
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-10-09 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Understanding Injection Molding and Its Benefits
>> Why Choose Injection Molding?
● Steps to Partner with an Injection Molding Manufacturer for Custom Solutions
>> Assess Your Product Requirements
>> Research and Select a Suitable Manufacturer
>> Collaborate on Mold Design and Engineering
>> Prototype and Sample Production
>> Approve the Mold and Start Mass Production
>> Post-Production Support and Continuous Improvement
● Key Considerations for a Successful Injection Molding Partnership
>> Material Selection Impacts Performance and Cost
>> Mold Design and Life Cycle Management
>> Lead Time and Cost Structure Transparency
>> Quality Control and Certifications
>> Effective Communication and Collaboration
● Overcoming Common Injection Molding Challenges
>> Managing Warping and Shrinkage
>> Initial Tooling Investment vs. Mass Production Savings
>> Designing for Manufacturability
>> Material and Process Compatibility
● Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
>> 1. What industries commonly use injection molding?
>> 2. How long does it take to produce an injection mold?
>> 3. Can injection molding produce parts with different colors or textures?
>> 4. What is the minimum order quantity for injection molded parts?
>> 5. How can I reduce costs when using injection molding?
Injection molding is one of the most popular and efficient manufacturing processes for creating custom plastic parts and products. Partnering with the right injection molding manufacturer allows companies to streamline production, reduce costs, and deliver high-quality parts tailored to specific needs. This comprehensive guide explains how to effectively collaborate with an injection molding manufacturer, emphasizing the benefits, steps, critical considerations, and common challenges to help you achieve the best results for your custom solution needs.
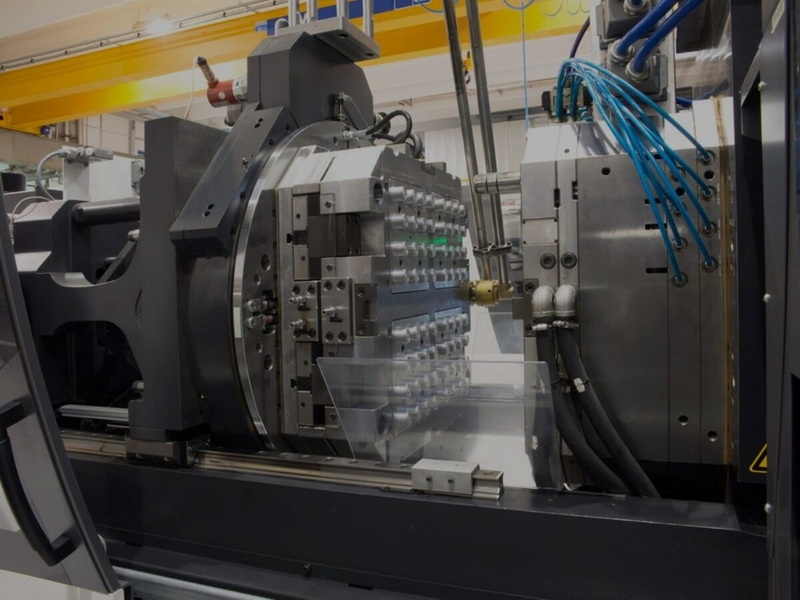

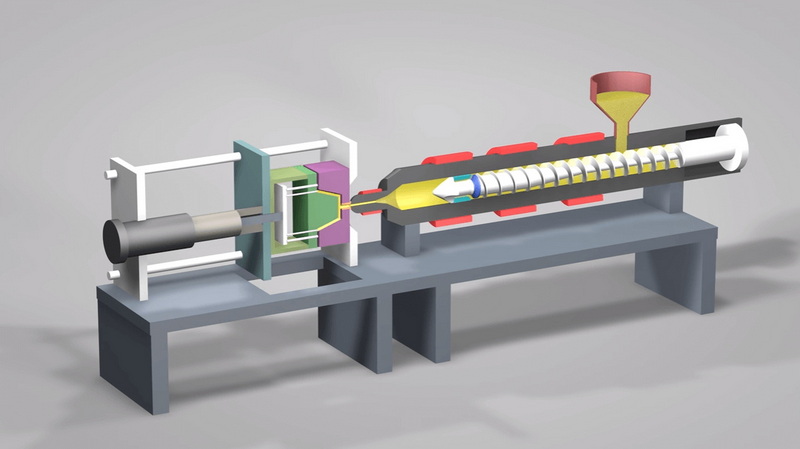
Injection molding is a manufacturing technique where molten plastic material is injected into a mold cavity, cooled, and then ejected as a finished part. This process is widely used in industries such as automotive, electronics, medical devices, and consumer goods for creating complex and durable parts.
- High Production Efficiency: Injection molding is particularly suited for producing large volumes of parts at a rapid pace, allowing companies to meet high demand efficiently.
- Consistent Quality: The process maintains tight dimensional tolerances and ensures uniformity in every part produced, which is essential for precision components.
- Versatile Material Choices: Injection molding supports a broad range of materials, including thermoplastics, thermosets, and elastomers, allowing manufacturers to tailor the properties of the final product to specific applications.
- Complex Shapes: The technology enables the creation of intricate geometries, undercuts, thin walls, and detailed surface finishes that would be difficult with other processes.
- Low Waste Generation: As excess plastic can often be reground and reused, injection molding is an environmentally efficient manufacturing method compared to subtractive techniques.
Begin by comprehensively defining your product specifications. This includes outlining:
- The type of plastic material needed based on mechanical, thermal, or chemical resistance requirements.
- The precise dimensions and tolerances for your parts.
- Surface finish demands such as polishing, texturing, or painting.
- Estimated order quantity, including initial volumes and planned scale-ups.
- Budget considerations, balancing between tooling costs and per-unit production expenses.
This preparation strengthens your ability to communicate clearly with your manufacturer and helps get accurate project evaluations.
Find an injection molding manufacturer that aligns with your needs by evaluating their:
- Experience with your product type or industry.
- Range of manufacturing capabilities beyond injection molding, such as CNC machining, 3D printing for rapid prototyping, or metal fabrication.
- Certifications like ISO 9001 or industry-specific compliances that reflect quality management systems.
- In-house engineering expertise for mold design and rapid tooling development.
- Flexibility to handle OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) services, customizing production from prototype to full-scale runs.
Successful partnerships involve co-developing mold designs that balance cost, quality, and manufacturability. Manufacturers often provide valuable input on design for manufacturability (DFM) principles, helping to avoid common pitfalls such as thick wall sections or sharp corners that can cause defects.
Tools like computer-aided design (CAD) and mold flow analysis software allow simulation of plastic flow inside the mold, pinpointing potential issues and optimizing gate locations, cooling channels, and cycle times before committing to tool building.
Prototyping is a crucial step for validating your design before full-scale production. Manufacturers use a combination of rapid prototyping technologies—often 3D printing and CNC machining—to create initial samples quickly and cost-effectively. These samples allow you to test fit, function, and aesthetics for design refinement, reducing costly changes after mold creation.
Once prototype approval is granted, the manufacturer proceeds with building the final mold tool, typically constructed from hardened steel or aluminum depending on production volume and part complexity. After tool manufacturing, trial runs ensure quality and process stability.
Mass production begins following these validations. Continuous monitoring through in-process inspections and Statistical Process Control (SPC) helps maintain consistent quality during production runs.
A reliable injection molding partner provides ongoing support beyond manufacturing, including:
- Rigorous quality control inspections throughout production.
- Packaging, assembly, and shipping tailored to customer requirements.
- Feedback loops to incorporate design improvements or cost-saving measures.
- Troubleshooting and rapid response in case of defects or delays.

Choosing the right material is critical because it determines the mechanical properties, appearance, and durability of your final product. Common choices include:
- Polypropylene (PP): Lightweight, chemical-resistant, and ideal for containers.
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Strong and impact-resistant, widely used in consumer electronics.
- Polycarbonate (PC): High impact strength and heat resistance for safety equipment.
- Nylon (PA): Excellent wear resistance suitable for mechanical components.
Material choice affects cycle times, mold wear, and part quality, so manufacturers often assist with recommendations based on your product's use case.
The mold's design significantly influences production efficiency and part consistency. Key elements include proper gating systems, cooling channel layout, and ejector mechanisms. Well-maintained molds prevent common issues such as flash, sink marks, and warping.
Choosing between aluminum and steel molds depends on production volume: aluminum molds are cheaper and suitable for short runs, while steel molds provide longevity for high-volume projects.
It is essential to clarify upfront:
- The expected timeline for prototype development, mold manufacturing, and production.
- Initial tooling costs, which can be a significant investment.
- Per-unit cost breakdown correlated with volume tiers.
Transparent communication on these fronts prevents delays, budget overruns, and misunderstandings during the project lifecycle.
Your partner's quality control processes safeguard against defects and ensure your parts meet required standards. Expect manufacturers to utilize:
- Dimensional inspections with coordinate measuring machines (CMM).
- Material certification and traceability.
- Process controls such as SPC charts to monitor stability.
ISO certification or industry-specific quality standards further signal a manufacturer's commitment to quality.
A successful partnership relies on open communication channels. Regular updates during mold building and production help you anticipate and resolve issues early. Many manufacturers provide online portals or project managers to maintain transparency.
Warping results from uneven cooling or internal stresses, causing parts to bend or twist. Overcoming this requires:
- Optimizing mold temperature and cooling layout.
- Adjusting wall thickness and material flow.
- Post-molding processes like annealing.
High upfront tooling costs can discourage smaller businesses. However, careful planning and using rapid prototyping can minimize risks and justify investment by delivering low-cost parts at scale.
Complex features such as deep undercuts or very thin walls increase mold complexity and cost. Early collaboration on design adjustments balances aesthetics and functionality with manufacturability.
Material choice must complement the injection molding process. Some materials require specialized machines or drying methods to avoid defects like bubbles or burn marks.
Partnering effectively with an injection molding manufacturer is crucial to producing high-quality, custom plastic parts efficiently and affordably. By thoroughly preparing product requirements, selecting the right manufacturing partner, collaborating during mold design, validating prototypes, and ensuring strict quality control, companies can overcome common challenges and optimize production outcomes. Through transparent communication and mutual expertise sharing, partnerships in injection molding can drive innovation while satisfying market demands and cost targets.
Injection molding is widely used in automotive, electronics, medical device manufacturing, consumer products, and packaging industries due to its versatility and efficiency.
Mold production typically takes between 4 and 8 weeks, depending on complexity, size, and tooling material.
Yes. Manufacturers can add colorants to plastic resins and apply specific finishes to mold surfaces to create various colors and textures on parts.
Minimum order quantities vary by manufacturer, but OEM injection molding services often start at a few hundred pieces per run.
Optimize your part design for manufacturability, choose cost-effective materials, and plan for larger production volumes to lower per-unit costs.
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal