
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2026-01-06 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● What Is a Rapid Prototyping Business?
● Why Rapid Prototyping Is a Strong Business Opportunity
● Core Rapid Prototyping Services to Offer
>> CNC Machining for Rapid Prototyping
>> 3D Printing for Rapid Prototyping
>> Sheet Metal and Fabrication Prototyping
>> Rapid Tooling, Molding, and Low‑Volume Production
>> Value‑Added Engineering and Design Support
● Step 1: Define Your Rapid Prototyping Niche and Target Market
● Step 2: Prepare a Solid Business Plan
● Step 3: Choose Location, Facilities, and Layout
● Step 4: Select Equipment and Software for Rapid Prototyping
● Step 5: Build a Skilled Rapid Prototyping Team
● Step 6: Design an Efficient Rapid Prototyping Workflow
● Step 7: Create a Strong Online Presence and Marketing Strategy
● Step 8: Pricing, Profitability, and Scaling
● Risk Management and Quality in Rapid Prototyping
● Customer Experience and Long‑Term Relationships
● FAQ
>> Q1: What is rapid prototyping in manufacturing?
>> Q2: How much does it cost to start a rapid prototyping business?
>> Q3: Which industries most often use rapid prototyping services?
>> Q4: How can a small shop compete in rapid prototyping?
>> Q5: What is the difference between rapid prototyping and mass production?
Rapid prototyping has become one of the most important tools for modern product development, helping startups and large OEMs turn concepts into functional parts in days instead of months. For entrepreneurs with experience in 3D printing, CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, mold making, or industrial design, starting a rapid prototyping business can be a powerful way to serve global brands that need fast, flexible, and cost‑effective manufacturing.[1][2]
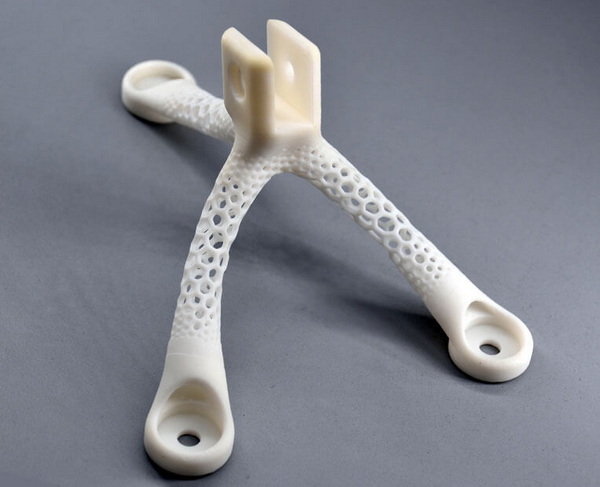
A rapid prototyping business provides services that transform digital 3D models into physical prototypes and low‑volume parts using technologies such as CNC machining, 3D printing, vacuum casting, sheet metal fabrication, and soft tooling. These services help customers validate design, perform functional testing, check assembly and ergonomics, and prepare for mass production with less risk and lower total cost.[2][1]
A professional rapid prototyping company usually integrates multiple processes—like CNC milling and turning, SLA/SLS 3D printing, metal fabrication, and mold manufacturing—so that clients can complete design verification and pilot production with a single partner. This one‑stop model is especially valuable for overseas OEM customers that need both speed and stable quality for complex product launches.[3][4]
The demand for rapid prototyping continues to grow across industries such as consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices, industrial equipment, and robotics, because companies want to shorten development cycles and launch more product variants. Rapid prototyping makes it easier to move from idea to physical part, reduce iteration time, and make data‑driven design decisions based on real testing instead of only simulations.[5][1]
Compared with traditional prototyping that depends heavily on hard tooling and long lead times, rapid prototyping combines flexible digital workflows and on‑demand production to deliver prototypes and short runs in days or weeks. This time advantage allows rapid prototyping businesses to charge premium prices for urgent projects while still delivering strong value to clients who are racing competitors to market.[1][2]
A successful rapid prototyping business normally builds a service portfolio around several complementary technologies, so that most development stages can be completed under one roof. The exact mix depends on your budget, technical background, and target industries, but the following capabilities are considered core in modern rapid prototyping.[4][3]
CNC machining (milling and turning) is one of the most widely used methods for rapid prototyping because it works with metals and engineering plastics, delivers tight tolerances, and produces functional parts suitable for mechanical testing. With CNC prototype machining, you can quickly manufacture housings, brackets, structural components, jigs, and fixtures for both prototypes and small‑batch production without investing in hard tooling.[6][7]
For a rapid prototyping business, CNC machining is particularly valuable when customers need high precision, specific alloys, or surface finishes close to mass‑production quality. Many rapid prototyping companies also use CNC machining to post‑process 3D printed parts—for example, adding tight‑tolerance holes, threads, or sealing surfaces to printed components.[8][6]
3D printing is often the first technology that comes to mind when discussing rapid prototyping, because it can create complex geometries directly from CAD without special tooling. Processes such as SLA, SLS, MJF, FDM, and metal 3D printing allow you to offer concept models, visual prototypes, functional plastic parts, and even metal components in a short time frame.[2][3]
In a rapid prototyping business, 3D printing is especially effective for early‑stage concept validation, ergonomic evaluation, and design iterations where customers may need many design changes before locking the final version. By combining 3D printing with painting, polishing, and assembly, your rapid prototyping shop can also deliver show models for exhibitions, marketing photos, and investor demonstrations.[3][1]
Sheet metal fabrication—including laser cutting, bending, stamping, and welding—is another important pillar of rapid prototyping for enclosures, brackets, chassis, and structural frames. For industries such as telecom, electronics, and industrial automation, sheet metal rapid prototyping provides durable metal housings and frames that are similar to or identical with final mass‑production parts.[9]
If your rapid prototyping business can combine sheet metal processing with CNC machining of mating components and 3D printed internal parts, you can offer complete prototype assemblies to OEM customers. This full‑system approach reduces the coordination burden on clients and makes your rapid prototyping services more attractive for complex equipment and machinery projects.[4][6]
Rapid prototyping is not limited to one‑off samples; many clients also want bridge‑to‑production solutions such as rapid tooling, soft molds, or low‑cavity injection molds. With rapid tooling, a prototyping company can provide dozens to thousands of parts in production‑grade materials so customers can perform reliability testing, certification, and market pilot runs before investing in high‑cavity hard tooling.[10][11]
Offering rapid tooling and precision batch production allows your rapid prototyping business to support customers from prototype through pre‑production and even stable low‑volume manufacturing. This not only increases revenue per project but also builds long‑term partnerships with clients who may later move more production work to your factory or recommend your rapid prototyping services to other teams.[11][4]
Beyond pure manufacturing, many successful rapid prototyping companies provide engineering and DFM support to help customers improve part performance and manufacturability. By reviewing wall thickness, draft angles, tolerances, and material choices, your team can suggest modifications that make rapid prototyping faster, more reliable, and more cost‑effective.[12][1]
This engineering‑driven approach turns your rapid prototyping services into a strategic resource rather than just a supplier, which encourages customers to involve you earlier in their product development cycles. As a result, your rapid prototyping business gains more influence over project planning and a better chance to win follow‑up work for tooling and production.[1][4]
Before investing heavily in machines and facilities, it is important to clearly define the niche and target customers for your rapid prototyping business. Different industries value different capabilities; for example, medical device companies may prioritize high‑accuracy plastic and metal parts, while consumer electronics brands may focus more on appearance models, surface finishing, and quick design iterations.[13][1]
Ask the following questions when defining your rapid prototyping niche:
- Which industries do you understand best?
- What materials and tolerances are you most confident to deliver?
- Do you prefer early‑stage concept models, functional prototypes, or low‑volume production?
By focusing your rapid prototyping services on clearly defined customer segments, you can choose the right equipment, hire suitable engineers, and create marketing messages that speak directly to your ideal clients.[13]
A professional business plan is essential for any rapid prototyping startup, especially if you need bank loans, investors, or government support for purchasing machines. The plan should describe your service scope, target markets, pricing model, investment budget, operating costs, sales strategy, and risk control measures for your rapid prototyping business.[13]
Key elements to include:
- Market analysis: demand trends, competitor capabilities, and pricing levels in rapid prototyping.[1]
- Service portfolio: CNC machining, 3D printing, sheet metal, tooling, or specific rapid prototyping methods you will offer.[3]
- Financial projections: expected utilization of machines, revenue per project, and payback period for your rapid prototyping equipment.[11]
A clear business plan helps you avoid unrealistic assumptions and supports more stable growth as your rapid prototyping company builds its international customer base.[13]
The location of your rapid prototyping workshop affects logistics costs, access to skilled workers, and convenience for clients who may visit for audits. Many rapid prototyping businesses position themselves close to industrial clusters where suppliers of raw materials, surface treatments, and logistics services are concentrated.[7][11]
Inside the factory, you will need to design a layout that separates cutting, printing, finishing, and inspection areas to support smooth workflow and safety. For a modern rapid prototyping environment, also consider dedicated zones for CAD/CAM programming, project management, and online meetings with global customers who expect professional communication and technical support.[9][4]

Equipment decisions are among the most critical investments when starting a rapid prototyping business because they define your capabilities, quality level, and lead times. Instead of buying every possible machine at once, many successful rapid prototyping entrepreneurs begin with a balanced combination of core equipment and then expand based on market feedback.[6][7]
Typical initial setup for a rapid prototyping company may include:
- 3‑axis and 4/5‑axis CNC machining centers for metal and plastic components.[6]
- CNC lathes or turning centers for shafts, pins, and rotational parts.[7]
- Industrial‑grade 3D printers (for example SLA or SLS) for rapid prototyping of complex geometries and visual models.[2]
- Sheet metal equipment such as laser cutting machines and press brakes for enclosure and bracket rapid prototyping.[9]
In addition to hardware, your rapid prototyping business will rely heavily on CAD and CAM software for design evaluation, programming toolpaths, and communicating with clients. Investing in reliable measurement tools—CMMs, height gauges, and surface testers—will also strengthen your quality reputation in the rapid prototyping market.[12][7]
Even with advanced machines, a rapid prototyping business cannot succeed without experienced engineers, programmers, and project managers. Rapid prototyping projects usually involve incomplete information, last‑minute changes, and tight delivery deadlines, so your team must be flexible, creative, and comfortable with continuous problem solving.[7][1]
Key roles in a rapid prototyping team include:
- Sales engineers who understand both manufacturing and customer communication.[4]
- CAD/CAM programmers who can optimize rapid prototyping processes and minimize machining or printing time.[8]
- Quality engineers who manage inspection standards, reports, and certifications required by international OEM customers.[12]
Continuous training on new materials, rapid prototyping methods, and digital tools will help your team maintain a competitive edge.[3]
A well‑designed workflow is what turns machines and staff into a truly competitive rapid prototyping business. Typical steps include RFQ handling, DFM review, quotation, order confirmation, process planning, manufacturing, finishing, quality inspection, packaging, and shipment—all within rapid lead times.[4][1]
To keep your rapid prototyping projects under control, consider:
- Standardized file formats and checklists when customers submit CAD and technical requirements.[12]
- DFM feedback to improve manufacturability and reduce risk of rework in rapid prototyping.[1]
- Digital tracking boards or project management systems so all departments see priorities and deadlines.[13]
Consistent, transparent processes will make overseas clients more confident in your rapid prototyping capabilities and more likely to place repeat orders.[4]
Because many customers search globally for rapid prototyping partners, your online visibility has a direct impact on how many RFQs you receive. A professional website that clearly communicates your rapid prototyping services, equipment list, material options, tolerances, and case studies is a basic requirement.[11][1]
To promote your rapid prototyping business, combine several channels:
- SEO‑optimized articles explaining CNC rapid prototyping, 3D printing methods, and case studies to attract organic search traffic.[1]
- Social media posts showcasing finished prototypes, surface finishes, and factory workflows to demonstrate your rapid prototyping strength.[4]
- Participation in industry exhibitions and online webinars focused on product development and rapid prototyping.[14]
Clear contact forms, instant quotation tools, and fast response times will help you convert website visitors into paying rapid prototyping customers.[1]
Setting the right pricing structure for your rapid prototyping services requires balancing machine time, material cost, engineering effort, and the urgency level of each project. Many operators of prototype shops find that offering both standard and express lead times—at different price levels—helps customers choose between speed and cost for rapid prototyping orders.[15][11]
To keep your rapid prototyping business profitable, monitor key metrics such as machine utilization, scrap rate, rework hours, and on‑time delivery. As order volume grows, you can scale by adding more machines, extending shifts, or partnering with trusted suppliers while still maintaining tight control over rapid prototyping quality.[7][11]
Because rapid prototyping projects often face changing requirements and tight schedules, strong risk management and quality systems are essential. Establishing clear inspection standards, incoming material checks, and final QC procedures helps avoid delays and maintains consistent results across multiple prototype iterations.[5][9]
Certification and documentation also matter: many international clients expect ISO‑style quality systems, material certificates, measurement reports, and traceable records for their rapid prototyping projects. By building a culture where every employee understands that rapid prototyping speed must always be matched with reliability, your business develops a reputation for both agility and trustworthiness.[5][9]
In rapid prototyping, communication quality is often as important as technical capability, because customers may change drawings and priorities several times during a single project. Providing clear timelines, proactive updates, and honest feedback about manufacturability helps build trust and reduces misunderstandings with overseas buyers who rely heavily on remote collaboration.[1][4]
Long‑term relationships in rapid prototyping are usually built by consistently delivering on time, keeping promises about quality, and offering suggestions that save customers time or money. When clients see your rapid prototyping team as a partner that protects their schedules and confidentiality, they are more likely to send higher‑value projects and recommend your services to other departments.[11][4]
Starting a rapid prototyping business is an attractive opportunity for entrepreneurs who understand manufacturing and want to help global customers bring products to market faster. By carefully selecting your niche, building a balanced mix of CNC machining, 3D printing, sheet metal, and tooling capabilities, and developing a disciplined workflow, your rapid prototyping company can deliver high‑quality prototypes and low‑volume parts under tight deadlines.[3][1]
As your rapid prototyping services grow, reinvestment in advanced equipment, skilled engineers, and digital tools will strengthen your ability to handle complex multi‑process projects for demanding OEM clients. With professional marketing, responsive communication, and consistent quality, a rapid prototyping business can become a long‑term strategic partner for brands, wholesalers, and manufacturers around the world.[7][4]
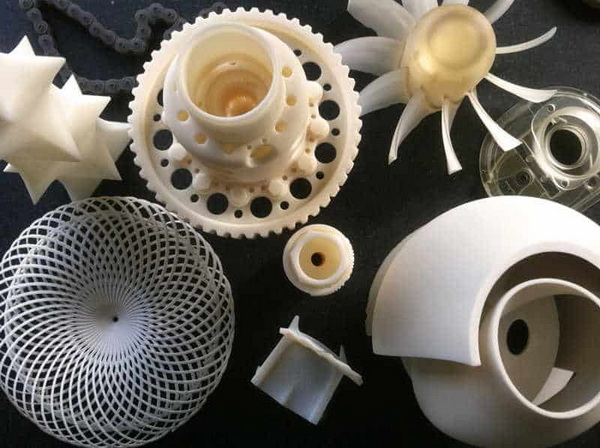

Rapid prototyping in manufacturing is a group of techniques—such as CNC machining, 3D printing, and casting—used to quickly create physical models or functional parts directly from CAD data. These rapid prototyping methods allow engineers to validate design, test fit and function, and refine products before investing in mass‑production tooling.[2][1]
Startup costs for a rapid prototyping business vary widely depending on equipment level, facility size, and location, ranging from relatively low budgets for basic 3D printing shops to much higher investment for full CNC machining and sheet‑metal capabilities. Entrepreneurs often reduce initial cost by leasing machines, purchasing certified pre‑owned equipment, or focusing on a narrower rapid prototyping niche in the early stages.[6][13]
Rapid prototyping services are widely used in consumer electronics, automotive, aerospace, medical devices, industrial machinery, and robotics, where companies need fast iterations and functional testing. Startups, design studios, and hardware accelerators also rely on rapid prototyping to validate product concepts and present physical samples to investors and customers.[14][1]
A small shop can compete in rapid prototyping by focusing on specific industries, materials, or part types, offering very responsive communication and flexible engineering support. By specializing and building a reputation for reliability and fast problem solving, even a compact rapid prototyping business can win repeat orders from international OEMs and design firms.[15][4]
Rapid prototyping focuses on quickly producing small quantities of parts for design validation, testing, or pilot runs, usually with flexible processes that minimize or avoid hard tooling. Mass production, by contrast, uses optimized, high‑volume processes and dedicated tools or molds to reduce unit cost once the final design is fully validated and stable.[2][11]
[1](https://www.fictiv.com/articles/rapid-prototyping-guide)
[2](https://formlabs.com/blog/ultimate-guide-to-rapid-prototyping/)
[3](https://bigrep.com/posts/rapid-prototyping-3d-printing/)
[4](https://www.shapeways.com/business/rapid-prototyping-services)
[5](https://www.datron.com/resources/blog/what-is-rapid-prototyping/)
[6](https://jiga.io/cnc-machining/cnc-prototyping/)
[7](https://uptivemfg.com/cnc-prototype-machining/)
[8](https://www.makerverse.com/resources/cnc-machining-guides/the-guide-to-cnc-machining-for-prototyping/)
[9](https://www.protolis.com/resources/manufacturing-guides/cnc-machining/)
[10](https://rmcplastics.com/rapid-prototyping-services-how-they-work/)
[11](https://rapidps.com)
[12](https://www.xometry.com/resources/design-guides/prototype-development-guide/)
[13](https://clickup.com/p/small-business/how-to-start-rapid-prototyping-firm)
[14](https://www.manufacturinghub.io/prototyping/7-rapid-prototyping-methods-you-need-for-your-hardware-startup/)
[15](https://www.practicalmachinist.com/forum/threads/making-a-prototype-shop-profitable.217163/)
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal