
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-11-04 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● The Foundations of Moulding Production
>> What Is Moulding Production?
>> Why Is Moulding Critical for Consistency?
● The Detailed Process of Moulding Production
>> Real-Time Process Monitoring and Automation
● Key Benefits to Product Quality and Consistency
>> Tolerance Control and Dimensional Accuracy
>> Cost-Effectiveness at Scale
● Advanced Technologies Elevating Moulding Production
>> 3D Printing and Rapid Prototyping
>> CNC Machining and Multi-Axis Turning
● Quality Control Systems in Modern Moulding
>> Automated Inspection and Defect Detection
>> Maintenance and Calibration
>> Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
● OEM Partnerships and Global Delivery
● Applications of Moulding Production Across Industries
>> Automotive
● Continuous Innovations in Moulding Production
● FAQ
>> 1. What are the most common moulding production processes?
>> 2. How do manufacturers ensure precision in moulding production?
>> 3. Is moulding production suitable for rapid prototyping?
>> 4. How do Chinese factories maintain quality for international customers?
>> 5. What certifications should international buyers look for in a moulding production partner?
In the landscape of advanced manufacturing, moulding production plays a pivotal role in ensuring product consistency and quality across numerous industries. For OEM brand owners, wholesalers, and manufacturers seeking global competitiveness, leveraging technologies such as injection moulding, CNC machining, sheet metal forming, and rapid prototyping enables precision, scalability, and reliability. Factories with expertise in these areas, particularly those in China like Shangchen, offer partners worldwide the benefit of repeatable, defect-free production runs — all while optimizing cost and speed.[11][12][13]
Moulding production is the process of shaping raw materials into finished parts by using carefully engineered moulds. These moulds can be manufactured from steel, aluminum, silicone, or rubber, depending on the output material and production requirements. The process is used to create everything from automotive components and medical devices to consumer electronics and specialized industrial goods.[2][5]
Moulding production delivers unmatched repeatability. Each part is formed inside the same precision cavity, under tightly controlled conditions. Whether using injection moulding, die-casting, or compression techniques, this closed-loop approach guarantees minimal deviation between units, reducing defects and lowering customer returns.[12][14][11]
All moulding production projects begin with a comprehensive design phase. Engineers and designers collaborate on a detailed 3D model, identifying every relevant surface, tolerance, and functional requirement. CAD software and simulation tools allow for early prediction and optimization of flow dynamics, cooling behavior, and potential problem areas like weld lines or air traps.[5][6]
Choosing the right material for both the mould and the final part is paramount. While steel is ideal for high-volume production due to its durability, aluminum can enable faster cycle times for smaller batches. Special composites and polymers, blended with reinforcements or additives, tailor parts for particular strength, clarity, or chemical resistance needs.[15][16]
Fabricating the mould involves CNC machining, electrical discharge machining (EDM), or even 3D printing — each technique selected according to the required accuracy and complexity. Surface finishing and polishing guarantee the correct part texture and dimensional fit.[8][5]
Once the mould is made, the core production cycle commences, encompassing:
- Clamping: The two halves of the mould are pressed together.
- Injection: Molten material is injected under controlled temperature and pressure.[4][7]
- Dwelling: The material fills every cavity, with pressure applied to eliminate voids.
- Cooling: The part solidifies and stabilizes.
- Mould Opening: Automated systems open the mould delicately.
- Ejection: The finished part is pushed from the cavity, followed by trimming and finishing steps to ensure proper fit and appearance.[7][4]
Cutting-edge factories deploy real-time sensors, robotics, and statistical process control systems to monitor every aspect of the moulding production cycle. Temperature, pressure, humidity, and shot size are constantly tracked, enabling immediate correction if deviations are detected. Automated quality checks, robotic part handling, and integrated data analytics enhance throughput while protecting product consistency.[14][17]
Moulding production achieves fine tolerances as strict as ±0.005", allowing critical aerospace, automotive, and medical parts to perform reliably in demanding environments. Repeatable precision means mating components fit securely, and assemblies function correctly every time.[18][19]
High-pressure moulding allows for exceptional detail, from microscopic texturing and branding to complex functional shapes. Proper mould maintenance and cleaning ensure surfaces remain flawless across thousands or millions of cycles.[19][15]
Whether using engineered plastics, specialty polymers, or metals, moulding production leverages rigorous material checks and blending systems. Consistency in the input material translates directly to finished part quality, with color, density, and strength held within stringent limits.[16][15]
Advanced ERP and MES systems enable factories to track materials and product batches from incoming raw stock to finished goods. Should an issue arise, traceability tools allow for rapid adjustment, recall, or fix, making quality management transparent and reliable.[13][17][20]
After upfront investment in tooling, moulding production supports cost-efficient bulk manufacturing. Automated operations minimize labor, and scrap rates remain low because material usage is optimized per cycle. Any excess polymer often gets recycled back into the process, further reducing waste.[13][15][18]
Rapid prototyping, made possible by 3D printing, enables fast design validation and iterative improvement. OEM clients can confirm fit and finish within days, then transition seamlessly to moulded mass production for scaling up.[21][16]
CNC machining enhances both mould construction and final part accuracy. Multi-axis turning and milling allow for complex shapes, holes, and undercuts — features difficult to achieve with traditional methods.[8][21]
For enclosures and brackets, high-precision sheet metal forming provides sturdy, consistent parts. Advanced bending, punching, and finishing technologies ensure each batch meets tight specs — essential for electronics and mechanical systems.
The rise of Industry 4.0 means moulding production increasingly integrates digital twins, machine learning, and data-driven optimization. As a result, factories can predict maintenance needs, prevent production interruptions, and guarantee consistent output quality over large volumes.[17]
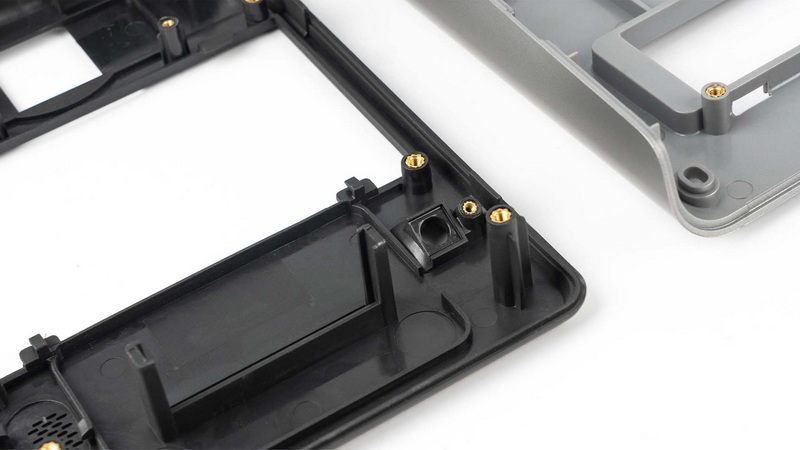

State-of-the-art camera systems, in-process measurement, and robotic pick-and-place solutions catch defects before parts leave the line. Critical dimensions and cosmetic features are checked and logged, supporting zero-defect delivery.[14][17]
Consistent quality relies on regular mould cleaning, periodic calibration, and preventive equipment maintenance. Hardened steel, advanced coatings, and anti-corrosion treatments prolong mould lifespan, guaranteeing that each run matches the original design.[12][14]
International standards (ISO 9001, ISO 13485, TS 16949) assure buyers of globally accepted quality levels. Leading Chinese factories maintain these certificates, supporting safe, compliant exports for demanding applications, including automotive safety and medical devices.[22]
OEM buyers rely on world-class moulding production partners to provide technical expertise, speed to market, and bulletproof quality assurance. Factories skilled in design-for-manufacturing (DFM), rapid prototyping, and batch production supply components that integrate seamlessly into global brands' supply chains. This partnership model gives international brands a competitive edge for price, quality, and reliability — enabling them to introduce innovative products faster, at lower cost, and at higher quality than competitors.[23][16][22]
Precision-moulded parts are critical for safety, fit, and reliability. Dashboard components, engine housings, and electrical connectors are all manufactured using regulated, repeatable moulding processes.
Hygienic and high-precision moulding is needed for syringes, diagnostic equipment, and device housings. Certifications and traceability ensure patient safety.[22]
Enclosures, switches, connectors, and mounting assemblies rely on moulding production for aesthetics and function. Repeatable production supports strict branding and global scaling.
Machine parts produced via moulding deliver robust strength, fatigue life, and resistance to corrosive environments, meeting the varying demands of manufacturing industries.
Manufacturers are embracing innovation to increase the performance and flexibility of moulding production. Developments in:
- Sustainable materials (bioplastics, recycled polymers).
- Hybrid production systems combining CNC, printing, and traditional moulding.
- Real-time AI optimization of settings for each batch.
- Completely automated, unmanned “lights-out” factories for consistent output and lower operational costs.
These advancements continue to propel the efficacy of moulding production as an indispensable backbone for modern industry.[24][17]
Moulding production forms the foundation of quality and consistency within modern manufacturing. Through technical precision, automation, advanced material science, and rigorous quality controls, it allows OEMs and global brands to deliver reliable products at volume with minimal defects. Factories equipped for rapid prototyping, CNC machining, and mass production drive not only superior results but also cost savings and innovation — giving buyers the tools they need for market success. As technologies and processes evolve, moulding production remains at the heart of efficient, scalable, and high-quality manufacturing worldwide.
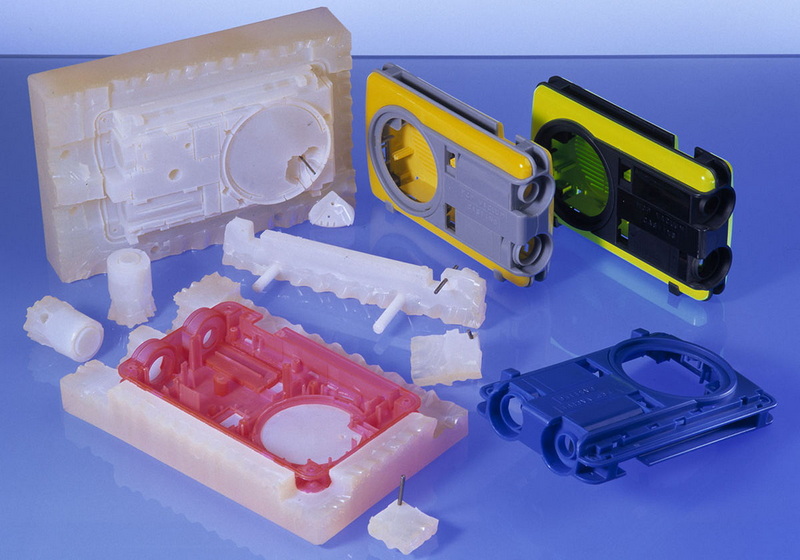

The most common processes are injection moulding, compression moulding, CNC machining, die-casting, and sheet metal forming, each suited to particular materials and product types.[15][18]
Precision is achieved by advanced mould design, high-quality materials, real-time process monitoring, and automated inspection systems to ensure every part meets exact specifications.[20][5][12]
Yes, modern moulding shops often combine 3D printing and CNC machining with traditional moulding to allow quick prototyping before large-volume production.[16][21]
Chinese suppliers apply strict certifications, use advanced machinery, and employ experienced engineers to guarantee internationally compliant products for OEM partners.[14][22]
Seek partners with ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO 13485 for medical-grade parts, and TS 16949 for automotive products to ensure robust process controls and world-class quality.[22]
[1](https://www.protolabs.com/resources/guides-and-trend-reports/designing-for-moldability-fundamental-elements/)
[2](https://www.extrememolding.com/blog/guide-to-mold-manufacturing-its-processes)
[3](https://www.cadrex.com/a-starter-guide-to-injection-molding)
[4](https://sybridge.com/injection-molding-guide/)
[5](https://www.3erp.com/blog/the-entire-process-of-mold-making/)
[6](https://www.aprios.com/insights/the-basics-of-plastic-injection-molding-a-guide-for-engineers)
[7](https://geomiq.com/injection-moulding-guide/)
[8](https://www.fictiv.com/articles/injection-molding-manufacturing-process)
[9](https://formlabs.com/blog/how-to-make-a-mold/)
[10](https://www.ksplastic.com/blog/comprehensive-guide-to-plastic-injection-molding/)
[11](https://thriam.com/impact-of-injection-molding-on-product-quality)
[12](https://www.racemoldgroup.com/en-US/newsc13-how-precision-molds-improve-product-quality-and-manufacturing-efficiency)
[13](https://advancedplastiform.com/injection-molding-for-mass-production/)
[14](https://www.cavaliertool.com/how-quality-molds-drive-success-a-guide-for-consumer-goods-professionals/)
[15](https://www.protolabs.com/resources/blog/the-advantages-and-disadvantages-of-injection-molding/)
[16](https://www.newayprecision.com/services/plastic-injection-molding)
[17](https://www.ensinger-pc.com/resources/blog/enhancing-efficiency-and-quality-the-role-of-automation-in-modern-injection-molding/)
[18](https://www.3ds.com/make/solutions/blog/injection-molding-what-are-advantages)
[19](https://www.kaysun.com/blog/top-benefits-of-plastic-injection-molding)
[20](https://www.protolabs.com/resources/guides-and-trend-reports/scientific-molding-helps-ensure-repeatable-part-function/)
[21](https://ims-tex.com/precision-injection-molding-the-manufacturing-benefits/)
[22](https://www.kenmold.com/blog/mold-tooling_bk_5)
[23](https://www.aprios.com/insights/why-injection-molding-is-essential-for-mass-production)
[24](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2351978918313593)
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal