








Content Menu
● Combining CNC and 3D Printing
● How CNC Enhances 3D Printing
● Benefits of CNC and 3D Printing Integration
● Applications of CNC in 3D Printing
>> Consumer Products and Prototyping
● Challenges and Solutions in Integration
● Future Trends in CNC and 3D Printing
● FAQs
>> 1. What Role Does CNC Play in 3D Printing?
>> 2. Can 3D Printing Replace CNC Machining?
>> 3. What Materials Are Suitable for Hybrid Manufacturing?
>> 4. How Does Hybrid Manufacturing Reduce Costs?
>> 5. What Industries Benefit Most from CNC and 3D Printing Integration?
In modern manufacturing, 3D printing and CNC machining are two groundbreaking technologies that have revolutionized how products are designed and produced. While each technology operates on fundamentally different principles—additive versus subtractive—the integration of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining within 3D printing workflows offers exciting opportunities for combining the strengths of both.
This article delves into what CNC in 3D printing means, the technologies involved, their integration, benefits, applications, and future trends. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how CNC enhances 3D printing processes and why this hybrid manufacturing approach is gaining traction in industries worldwide.
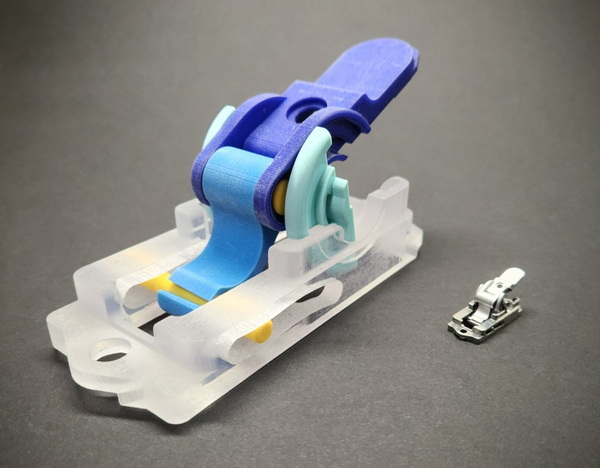
CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control, a process where computers control machine tools to perform precise cutting, drilling, milling, or turning operations on raw materials. CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing technique—in which material is carefully removed from a solid block to create a part according to digital design instructions.
The CNC process uses CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software to generate code that guides powerful cutters or lathes to exact locations, achieving complex shapes with high precision. CNC machining is widely used in aerospace, automotive, medical, and consumer product manufacturing due to its accuracy and repeatability.[6][11]
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, builds objects layer by layer from raw materials such as plastics, resins, or metals based on digital 3D models. Unlike CNC, which removes material, 3D printing adds material only where needed, allowing for the creation of highly complex geometries, internal channels, and lightweight lattice structures impossible or cost-prohibitive with traditional processes.
3D printing offers tremendous design freedom and is used extensively for rapid prototyping, custom tooling, and small-batch production. It reduces lead times, minimizes material waste, and facilitates innovation across multiple sectors.[12][6]
Though both CNC machining and 3D printing have their unique strengths and limitations, integrating these technologies can create a hybrid manufacturing process that leverages the best of both worlds.
In a typical hybrid workflow:
- A part is first produced using 3D printing, often to near-net-shape.
- The printed part is then precisely machined via CNC to improve surface finish, accuracy, and add critical features such as threads or holes.
This fusion allows manufacturers like Shangchen to create complex, custom parts with rapid turnaround, high-level detail, and mechanical strength suitable for demanding applications.[13][14]
CNC machining primarily adds value to 3D printed parts in these ways:
- Precision Finishing: CNC removes any excess material or roughness inherent in 3D printing, achieving tight tolerances and smooth surfaces.
- Feature Addition: It can machine intricate details, functional threads, or holes that 3D printers cannot accurately produce.
- Material Strength: By selectively machining and post-processing, CNC improves part strength and durability.
- Dimensional Accuracy: CNC ensures parts meet exact engineering specifications, especially critical in aerospace, medical, and automotive sectors.[2][15]
The combination of CNC and 3D printing provides several manufacturing advantages:
- Design Freedom and Accuracy: 3D printing's complex geometries are complemented by CNC's precision finishing.[1]
- Cost Efficiency: Material wastage is minimized by additive manufacturing, with CNC machining refining only essential areas, reducing overall waste and cost.[2]
- Shorter Lead Times: Rapid prototyping with 3D printing combined with swift CNC finishing accelerates product development cycles.[3]
- Material Versatility: This integration allows working with a wider range of materials, including high-strength metals and composites.[1]
- Expanded Applications: Enables manufacturing for sectors requiring lightweight, strong, customized parts such as aerospace, healthcare, automotive, and consumer goods.[16][1]
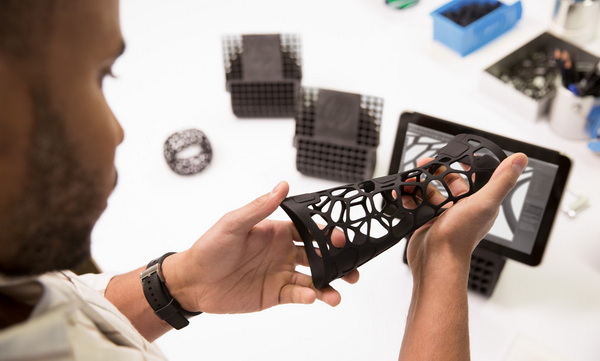
Parts require lightweight designs with complex internal structures achieved by 3D printing, followed by CNC machining to meet tight tolerances and surface finishes essential for high performance and safety.[17][1]
Custom implants and prosthetics are 3D printed to patient-specific shapes, then CNC machined for smooth surfaces and accuracy to improve biocompatibility and function.[16][2]
Hybrid manufacturing allows creation of detailed prototypes and small-series products that combine aesthetic appeal with functional durability.[14]
3D printing produces custom jigs and fixtures quickly, and CNC machining fine-tunes them for precision fit and function in manufacturing lines.[5]
Integrating CNC with 3D printing requires careful coordination:
- Data Exchange and Workflow: Seamless transfer between CAD/CAM software and machines is crucial to avoid errors.
- Workpiece Repositioning: Components must be accurately positioned when switching from printing to machining to maintain alignment.
- Material Compatibility: The chosen materials should suit both additive and subtractive processes without deformation or damage.
- Equipment Investment: Hybrid systems can be costly, but many manufacturers optimize existing 3D printing and CNC resources.[4][2]
Proper software solutions and skilled operators play key roles in overcoming these challenges to fully unlock the benefits of hybrid manufacturing.
The manufacturing industry continues evolving towards more integrated systems:
- Hybrid Machines: New equipment combining 3D printing and CNC machining within a single platform is emerging, automating workflows and reducing handling time.[7]
- Multimaterial Manufacturing: Combining different materials within one part through additive and subtractive methods advances functionality and design possibilities.[2]
- Smart Manufacturing: AI-driven process control and real-time monitoring improve precision, reduce errors, and optimize production.[4]
These innovations promise to broaden the reach and impact of the CNC and 3D printing synergy.
CNC in 3D printing represents a paradigm shift in manufacturing by merging additive and subtractive techniques. This hybrid approach maximizes design freedom, precision, material diversity, and cost-efficiency while enabling rapid prototyping and precision production. Factories like Shangchen harness this integration to deliver custom OEM services that meet the complex demands of global industries such as aerospace, healthcare, automotive, and consumer products. As technology advances, the symbiosis between CNC machining and 3D printing will continue to transform how parts are designed and manufactured for higher quality and faster delivery.
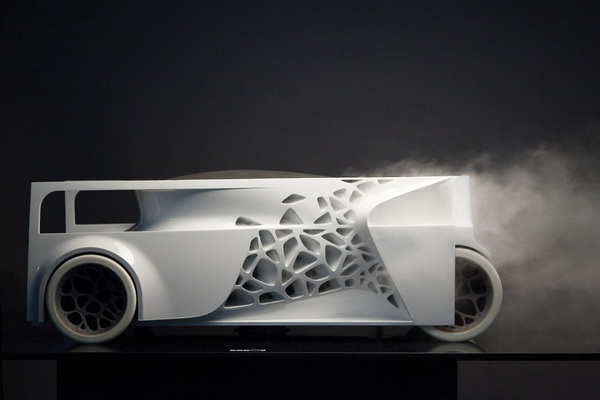
CNC machining refines 3D printed parts by improving dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and adding detailed features like threads or holes that printing alone cannot achieve. This hybrid process produces functional, high-quality parts faster than using each technology separately.
No, they serve different purposes. 3D printing excels at rapid prototyping and complex geometries, while CNC machining provides precision finishing and strength for final production. Together, they complement each other for optimized manufacturing.
Materials compatible with both 3D printing and CNC machining include various plastics, metals like aluminum and titanium, and composites. The hybrid process allows leveraging each material's benefits for complex, high-performance parts.
By additive manufacturing parts near-net-shape, it reduces raw material waste. CNC machining refines only critical surfaces or features, saving time and materials, resulting in overall cost reduction and faster lead times.
Aerospace, automotive, medical, consumer products, and tooling industries benefit greatly. These sectors demand complex designs, high precision, lightweight structures, and custom solutions achievable efficiently through hybrid manufacturing.
[1](https://www.cnchonscn.com/a-integration-of-3d-printing-technology-and-cnc-parts-machining.html)
[2](https://www.3erp.com/blog/cnc-machining-3d-printed-parts/)
[3](https://amfg.ai/2023/11/06/combine-3d-printing-and-cnc-machining/)
[4](https://www.pcbway.com/blog/CNC_Machining/Hybrid_Manufacturing_Technology_Combining_3D_Printing_and_CNC_Machining_d06a3493.html)
[5](https://bigrep.com/posts/cnc-or-3d-printing/)
[6](https://www.tctmagazine.com/digital-manufacturing-3d-printing-and-cnc-machining/)
[7](https://meltio3d.com/3d-printing-cnc/)
[8](https://www.harveyperformance.com/in-the-loupe/cnc-machining-3d-printing/)
[9](https://protoandgo.com/en/mixed-materials-in-prototyping-when-to-combine-3d-printing-and-cnc-for-best-results/)
[10](https://www.protolabs.com/resources/design-tips/balancing-cnc-machining-and-3d-printing-for-metal-parts/)
[11](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_numerical_control)
[12](https://ultimaker.com/learn/3d-printing-vs-cnc-comparing-additive-and-subtractive-manufacturing/)
[13](https://www.sc-rapidmanufacturing.com/3d-printing.html)
[14](https://www.sc-rapidmanufacturing.com/news/On-Demand-Production.html)
[15](https://www.xometry.com/resources/3d-printing/3d-printing-vs-cnc-machining/)
[16](https://www.hubs.com/knowledge-base/3d-printing-vs-cnc-machining/)
[17](https://www.sc-rapidmanufacturing.com/products/CNC-Process.html)
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal