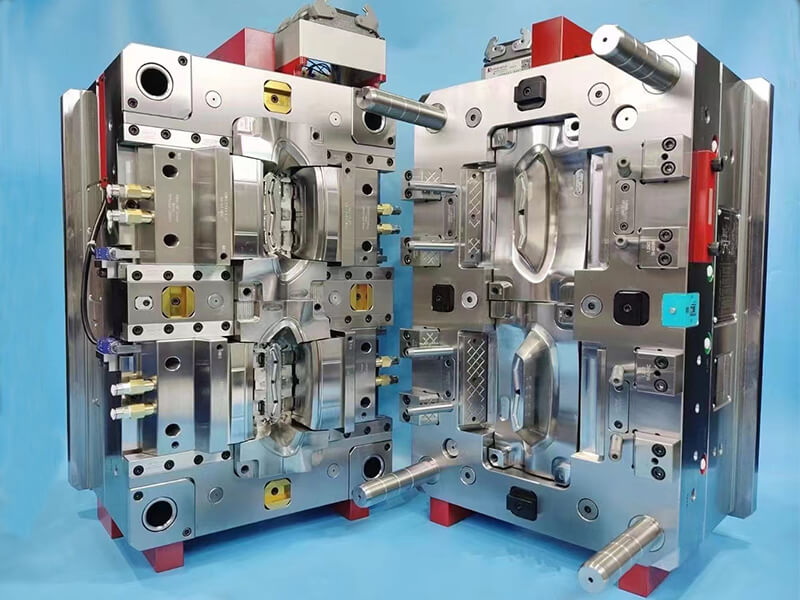
Automation streamlines mold changeovers, enables continuous 24/7 production, and leverages rapid prototyping to compress timelines. Automated inspection and real-time feedback allow immediate process improvement, substantially shortening time from order to delivery.[2][4]
Automation delivers consistent part accuracy, real-time defect detection, and process optimization, resulting in higher product quality, reduced scrap, and lower rework rates.[1][4][5][2]
Flexible automation, including robotics and rapid prototyping, allows for quick changeovers and supports small batch production, making it viable for low-volume, high-variety manufacturing when quality and speed are priorities.[1][3]
Key technologies include collaborative robots (cobots), machine vision inspection systems, AI-driven process controls, IoT-enabled real-time monitoring, and advanced servo-hydraulic machines.[3][4][1][2]
Manufacturers must address high initial costs, integration with legacy systems, and workforce upskilling needs. Strategic planning, system compatibility, and ongoing process optimization are essential for success.[4][5][2][3]
[1](https://newji.ai/japan-industry/latest-trends-in-injection-molding-technology-and-the-benefits-of-implementation/)
[2](https://www.marketreportanalytics.com/reports/automated-injection-molding-machine-347121)
[3](https://mouldersconsulting.co.uk/the-future-of-injection-moulding-key-trends-for-2025/)
[4](https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/injection-molding-machine-market)
[5](https://www.fictiv.com/articles/injection-molding-trends-2025)
[6](https://www.accio.com/business/trend-in-leading-injection-molding-machines)
[7](https://advancedplastiform.com/the-future-of-injection-molding/)
[8](https://thriam.com/the-future-of-injection-molding-trends-and-predictions-for-2025-and-beyond.php)
[9](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/automatic-injection-molding-machine-market-getne)
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal