
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-10-10 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Introduction to Rapid 3D Print Prototype and Batch Production
>> What is Rapid 3D Print Prototype?
>> Understanding Batch Production
● Key Benefits of Rapid 3D Print Prototype
● Advantages of Batch Production
● When to Choose Rapid 3D Print Prototype
● When Batch Production Makes Sense
● Integrating Rapid 3D Print Prototype and Batch Production
● Real-World Applications of Rapid 3D Print Prototypes and Batch Production
>> Automotive
● Challenges and Limitations to Consider
>> Limitations of Rapid 3D Print Prototype
>> Drawbacks of Batch Production
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the typical turnaround time for a rapid 3D print prototype?
>> 2. Can rapid 3D print prototypes be used for functional testing?
>> 3. How does batch production handle quality control?
>> 4. Is it possible to customize products in batch production?
>> 5. What materials are commonly used in rapid 3D print prototypes and batch production?
In today's fast-paced manufacturing landscape, businesses regularly face the decision between rapid 3D print prototype services and batch production methods. Understanding the strengths and ideal applications of each can save costs, reduce time-to-market, and ensure product quality. Whether you run an OEM brand, wholesale business, or production company, this comprehensive guide will clarify when to choose rapid 3D print prototype versus batch production.
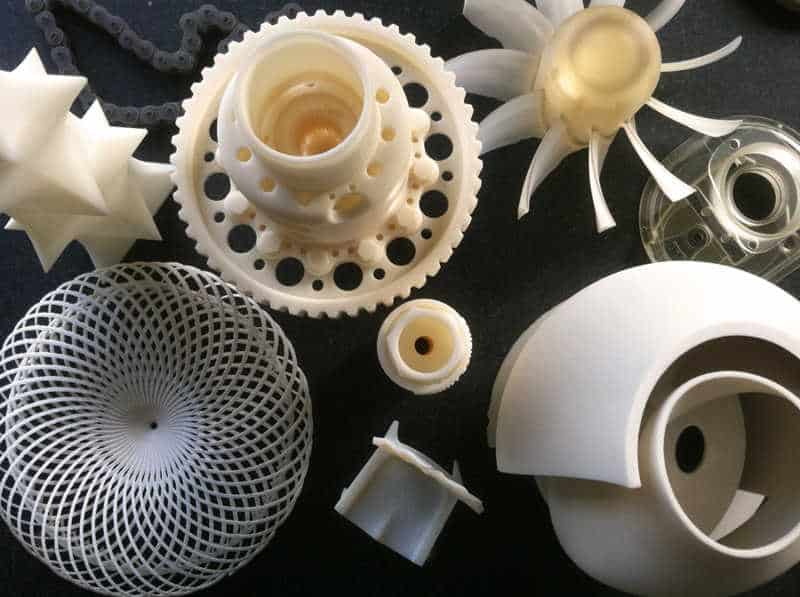

Manufacturing solutions have diversified into numerous techniques, each tailored to specific stages of product development and market demands. Rapid 3D print prototypes are revolutionizing how designs transition from concept to reality, while batch production stands as a cornerstone for large-scale manufacturing and precision parts.
Rapid 3D print prototype refers to the fast, additive manufacturing process that creates physical models directly from CAD designs using various materials such as resins, plastics, and metals. These prototypes help designers and engineers visualize, test, and refine products quickly without the need for expensive molds or tooling.
This technology employs various types of 3D printing such as stereolithography (SLA), selective laser sintering (SLS), fused deposition modeling (FDM), and direct metal laser sintering (DMLS), each suitable for different prototype requirements, balancing quality, speed, and cost.
Batch production is a traditional but highly efficient manufacturing technique where products are produced in groups or batches rather than continuously. This method is especially suitable for precision CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, turning, and other subtractive manufacturing processes. Batch runs ensure consistent quality across a series of parts with scalability, allowing OEMs to control costs when moving into mass production.
Batch production balances economies of scale with maintaining enough flexibility to accommodate product variants within certain volumes, making it ideal for small to medium production runs where product specifications are stable.
Rapid 3D print prototypes offer numerous advantages right from the proof-of-concept phase up to functional testing. Some of the pivotal benefits include:
- Speed: Prototypes can be produced in days or even hours depending on complexity, drastically shortening the product development cycle.
- Flexibility: Easy to modify CAD files and reprint revised versions quickly, allowing more design iterations in a shorter timeframe.
- Cost-Effective: No initial tooling or setup fees required, which is especially beneficial for low-volume or unique parts.
- Customization: Complex geometries and intricate details are achievable without additional cost or lead time.
- Material Variety: Options range from plastics and composites to metals for functional testing, enabling realistic prototype behavior.
- Sustainability: Additive manufacturing generates less material waste compared to subtractive processes like machining.
This technology excels in facilitating product development iterations, reducing R&D time, and aligning designs with consumer demands before committing to mass production.
While rapid prototyping is ideal for early stages, batch production provides advantages crucial for later stages when consistency and volume matter:
- Cost Efficiency at Scale: Unit costs decrease significantly once initial tooling and machine setups are complete, optimizing cost per piece.
- High Precision and Quality: CNC machining, turning, and sheet metal fabrication provide tight tolerance and superior repeatability across all units.
- Material Strength and Variety: Industrial-grade metals and alloys ensure products meet strength, performance, and longevity requirements.
- Surface Finish and Post-Processing: Advanced finishing processes including polishing, painting, coating, and heat treatments can be easily integrated.
- Reliable Supply Chain: Uniform production processes support predictable delivery schedules and inventory management.
Batch production is the go-to choice for OEMs when moving from prototyping to medium scale manufacturing or fulfilling bulk orders, ensuring products meet exacting standards and volumes demanded by the market.
Rapid 3D print prototypes are the preferred option when:
- You require initial design validation quickly without costly delays or tooling expenses.
- Testing of form, fit, and function is necessary early in the development phase to catch design flaws.
- Iterative design changes are anticipated, allowing swift adjustments and multiple revisions.
- Producing low volume, unique, or specialized parts that do not justify mass production tooling expenses.
- The project demands fast time-to-market, especially in competitive industries where innovation cycles are compressed.
- Exploring complex geometries or lightweight structures that are difficult or impossible to manufacture by traditional methods.
- Budget constraints limit spending on expensive mold tooling or batch runs before the design is fully validated.
In these cases, rapid 3D print prototyping accelerates innovation and reduces risk, offering a practical way to test ideas before large investments.
Batch production should be considered when:
- Product designs have been finalized after thorough prototyping and validation.
- Medium to large quantities of parts are necessary to meet wholesale, retail, or industrial demand.
- High precision and strict quality control are mandated, especially for safety-critical components.
- Material properties and mechanical performance requirements exceed the capabilities of typical 3D printing materials.
- The product requires multiple finishing steps such as polishing, coating, or surface treatment not easily performed on 3D printed parts.
- Cost per part must be minimized and volumes justify the upfront tooling and setup expenses.
- Delivering consistent, repeatable quality is essential for brand reputation and operational efficiency.
Batch production offers a stable, cost-effective path to market for mature products ready for scaled manufacturing runs.
The most successful manufacturing strategies combine rapid prototyping with batch production to leverage the strengths of both methods. This integration often follows a staged workflow:
- Launch with rapid 3D print prototypes to validate concepts, conduct user testing, and optimize function.
- Use prototypes to obtain necessary certifications or comply with regulatory requirements.
- Refine designs through multiple iterative 3D printed models based on feedback.
- Once validated, transition to batch production for consistent, high-quality parts in larger quantities.
- Employ CNC machining, turning, and sheet metal fabrication to meet performance and finish specifications.
- Scale production volumes in batches, adjusting batch sizes as demand evolves.
This hybrid approach balances agility and cost efficiency, helping brands innovate fast while delivering reliable products.
Rapid 3D print prototypes and batch production are used extensively across diverse industries:
Rapid 3D print prototypes are perfect for testing intricate enclosure designs and button placements quickly. Batch production then assembles consistent, durable parts such as housings and mounts in high volumes.
Rapid prototypes allow testing of new parts for fitment and function, while batch production creates machined engine components, brackets, or interior fittings using metals with strict tolerances.
Anatomical models printed via 3D technology aid surgical planning and customized device prototyping. Batch production ensures that medical instruments or implants meet rigorous biocompatibility and accuracy standards.
Functional prototypes demonstrate machine parts or assemblies, and batch production delivers robust, precise replacement parts and structures needed for heavy-duty operation.
Complex and customized design prototypes help brands visualize products. Batch manufacturing enables consistent production of jewelry, watch components, or wearables at scale.
- Mechanical strength and durability may be lower than fully machined or molded parts.
- Surface finish from 3D prints may require additional smoothing or coating for aesthetics.
- Some additive manufacturing materials do not yet match industrial-grade metals or plastics.
- Size constraints based on printer build volume.
- Cost effectiveness diminishes at high volumes compared to batch production.
- Upfront tooling, fixture design, and machine programming require time and investment.
- Lead times can be longer due to tooling and setup requirements.
- Less adaptive to late-stage design changes without significant cost.
- Batch sizes and runs may be less flexible, causing inventory risks.
- Initial costs may be prohibitive for startups or low-volume products.
Choosing between rapid 3D print prototypes and batch production depends heavily on your project stage, budget, and volume requirements. Rapid 3D print prototypes empower quick iteration, product testing, and customization but have limitations in strength and finish for final products. Batch production offers high-quality, scalable manufacturing once designs are validated, providing cost efficiencies at volume. Many companies find the optimal path by combining both approaches to accelerate innovation and ensure market readiness.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of each production method enables OEMs, wholesalers, and brands to optimize development workflows, reduce costs, and improve product quality—meeting customer expectations in increasingly competitive global markets.
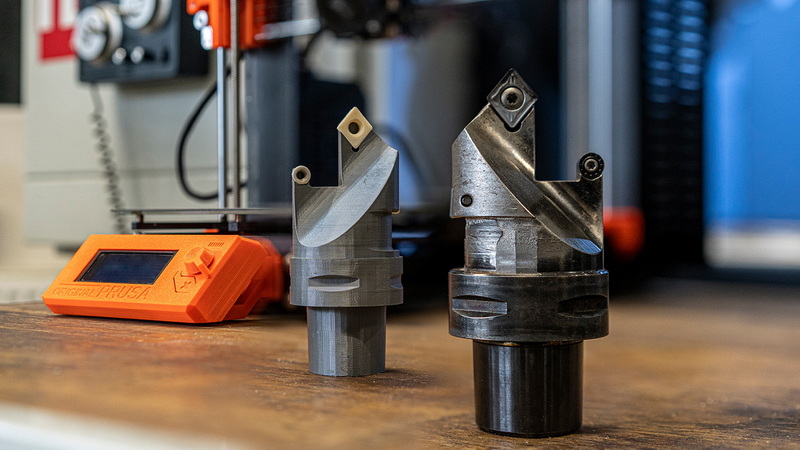

Turnaround time varies by complexity but generally ranges from a few hours to several days, offering significantly faster results than traditional methods.
Yes, especially with metal or high-performance plastics, prototypes can undergo functional tests, though mechanical properties may differ slightly from final production parts.
Batch production incorporates strict quality assurance processes including dimensional inspections, material testing, and surface finish verification to maintain consistency.
Customization in batch production is possible but typically limited; continuous rapid prototyping is more suitable for one-off or highly customized parts.
Rapid prototypes often use resins, ABS, PLA, and selective metals, while batch production uses industrial materials like aluminum, steel, copper alloys, and engineering plastics.
content is empty!
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Norway
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Czech Republic
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Denmark
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Hungary
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Ireland
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Finland
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Greece
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Sweden
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Turkey
How Vacuum Mold Casting Compares to Silicone Mold Casting for Precision Parts