
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-11-21 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Understanding 3D Printing and CNC Machining
● Faster Prototyping and Shorter Lead Times
● Cost-Effective for Low Volume and Complex Parts
● Unmatched Design Freedom and Complexity
● Minimizing Material Waste and Promoting Sustainability
● Enhanced Customization and On-Demand Manufacturing
● Low Skill Barrier and Automation Potential
● Considerations and Limitations
● FAQ
>> 1. What materials can be used in 3D printing compared to CNC machining?
>> 2. Can 3D printing completely replace CNC machining?
>> 3. How does cost compare between 3D printing and CNC machining?
>> 4. What about surface finish and precision quality?
>> 5. How fast is 3D printing compared to CNC machining?
3D printing technology has fundamentally changed the manufacturing landscape, offering significant advantages over traditional CNC machining methods. For companies like Shangchen, which specialize in rapid prototyping, CNC machining, precision batch production, turning, sheet metal fabrication, 3D printing, and mold production, understanding these advantages is essential for delivering competitive OEM solutions to international brands, wholesalers, and manufacturers.
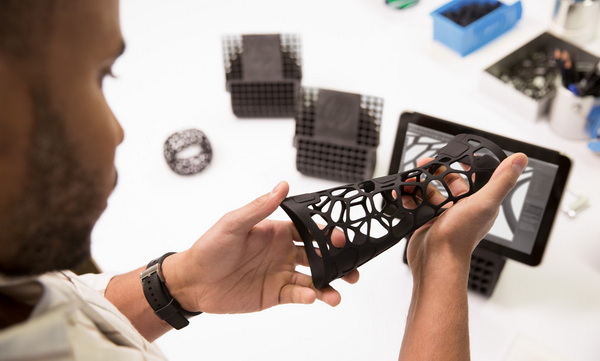
This article explores the numerous advantages of 3D printing compared to CNC machining, highlighting key factors like design flexibility, cost-effectiveness, speed, and sustainability. We will explain why 3D printing is becoming a preferred choice for many manufacturing applications and how it complements CNC machining to meet diverse production needs.
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, creates parts by adding material layer by layer according to a digital model. It enables the production of complex geometries, including intricate internal features, with minimal tooling or setup. Common 3D printing materials include various plastics, resins, metals, and composites.
In contrast, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that removes material from a solid block using precision cutting tools guided by computer programming. CNC excels at producing parts with high precision, excellent surface finish, and full material strength.
One of the strongest advantages of 3D printing is its ability to deliver parts quickly without the need for tooling. CNC machining often requires extensive setup time, including fixture creation and toolpath programming, which can take days or weeks depending on complexity.
3D printing drastically shortens this timeline as designs can be converted directly from CAD models into printable files and produced rapidly, often within hours. This rapid turnaround is invaluable during product development cycles that demand multiple design iterations and fast validation of prototypes.
CNC machining setup costs — from tooling and programming to machine time — make it less economical for small batch production or prototypes. 3D printing avoids these fixed costs, making it highly cost-efficient for low-volume parts, one-offs, or customized components.
Additionally, parts with complex shapes, internal channels, or lattice structures are expensive or impossible with CNC but can be produced easily and affordably with 3D printing. This cost advantage allows manufacturers to innovate without incurring prohibitive expenses.
3D printing enables the creation of geometries that are either impossible or very challenging for CNC machining. Examples include hollow parts, internal lattice structures for weight reduction, conformal cooling channels in molds, and organic shapes inspired by nature.
This design freedom fosters innovation and lightweighting — essential to industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, where performance and material efficiency are critical.
As an additive process, 3D printing uses only the material necessary to build a part, producing minimal waste compared to CNC machining, which cuts away excess material and generates chips, sometimes up to 90% of the original stock.
The reduction in material waste not only cuts raw material costs but also supports environmental sustainability goals by reducing scrap and energy use associated with material recycling and disposal.
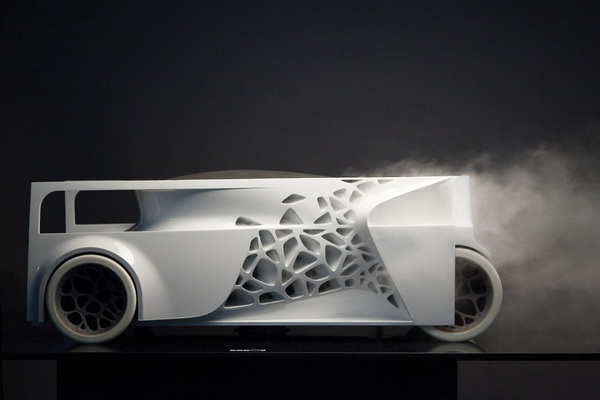
3D printing is highly suited for customized products and rapid design changes without interrupting production flow. OEMs and brands can offer personalized components or small runs with unique specifications without incurring the overhead of retooling or new CNC program development.
This flexibility supports trends toward mass customization and agile manufacturing, allowing companies like Shangchen to respond faster to market demands and customer needs.
Operating a 3D printer generally requires less specialized training than a CNC machining center, which demands expert programmers and machinists for toolpath creation, fixture design, and machine upkeep.
Furthermore, 3D printing's highly automated workflow—from design file to finished part—reduces labor intensity and allows for more scalable setups in office-friendly or small factory environments.
While 3D printing offers many benefits, it is important to balance these with some current limitations. Parts usually have lower mechanical strength compared to CNC-machined counterparts, often around 10–20% less due to the layered building process and material composition.
Precision and surface finish from 3D printing typically need post-processing to match CNC machining standards. Also, CNC machining remains more cost-effective at high production volumes where setup costs are amortized, and it's critical for parts requiring high tolerance and engineering-grade material properties.
3D printing presents several compelling advantages over CNC machining, especially in rapid prototyping, cost efficiency for complex and low-volume parts, design freedom, waste minimization, and customization. While CNC machining excels in precision, material properties, and scalability for large runs, the complementary use of 3D printing enables manufacturers like Shangchen to offer flexible, innovative, and cost-effective OEM production solutions on a global scale.
By integrating 3D printing into manufacturing workflows alongside CNC machining, businesses can accelerate product development, reduce costs, and respond dynamically to changing market demands, ensuring competitive advantage in today's fast-paced industrial environment.

3D printing supports a diverse range of materials, including plastics, resins, metals (like aluminum, titanium, stainless steel), and composites. CNC machining uses solid blocks of metals, plastics, and some composites, typically offering parts with native material properties and higher structural strength.
No. 3D printing and CNC machining serve different purposes. CNC machining remains essential for high-precision, high-strength parts and large production runs. 3D printing excels in rapid prototyping, complex geometries, and low-volume manufacturing but does not match CNC in scale or certain mechanical properties.
3D printing is generally more cost-effective for prototypes, complex parts, and single units or small batches due to lack of tooling costs. CNC machining becomes more economical for larger production volumes where setup costs are spread over many parts.
CNC machining produces parts with superior surface finish and tighter tolerances. 3D printed parts often require finishing processes like sanding, polishing, or heat treatment to improve aesthetics and functional performance.
3D printing offers faster start-to-finish turnaround for simple or moderate-sized parts, especially in prototyping phases. CNC machining requires setup but may have faster per-part production time once running efficiently, especially for larger batch runs.
[1](https://www.xometry.com/resources/3d-printing/3d-printing-vs-cnc-machining/)
[2](https://ultimaker.com/learn/3d-printing-vs-cnc-comparing-additive-and-subtractive-manufacturing/)
[3](https://www.americanmicroinc.com/resources/cnc-machining-3d-printing/)
[4](https://www.hubs.com/knowledge-base/3d-printing-vs-cnc-machining/)
[5](https://jlc3dp.com/blog/3d-printing-vs-cnc-machining)
[6](https://xometry.pro/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/EN-3d-printing-vs-cnc-machining.pdf)
[7](https://www.reddit.com/r/hobbycnc/comments/vabew6/3d_printing_vs_cnc_machine/)
[8](https://www.stratasys.co.jp/contentassets/c7d18093035d4b4cb9151b7052bfaef4/wp_fdm_3dpvscnc_0621a.pdf?v=4966da)
[9](https://xometry.pro/en/articles/cnc-machining-vs-3d-printing/)
[10](https://www.raise3d.com/blog/comparing-cnc-machining-and-fff-3d-printing/)
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal