
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-10-25 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● What Is Vacuum Mold Casting?
● Core Steps in the Vacuum Mold Casting Process
>> Material Preparation and Degassing
>> Casting and Vacuum Application
● Evolution and Innovations in Casting Materials
>> Advanced Polyurethanes and Hybrids
>> Silicone Elastomers and Flexible Composites
>> Sustainable and Recyclable Materials
>> Multi-Material and Overmolded Structures
● Innovations in the Manufacturing Process
>> Automation and Digital Optimization
>> Advanced Curing and Material Modification
● Key Benefits and Competitive Advantages
● Expanding Applications Across Industries
>> Electronics and Consumer Goods
>> Industrial and Specialized Manufacturing
● Challenges and Solutions in Vacuum Mold Casting
● Future Directions and Industry Trends
>> Artificial Intelligence and Automation
>> Hybrid and Digital Manufacturing
● FAQ
>> 1. What types of materials are used in vacuum mold casting?
>> 2. How does vacuum mold casting benefit industrial production compared to injection molding?
>> 3. Can vacuum mold casting produce multi-material or overmolded parts?
>> 4. What are the main limitations compared to other methods?
>> 5. Which sectors benefit the most from vacuum mold casting?
Vacuum mold casting has emerged as a cornerstone of modern rapid prototyping and low- to medium-volume production, particularly over the past decade. With industry leaders continuously advancing material science, process automation, and digital integration, Vacuum Mold Casting now enables manufacturers across automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, and medical industries to deliver high-quality, precise, and durable products at exceptional speed and cost-efficiency. This article explores the evolution and latest innovations in vacuum mold casting materials, their practical applications, process advancements, future trends, and addresses frequently asked questions.[11][12][13]
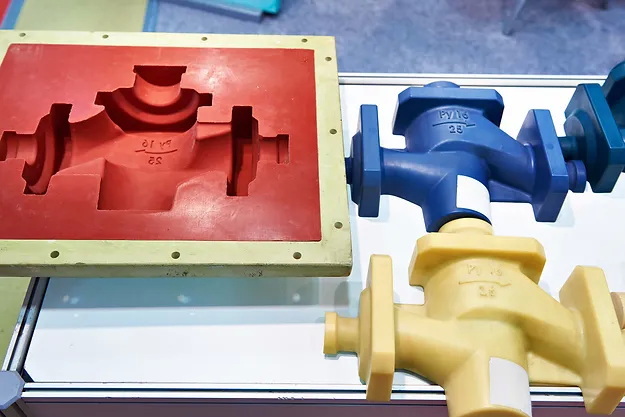
Vacuum mold casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid polymer resin is poured into a silicone mold under vacuum pressure. This forces the material into every geometric detail, eliminates air bubbles, and produces a finished part that closely mimics the master pattern—often indistinguishable from an injection-molded component. The ability to achieve such accuracy and surface finish, with flexible low volumes and multi-material options, makes vacuum mold casting an unrivaled choice for functional prototypes, end-use parts, and complex assemblies.[1][14][11]
The process begins with a master model—an exact replica of the intended final product. This model is typically produced using precision 3D printing (e.g., SLA, DLP) or CNC machining. The material and perfection of the master model are critical because every detail, texture, or flaw is transferred to the subsequent cast parts.[5][6][7]
- The master model is placed in a casting box, and flexible silicone rubber is poured around it.
- Silicone is the preferred choice due to its ability to capture fine details, flexibility, and ease of demolding.[7][9]
- After curing at room or controlled temperatures, the mold is carefully cut open and the master is removed, leaving behind a cavity that perfectly matches the original design.
Resins—commonly advanced polyurethanes or elastomers—are carefully measured, mixed (with potential colorants or additives), and placed in a vacuum chamber to remove entrapped air. Proper degassing ensures defect-free, structurally sound parts with superior surface finishes.[6][5][7]
- The mold is reassembled and placed within a vacuum casting chamber.
- The resin is poured into the mold under vacuum, ensuring complete fill of all intricate spaces and eliminating air pockets.
- Vacuum application is particularly vital for thin-walled or complex geometries, enhancing dimensional accuracy and part integrity.[8][5][7]
- Once filled, the mold is placed in an oven for controlled curing—typically at temperatures around 70°C for several hours.
- After curing, the mold is opened, and cast parts are removed.
- Any excess material ("flash") is trimmed, and additional surface finishing (e.g., sanding, polishing) ensures the desired appearance and consistency.[1][5][6]
High-performance polyurethane resins now simulate the mechanical performance, clarity, and flexibility of commercial-grade thermoplastics. These materials are available in numerous hardness levels, color options, and specialty grades for temperature resistance, chemical exposure, or optical clarity.[14][15][11]
Material blends can achieve both rigid and flexible parts, suitable for seals, gaskets, grips, and functional prototypes requiring durability with elasticity. Enhanced silicone chemistries improve longevity and reusability of molds, supporting higher production volumes and lower operational costs.[16][7][11]
Sustainability is prioritized:
- Some suppliers now offer partially bio-based or recycled resin options.
- Recyclable silicone mold compounds reduce landfill waste.
- Production facilities integrate closed-loop systems to reclaim and reuse excess material.[13][17]
- Integration of soft and rigid zones, multi-color features, and embedded inserts (such as metal frames or threaded bushings) is possible in a single casting cycle.
- Overmolding techniques reduce assembly steps and boost product functionality, especially in consumer, automotive, and electronic applications.[17][11]
Modern vacuum mold casting lines employ:
- Automated resin mixing and dispensing for consistent quality.
- Robotics and IoT-enabled process controls for optimal curing and efficient defect detection.
- Digital twin technology, which allows manufacturers to simulate mold design and predict flow patterns, minimizing trial and error.[12][18][11]
- High-resolution 3D prints now serve as direct master patterns, speeding up the tooling phase and ensuring the highest fidelity on micro-textures and complex shapes.
- This accelerates product development timelines and improves surface finish with minimal manual dressing.[19][5][11]
- Innovative curing systems—such as fast infrared ovens and pressure-assisted processes—reduce cycle times and shore up resin performance for tougher, more reliable end-use parts.[15][20]
- Chemical additives and nano-fillers embedded in resins deliver enhanced abrasion resistance, electrical conductivity, or environmental robustness.[11][15]

Vacuum mold casting delivers:
- High repeatability and exceptional detail for short-run production (from 10 to 500+ parts per mold).
- Faster prototyping and time-to-market compared to CNC-only or injection molding routes.
- Superior cost savings when mold amortization is unfeasible for traditional molding.
- Material versatility: simulating ABS, PP, PC, silicone, rubber, and more.[6][14][16]
- Eco-efficiency through low waste, recyclable tooling, and energy-efficient operations.
- Customization: tailored colors, durometer, appearance, and physical properties.[13][14][17]
Vacuum mold casting empowers these sectors with lightweight, custom parts (interior panels, housings, air ducts) that demand high strength, precise tolerances, and innovative features for each new vehicle or aircraft model.[17][13]
Biocompatible materials enable rapid development of prosthetics, anatomical models, dental devices, and functional prototypes for surgical testing, elevating patient care and research speed.[21][17]
- Soft-touch casings, transparent lenses, and snap-fit assemblies for consumer devices are created using multi-material casting or embedded functional features.
- Rapid iteration of new product designs is possible, accelerating innovation cycles.[22][17]
Complex housings, gaskets, or flame-retardant components for industrial, energy, or heavy-equipment markets benefit from specialty casting resins that match demanding operational specifications.[12][15][17]
Despite transformative advantages, challenges persist:
- Unsuitable for very high-volume (millions) production due to mold wear and per-part costs, but excels at flexible short-to-medium runs.[14][17]
- Certain high-performance thermoplastics and filled composites remain incompatible due to casting temperature and viscosity limitations, though hybrid solutions and continuous R&D are reducing these gaps.[17]
- Requires skilled personnel and precise process control; new automation and digital quality monitoring aim to mitigate this.[11][13]
AI and smart sensors are making vacuum mold casting lines more autonomous, predicting equipment maintenance, adjusting material ratios in real time, and learning from production data to reduce errors and downtime.[12][13][11]
Accelerated adoption of recyclable and bio-based materials, closed-loop production systems, and lean manufacturing approaches continues to drive down both costs and environmental impact.[13][17]
Combining vacuum mold casting with additive manufacturing and digital simulation offers previously inconceivable speed, customization, and design flexibility—positioning vacuum mold casting as central to the "smart factory" movement.[11][13][17]
Vacuum mold casting has moved beyond rapid prototyping to become a vital, versatile platform for modern manufacturing. Driven by continuous advances in material sciences, automated production, and sustainable practices, this process now supports everything from complex prototyping to end-use small-batch and bridge manufacturing—across nearly every sector. Companies embracing these innovations are set to lead their industries in product quality, speed to market, and sustainable performance.

Most commonly, polyurethane resins, silicone elastomers, and specialized composites are used, offering flexibilities from rigid to soft, transparent to opaque, with custom physical properties for diverse industry needs.[15][16][11]
Vacuum mold casting is ideal where rapid prototyping or low-volume production is required. It offers faster turnaround, lower initial tooling costs, and enables the use of a wider variety of materials, while still delivering detailed, functional, and durable parts.[14][13][17]
Yes, modern advances allow for parts with different hardness, colors, or embedded components to be cast in one cycle, streamlining assembly and enhancing functionality.[17][11]
Main limitations include lower cost-effectiveness at ultra-high volumes and less compatibility with some specialty plastics; however, ongoing innovations continue to close these gaps.[14][11][17]
Automotive, aerospace, medical, consumer electronics, and industrial sectors all benefit due to the speed, flexibility, and precision vacuum mold casting offers for complex parts and short production runs.[21][22][13][17]
[1](https://formlabs.com/blog/vacuum-casting-urethane-casting-polyurethane-casting/)
[2](https://www.makerverse.com/resources/casting/vacuum-casting-everything-you-need-to-know/)
[3](https://www.rapiddirect.com/blog/vacuum-casting-design-guide/)
[4](https://ame-3d.co.uk/news/a-complete-guide-to-vacuum-casting-polyurethane-casting)
[5](https://xdmining.in/2024/10/02/elementor-11005/)
[6](https://objectify.co.in/a-comprehensive-guide-to-vacuum-casting-everything-you-need-to-know/uncategorized/)
[7](https://www.zintilon.com/blog/vacuum-casting/)
[8](https://www.protolis.com/resources/manufacturing-guides/vacuum-casting/)
[9](https://blog.isa.org/what-are-vacuum-casting-factories-a-comprehensive-guide-to-the-manufacturing-process)
[10](https://www.ansini.co.uk/news/guide-to-vacuum-forming/)
[11](https://www.nicerapid.com/blog/beyond-prototyping-material-and-process-breakthroughs-in-vacuum-casting/)
[12](https://www.sc-rapidmanufacturing.com/increasing-operational-efficiency-with-vacuum-mold-casting-technologies.html)
[13](https://www.makerverse.com/resources/casting/the-biggest-trends-in-vacuum-casting-for-2025/)
[14](https://www.makerverse.com/resources/casting/10-main-benefits-of-vacuum-casting/)
[15](https://www.useencasting.com/blog/best-vacuum-casting-techniques-for-production-efficiency/)
[16](https://us.arrk.com/what-materials-can-be-vacuum-cast-ways-used-in-the-industry/)
[17](https://www.ltc-proto.com/blog/innovations-in-vacuum-casting-material-breakthroughs-and-technological-advancements/)
[18](https://www.hasungmachinery.com/the-development-trend-of-vacuum-pressure-casting-machine-in-future-manufacturing-industry)
[19](https://www.ditaiplastic.com/trends-and-developments-in-vacuum-forming-technology/)
[20](https://www.3erp.com/blog/vacuum-casting/)
[21](https://www.materialise.com/en/inspiration/articles/vacuum-casting-medtech-volume-production)
[22](https://www.in3dtec.com/enhancing-electronic-products-with-vacuum-casting-technology/)
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal