
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-11-03 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● 1: Clarifying Your Moulding Production Objectives
● 2: Core Capabilities to Assess in a Moulding Production Partner
● 3: A Practical Roadmap to a Successful Partnership
● 4: Industry Scenarios and Best Practices
● 5: The Role of Technology in Modern Moulding Production
● 6: Due Diligence Checklist for Selecting a Moulding Partner
● 7: Why Integrated OEM Partners Deliver Superior Outcomes
● 8: Shangchen's Global OEM Capabilities and Value Proposition
● 9: Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
● FAQ
>> 1: How do you evaluate moulding production capabilities for new projects?
>> 2: What is a typical timeline from concept to full production in moulding production?
>> 3: Which quality metrics matter most in moulding production?
>> 4: What questions should be asked about post-moulding finishing?
>> 5: How important is intellectual property protection when selecting a partner?
Selecting a moulding production partner is a strategic decision with far-reaching implications for quality, cost, and speed to market. A capable partner should offer end-to-end support—from early design and prototyping through to high-volume production and final assembly—while maintaining strict quality controls and clear communication. For international brands, distributors, and manufacturers seeking reliable OEM services, finding a partner with robust technical capabilities, strong project management, and scalable capacity is essential. This article outlines a structured approach to evaluating moulding production partners, highlights practical considerations, and provides actionable steps to establish a successful collaboration. It also demonstrates how a Chinese factory with broad expertise in rapid prototyping, CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, tooling, and moulding production can serve global clients effectively.

Before evaluating potential partners, define the project's core requirements to ensure alignment and avoid costly redesigns later.
- Part family and material selection: Decide whether parts are plastic, metal, or composite, and identify materials that meet mechanical and environmental performance needs.
- Production volume and lifecycle: Distinguish between rapid prototyping, pilot runs, and long-term production to determine tooling durability, cycle times, and cost per part.
- Tolerances and finishes: Establish critical dimensional tolerances, surface textures, and functional requirements that drive process choice and tooling design.
- Time-to-market pressures: If speed is paramount, emphasize concurrent engineering, design-for-manufacture (DFM) feedback, and quick-turn tooling options.
- Post-moulding needs: Consider assembly, painting, coating, insertion molding, and other secondary operations that the partner must support.
- Regulatory and compliance requirements: Identify any industry-specific standards (for example, medical, automotive, or consumer electronics) that the partner must meet and document.
A comprehensive evaluation should cover both technical prowess and organizational maturity.
- End-to-end manufacturing spectrum: From design assistance and tooling fabrication to moulding, secondary operations, and final assembly, a full-service partner reduces integration risk.
- Tooling design and durability: In-house mould design, material choices (steel vs aluminum), cooling system sophistication, ejection mechanisms, and lifecycle tracking are crucial for predictability.
- Process control and quality systems: Look for robust SPC, first article inspection, continuous improvement programs, and formal CAPA procedures.
- Material and process expertise: Access to a broad range of resins, polymers, metals, and surface finishes, plus compatibility with various moulding processes (injection, compression, transfer, blow as applicable).
- Automation and scalability: Ability to scale from pilot to high-volume production with automation, robotics, and smart scheduling to sustain throughput.
- Quality assurance and traceability: Documented QA protocols, lot traceability, and test data retention supporting audits and regulatory needs.
- IP protection and data security: Clear NDAs, controlled access to digital designs, and secure data transfer practices are essential in OEM collaborations.
- Shortlist with criteria: Build a concise set of selection criteria based on materials, part geometry, tolerances, required certifications, and track record in similar industries.
- Early design collaboration: Seek feedback on manufacturability and potential cost-reduction opportunities through DFM recommendations.
- Prototyping and pilot runs: Validate moulding decisions, tool integrity, material behavior, and process windows before committing to large-scale production.
- Define a transparent quality regime: Agree on sampling plans, acceptance criteria, inspection methods, and corrective action processes.
- Establish clear communication channels: Assign dedicated project managers, set regular review cadences, and use shared dashboards to track milestones.
- Plan for risk and change management: Implement contingency options for tool wear, maintenance gaps, and supply disruptions.
- Medical device components: Prioritize sterile handling, traceability, cleanroom considerations, and validated processes. Seek partners with rigorous documentation and regulatory alignment.
- Automotive and aerospace parts: Demand durable moulds, certified materials, rigorous process validation, and traceability. Emphasize long-term tool supply, preventative maintenance, and risk mitigation strategies.
- Consumer electronics housings: Emphasize aesthetic quality, color consistency, and fast changeovers. Value modular tooling, cosmetic decorating capabilities, and rapid iteration cycles.
- Industrial components and enclosures: Focus on cost-per-part, tool life, automation, and predictability. Look for lean manufacturing practices and scalable automation to support high volumes.
- Simulation and digital twins: Virtual analyses of flow, warp, and cooling reduce physical iterations and accelerate design optimization.
- Precision machining and mould fabrication: Advanced CNC, EDM, and milling techniques enable tight tolerances and longer tool life.
- Automation and robotics: Robotic pick-and-place, inspection, and assembly lines increase repeatability while lowering human error and labor costs.
- Real-time monitoring and data analytics: Sensors track temperature, pressure, cycle counts, and part quality to preempt issues and sustain consistency.
- Surface engineering and finishing: A broad range of finishes—from polishing and texturing to painting and coating—can be integrated to meet aesthetic and functional requirements.
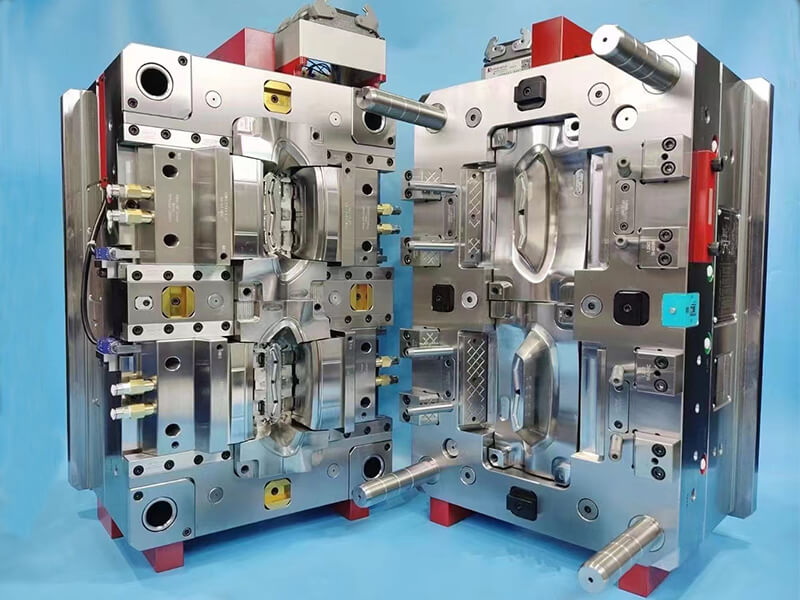
- Technical fit: Confirm compatibility with your material, geometry, and precision needs; verify in-house tooling capability and process expertise.
- Quality infrastructure: Review certifications, quality manuals, inspection equipment, and data traceability practices.
- Delivery reliability: Assess lead times, on-time performance, capacity transparency, and the ability to meet fluctuating demand.
- Communication and culture: Evaluate responsiveness, language alignment, and collaborative mindset for effective problem solving.
- Intellectual property safeguards: Ensure robust NDAs, restricted access to designs, and clear ownership terms for tools and moulds.
- Reduced lead times: Streamlined workflows and fewer handoffs accelerate development and time-to-market.
- Consistent quality and traceability: Integrated control improves consistency across batches and simplifies compliance reporting.
- Economies of scale: Centralized tooling, standardized processes, and automation lower unit costs at higher volumes.
- Faster iteration cycles: Access to rapid prototyping, iterative testing, and early production feedback shortens product development cycles.
- Extensive manufacturing portfolio: From rapid prototyping and CNC machining to sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, moulding production, and tooling development, Shangchen offers a one-stop OEM ecosystem.
- Global collaboration readiness: Experienced in partnering with international brand owners, wholesalers, and manufacturers needing reliable, scalable supply chains.
- Quality-first philosophy: Emphasis on precision engineering, repeatability, and capacity flexibility to respond to changing demand and design requirements.
- Competitive advantages for moulding production: Cost-effective tooling, rapid prototyping, and robust finishing and assembly services to accelerate time-to-market for diverse industries.
- Case-friendly engagement model: Transparent project management, detailed documentation, and a focus on protecting intellectual property, ensuring confidence for long-term partnerships.
- Skipping pilot production: Jumping to full-scale production without validation risks costly recalls or failures.
- Inadequate tool thermal management: Poor cooling or heat transfer management can yield inconsistent parts and higher defect rates.
- Overlooking post-moulding requirements: Neglecting finishing, assembly, or testing can derail the final product's performance and aesthetics.
- Weak IP controls: Insufficient confidentiality and data security measures can jeopardize proprietary designs and tooling.
- Insufficient long-term planning: Failing to establish spare parts, maintenance, and tooling support can disrupt supply during growth.
Choosing the right moulding production partner is a foundational decision that shapes product quality, development timelines, and total cost of ownership. A strong partner offers end-to-end capabilities, rigorous quality control, scalable capacity, and proactive collaboration on design-for-manufacture improvements. By conducting thorough evaluations, aligning on a realistic project trajectory, and partnering with a proven OEM provider—such as Shangchen (SC-RapidManufacturing)—brands can achieve reliable supply chains, faster product introductions, and sustainable competitive advantages in global markets.
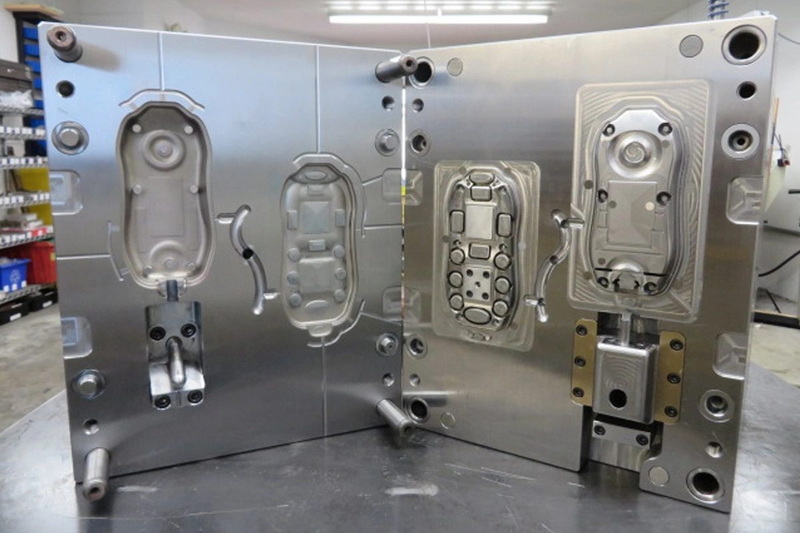

Answer: Begin with a detailed capability assessment covering material compatibility, suitable moulding methods, in-house tooling design and fabrication capabilities, quality system maturity, pilot run availability, and proven delivery performance; review relevant case studies and client references to gauge performance in similar applications.[1]
Answer: The timeline generally includes concept refinement and DFMEA, mould design and fabrication, prototype tooling and trials, process validation, and ramp-up to steady production; complexity, volume, and regulatory requirements influence duration, with proactive collaboration shortening cycles.[1]
Answer: Key metrics include first article inspection results, Cp/Cpk for critical dimensions, process capability indices, defect rates, on-time delivery, end-of-line yield, and traceability documentation to support audits and continuous improvement.[1]
Answer: Inquire about available surface finishes, coating options, painting capabilities, assembly services, inspection criteria for finished parts, and any impact on tolerances or functional properties.[1]
Answer: IP protection is essential to prevent sensitive design information from leaking; require robust NDAs, secure data transfer protocols, strict access controls, and clear ownership terms for moulds and tooling.[1]
[1](https://flambeau.co.uk/industry-market-trends/find-injection-moulding-partner/)
[2](https://eds-international.com/blog/plastic-injection-molding-partner-guide/)
[3](https://www.crescentind.com/blog/using-a-procurement-checklist-to-select-an-injection-molding-partner)
[4](https://www.kaysun.com/blog/evaluating-injection-molder-partnerships)
[5](https://kruger.industries/how-to-identify-injection-moulding-partner/)
[6](https://rosti.com/resources/blogs/6-considerations-when-choosing-a-plastic-injection-molder/)
[7](https://exothermic.com/news/how-to-evaluate-reaction-injection-molding-companies-for-your-next-project)
[8](https://www.becgroup.com/blog/choosing-the-right-injection-moulding-partner-key-factors-to-consider/)
[9](https://xcmachining.com/choosing-an-injection-molding-partner/)
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal