
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-09-16 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Understanding Sheet Metal Fabrication in Automotive Industry
● Essential Sheet Metal Fabrication Techniques for Automotive Parts
>> Sheet Metal Cutting Techniques
>>> Laser Cutting
>>> Plasma Cutting
>>> Shearing
>> Sheet Metal Forming Techniques
>>> Bending
>>> Stamping
>> Sheet Metal Joining Techniques
>>> Welding
>>> Riveting and Mechanical Fastening
● Material Selection for Automotive Sheet Metal Fabrication
● Quality Control and Precision Measures
● Production Optimization and OEM Service Strategies
● Emerging Trends in Automotive Sheet Metal Fabrication
● FAQ
>> 1. What cutting techniques are most effective for automotive sheet metal fabrication?
>> 2. Which forming methods are commonly used in automotive sheet metal fabrication?
>> 3. How does welding contribute to automotive sheet metal assembly?
>> 4. What materials are preferred for automotive sheet metal fabrication?
>> 5. How can OEMs improve sheet metal fabrication efficiency?
Sheet metal fabrication plays a vital role in the automotive industry, serving as the backbone of countless vehicle components, from structural chassis parts to intricate body panels and interior trim. The process involves transforming flat sheets of metal into shaped, functional parts through cutting, forming, and joining techniques tailored to meet the rigorous demands of automotive applications. For automotive OEMs and suppliers, understanding and implementing best practices in Sheet Metal Fabrication is essential to ensure parts' durability, precision, and cost-effectiveness.
This article offers a comprehensive overview of the best sheet metal fabrication practices specifically optimized for automotive industry applications. It provides in-depth guidance on cutting, forming, and joining methods, material selection, quality control measures, and production optimizations suited for high-volume and precision manufacturing. With insights embraced by leading automotive fabricators, this guide is designed to help OEMs and manufacturers optimize their sheet metal fabrication operations for superior automotive part performance and production efficiency.

Sheet metal fabrication is the manufacturing process that involves cutting, bending, stamping, and assembling flat metal sheets into functional components. In automotive manufacturing, these fabricated metal parts must meet stringent requirements such as weight optimization, structural integrity, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal.
Common materials employed include aluminum alloys prized for their lightweight and corrosion resistance, carbon steel known for strength and cost-effectiveness, stainless steel valued for durability and surface finish, and specialty alloys tailored for critical performance applications. Components fabricated through sheet metal processes encompass vehicle body panels, chassis frames, engine mounts, brackets, door structures, and dashboard assemblies.
The ability to deliver parts that meet precise dimensional tolerances and surface finish quality is essential in automotive fabrication. This precision enables efficient assembly, optimal vehicle safety and performance, and reduces costly rework or rejects.
The fabrication of automotive sheet metal parts involves several specialized techniques specifically selected based on part design, material, and production requirements. These techniques are broadly categorized into cutting, forming, and joining methods.
Laser cutting is a highly precise, thermal cutting method employing a focused high-powered laser beam that melts or vaporizes the metal along programmed paths. The process is controlled by CNC systems, allowing for complex shapes and intricate designs with exceptional accuracy.
Laser cutting is widely used for outer body panels, engine components, and detailed trim parts where clean edges and minimal secondary finishing are desired. It produces narrow kerfs with little heat distortion, preserving material properties.
Advantages include minimal material waste, compatibility with various metals including aluminum and steel, and the ability to handle both thin and moderately thick sheets. Furthermore, laser cutting is a non-contact process that reduces mechanical stresses on the workpiece.
Plasma cutting utilizes a jet of ionized gas at extremely high velocity and temperature to melt and blow away metal material, effectively slicing through thicker sheets. It is highly suitable for automotive components like chassis parts that require heavy-gauge metal cutting.
While plasma cutting offers faster processing for thick materials compared to laser cutting, its precision is slightly lower, making it ideal for structural parts rather than fine-detailed bodywork.
Its versatility across metal types and thicknesses and its relatively lower equipment cost contribute to its popularity in automotive fabrication for heavy structural components.
Shearing is a mechanical cutting process that applies high force through paired blades to slice sheets along a straight line. It is generally used when high-speed cutting of simple shapes is needed, particularly for flat parts without tight tolerances such as brackets and base plates.
Shearing is a cost-effective approach for initial sheet sizing before more detailed fabrication processes but is less suitable for intricate geometries due to the linear cut limitation.
Bending uses press brake machines to deform sheet metal into angles and curves, vital for fabricating parts like door frames, structural reinforcements, and mounting brackets. The machine applies controlled force at precise points, controlled by CNC to form consistent bends that meet tight angle and radius tolerances.
Bending is essential to achieve the 3D shapes needed for automotive assemblies. Careful setup of tooling and parameters ensures parts maintain strength and dimensional accuracy after bending.
Stamping is a high-volume process in which sheet metal is pressed into dies to produce specific shapes and features, such as body panels, fender contours, and decorative trims. It includes methods like blanking (cutting a shape from sheet), punching (creating holes or cutouts), embossing (raising or indenting patterns), and deep drawing (forming complex depressions).
Due to its efficiency in mass production and its ability to create detailed and consistent features rapidly, stamping is a cornerstone of automotive exterior part fabrication.

Welding is the process of permanently joining metal parts by melting and fusing them together. Common welding methods in automotive fabrication include spot welding (widely used for assembly of body panels), MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding for thicker sections, and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding for high precision joints.
Welding ensures structural stability in critical automotive assemblies such as chassis, frame structures, and exhaust components. It offers high strength and durability but requires clean surfaces and skilled operators to maintain weld quality.
Riveting involves joining metal sheets by inserting rivets through aligned holes and deforming them to hold parts together. This cold joining technique is useful for joining dissimilar metals or where welding heat could damage materials or coatings.
Mechanical fasteners like screws and bolts provide flexibility in assembly and maintenance but are less common in large structural components due to added weight.
Material choice is critical to achieving the desired balance of weight, strength, corrosion resistance, and cost-efficiency.
- Aluminum: Increasingly favored in modern automotive design for its lightweight properties that aid fuel efficiency and handling. Aluminum parts require special consideration in fabrication due to their softness and thermal conductivity.
- Carbon Steel: Still dominant for vehicle frames and internal support due to cost-effectiveness and high strength.
- Stainless Steel: Preferred where corrosion resistance and aesthetics are priorities, such as in exhaust systems and trims.
- Specialty Alloys: Some high-performance vehicles utilize nickel, titanium, or advanced composites in critical areas for enhanced strength-to-weight ratios.
Each material path affects tooling selection, process parameters, and finishing techniques, requiring fabricators to tailor their approach accordingly.
Achieving consistent high quality in automotive sheet metal parts requires rigorous quality control protocols. Advanced CNC machinery ensures precise cutting, bending, and forming operations that adhere to design specifications.
Inspection techniques include Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) for dimensional verification, 3D laser scanning for complex shapes, and automated visual systems to detect surface defects. These help maintain strict tolerances necessary for seamless vehicle assembly and safety compliance.
Implementing in-process quality control checkpoints reduces rework, scrap rates, and ensures delivery of parts that meet or exceed industry standards.
For automotive OEMs and fabricators, efficiency and scalability are essential.
- Rapid Prototyping: Utilizing 3D printing and CNC machining enables fast validation of designs and tooling prior to mass production.
- Lean Manufacturing: Reducing waste through just-in-time production, streamlined workflows, and continuous improvement ensures cost savings and faster turnarounds.
- Advanced Software: CAD/CAM systems optimize cutting paths and bending sequences, maximizing sheet utilization and minimizing cycle times.
- Integrated Supply Chains: Secure sourcing of quality raw materials and reliable logistics reduces downtime and maintains consistent production flow.
Collaborating with sheet metal fabrication partners like Shangchen (sc-rapidmanufacturing.com), who offer comprehensive services including CNC machining, 3D printing, batch production, and mold making, helps OEMs maintain competitiveness in global automotive markets.
The automotive industry is embracing new fabrication technologies to meet evolving challenges:
- Hydroforming: Uses high-pressure fluid to form complex, lightweight, and strong components with smooth contours, increasingly used for chassis and exhaust systems.
- Automation and Robotics: Automated welding and assembly lines improve consistency, reduce errors, and increase throughput.
- Lightweight Materials: Adoption of advanced aluminum alloys and composites to reduce vehicle weight and emissions.
- Smart Manufacturing: AI-driven quality control tools and predictive maintenance help optimize fabrication efficiency and product reliability.
Embracing these trends positions manufacturers to deliver innovative, high-quality automotive components for the future.
Best practices in automotive sheet metal fabrication revolve around selecting appropriate cutting, forming, and joining techniques tailored to the specific part and material requirements. Integration of precise laser cutting, efficient plasma cutting, accurate bending, and robust welding ensures parts meet stringent automotive standards for fit, function, and durability. Quality control mechanisms and production optimizations further guarantee consistent outcomes at scale.
For OEMs and fabricators alike, partnering with versatile sheet metal manufacturing specialists capable of CNC machining, rapid prototyping, and batch production is key to maintaining competitive advantages in the automotive sector. Continual adoption of emerging fabrication technologies will also drive further improvements in vehicle performance, safety, and sustainability.
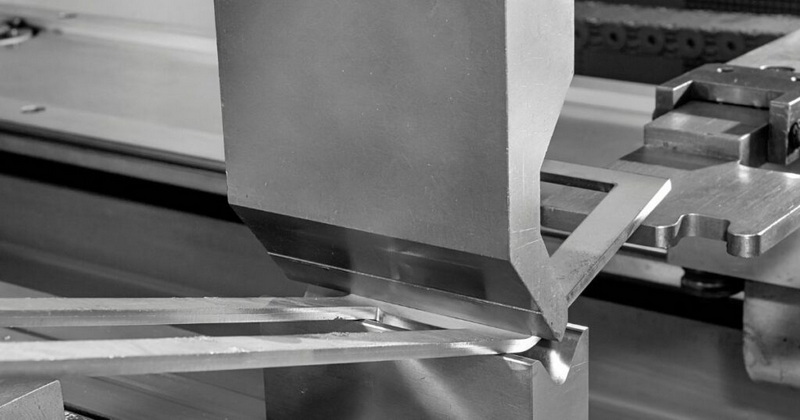
Laser cutting is favored for precision and complexity, plasma cutting for thick sheet metal and structural parts, while shearing suits fast, straight cuts on less intricate components.
Press brake bending and stamping are primary forming methods, enabling complex shapes and high-volume consistent parts such as panels, brackets, and frames.
Welding provides strong, permanent joints for structural integrity in chassis and body panels. Spot, MIG, and TIG welding techniques are used depending on part requirements.
Aluminum, carbon steel, stainless steel, and specialty alloys are common choices, each selected for their strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness.
By incorporating rapid prototyping, lean manufacturing, advanced CAD/CAM software, and collaboration with flexible fabrication partners offering CNC machining and diverse production capabilities.
[1](https://www.dekmake.com/automotive-sheet-metal-fabrication/)
[2](https://gilchriststeels.co.uk/the-full-guide-to-sheet-metal-fabrication/)
[3](https://waykenrm.com/blogs/automotive-sheet-metal-fabrication-different-techniques-and-materials/)
[4](https://www.machining-custom.com/blog/automotive-sheet-metal-fabrication.html)
[5](https://redeyeracecars.com/blogs/our-blogs/sheet-metal-fabrication-101-a-beginner-s-guide)
[6](https://www.rapiddirect.com/blog/sheet-metal-fabrication-ultimate-guide/)
[7](https://cumulusquality.com/mastering-sheet-metal-fabrication-a-step-by-step-guide-using-cumulus-pro/)
[8](https://geomiq.com/sheet-metal-guide/)
[9](https://crmetal.com/blog/the-complete-guide-to-sheet-metal-fabrication-techniques/)
[10](https://yijinsolution.com/sheet-metal/automotive-sheet-metal-fabrication/)
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal