
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-10-23 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● What is Vacuum Mold Casting?
● Stages and Lead Time of Vacuum Mold Casting
● Comparing Lead Times with Other Prototyping Methods
>> 3D Printing
● Factors Influencing Lead Times in Prototyping
● Advantages of Vacuum Mold Casting Regarding Lead Time
● Practical Applications of Vacuum Mold Casting
● Common Misconceptions About Lead Times
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the typical lead time for Vacuum Mold Casting?
>> 2. How does Vacuum Mold Casting compare with 3D printing lead times?
>> 3. Is Vacuum Mold Casting suitable for high volume production?
>> 4. What factors influence lead time in Vacuum Mold Casting?
>> 5. Can Vacuum Mold Casting parts be used for functional testing?
When selecting a prototyping method, understanding the lead time—the duration between concept and finished part—is key to meeting project deadlines and budget requirements. This article delves into comparing lead times between Vacuum Mold Casting and other prevalent prototyping technologies such as 3D printing, injection molding, and CNC machining. It highlights the strengths and limitations of each method to guide designers, manufacturers, and product developers in making informed choices.
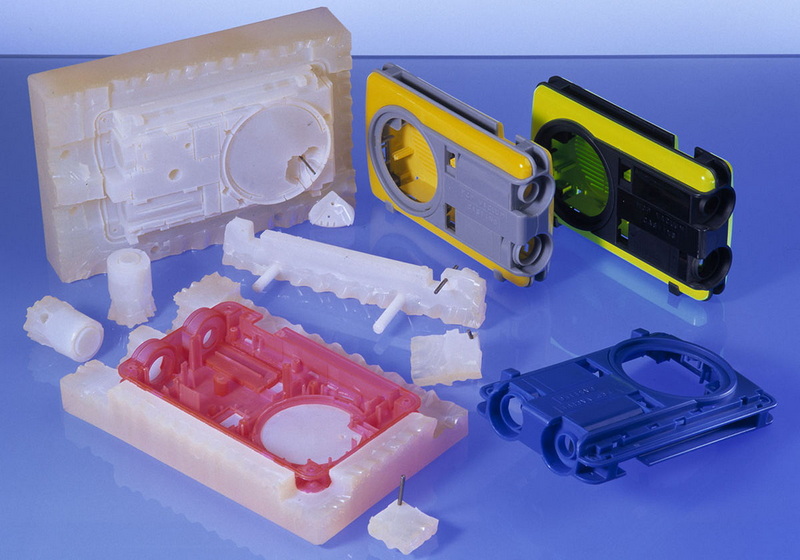
Vacuum Mold Casting is a specialized technique for producing precise, high-quality prototype parts and low-volume production components. It involves creating a master model (often produced through 3D printing or CNC machining), forming a flexible silicone mold around it, and then casting liquid resin into the mold under vacuum conditions. The vacuum environment removes air bubbles, resulting in parts with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
This technique supports producing a wide range of materials, primarily polyurethane resins that simulate thermoplastics and rubber, making it highly versatile for functional and aesthetic prototypes.
The lead time for Vacuum Mold Casting breaks down into several stages:
1. Master Pattern Creation: This typically takes 1 to 3 days. The master is a high-quality part produced by 3D printing or CNC machining, serving as the mold template.
2. Silicone Mold Fabrication: Creating the silicone mold generally takes 5 to 7 days, depending on complexity and size.
3. Casting Process: Casting resin parts under vacuum and allowing them to cure takes about 1 to 2 weeks for small batch runs.
Adding these phases, the total lead time ranges from 1 to 3 weeks. This timeframe balances the speed of mold creation with the detail and quality assurance of the parts produced.
3D printing delivers prototypes extremely fast, often within hours to a few days depending on the technology (e.g., FDM, SLA, or SLS) and part complexity. It is the quickest for single prototypes or very low-volume needs but may require post-processing to improve surface finish and strength.
The lead time for 3D printing is typically:
- Design to finished prototype: hours to a few days
- Ideal for: One-off parts, complex geometries, rapid iteration
- Limitations: Surface finish roughness, limited material options, lower strength versus molded parts
While 3D printing excels at delivering rapid, intricate prototypes, it slows for higher volumes, where vacuum casting becomes more competitive.[9][10]
Injection molding involves high upfront cost and longer lead times due to the need to produce durable metal molds. The process includes CNC machining of steel molds, which can take 2 to 4 weeks or longer depending on complexity.
Lead time considerations:
- Mold fabrication: 2 to 4+ weeks
- Production cycle time: seconds to minutes per part
- Ideal for: Large volume runs with consistent high quality
- Limitations: High upfront mold costs, not suitable for small batch or rapid prototyping
Injection molding is unmatched for mass production but less practical for prototypes due to its lead times and tooling expenses.[11][12]
CNC machining directly fabricates parts from solid blocks of material, often metals or plastics. It is suitable for high-precision prototypes and small series production.
Lead time details include:
- Programming and setup: 1 to 3 days
- Machining time: hours to several days depending on complexity
- Ideal for: Functional prototypes and master patterns for molds
- Limitations: Increased time and cost for complex geometries, material wastage
CNC machining can be a bottleneck for complex shapes but offers excellent control over dimensional accuracy and material properties. It is often used in combination with vacuum casting, making the initial master pattern.[13][14]

Several elements impact the turnaround time for vacuum mold casting and other methods:
- Part complexity: Increased intricacy demands longer master pattern and mold-making times.
- Batch size: Vacuum casting suits low to medium batches; injection molding favors large production.
- Material requirements: Specialized materials, especially those requiring longer curing times, can extend lead time.
- Post-processing needs: Some methods require finishing steps such as sanding or painting, adding to total time.
- Iteration cycles: Prototyping often involves multiple cycles, where fast methods like 3D printing speed up design validation.
Vacuum Mold Casting strikes a balance among prototyping techniques by offering:
- Faster mold production than injection molding due to silicone molds instead of metal
- Ability to produce multiple quality parts per mold, reducing total lead time for small batches
- Superior surface finish and material variety compared to 3D printing
- Cost-efficiency for parts ranging from 10 to 100 units without large tooling investments
These factors make Vacuum Mold Casting especially attractive in scenarios where part quality and moderate lead time are critical.[15][16]
Vacuum Mold Casting is extensively utilized in:
- Product development cycles: For functional parts, fit checks, and design verification
- Low-volume production: Limited markets or regional distribution without large tooling costs
- Aesthetic prototypes: Consumer products needing realistic finishes and accurate colors
- Medical devices: Custom parts with biocompatible resins
- Automotive and aerospace: Production of non-load-bearing components for testing or limited use
Its relatively quick turnaround and quality results present a strong alternative or complement to other prototyping and production methods.[17][15]
- Vacuum Mold Casting is slower than 3D printing: While 3D printing is faster for single pieces, vacuum casting outperforms when producing small batches.
- Injection molding is always faster: Injection molding speeds in production but requires long delays for mold fabrication.
- CNC machining is the fastest for prototypes: Machining is precise but not always quickest, especially for complex or multiple pieces.
By understanding these nuances, teams can better align production schedules with business needs.
Vacuum Mold Casting offers a versatile prototyping method with moderate lead times generally ranging from one to three weeks, ideal for small to mid-sized production runs where quality and material fidelity are essential. Compared with ultra-rapid 3D printing, it provides superior finishes and material options yet requires longer lead time. Against injection molding, it boasts dramatically reduced mold preparation time and costs, though it sacrifices per-part speed. CNC machining remains a valuable complementary tool, often providing masters for casting molds.
Select Vacuum Mold Casting if your project demands high-quality prototypes or low-volume production components delivered on reliable timelines without the heavy upfront costs and delays associated with metal tooling.

The typical lead time ranges from 1 to 3 weeks, covering master pattern creation, mold making, and casting.
3D printing is faster for single prototypes (hours to days), while Vacuum Mold Casting suits small batches needing improved finish and durability (1-3 weeks).
No, it is optimized for low to medium volume production; high volume favors injection molding due to faster cycle times after mold setup.
Complexity of design, batch size, material curing time, and post-processing needs all affect overall lead time.
Yes, vacuum cast parts using polyurethane resins closely mimic various plastics, making them suitable for many functional prototype tests.
[1](https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/proceedings-of-the-international-conference-on-engineering-design/article/comparison-of-contemporary-prototyping-methods/B305887C698181D6061940BD05F03122)
[2](https://www.worldscientific.com/doi/10.1142/S2424862219500179)
[3](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0890695597001375)
[4](https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1007/978-3-031-17615-9_4)
[5](https://scholarworks.sjsu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1015&context=mech_eng_pub)
[6](https://www.lri.fr/~mackay/pdffiles/Prototype.chapter.pdf)
[7](https://www.naun.org/main/NAUN/mcs/16-591.pdf)
[8](https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/21650349.2023.2222115)
[9](https://www.makerverse.com/resources/casting/polymer-3d-printing-vs-vacuum-casting/)
[10](https://jlc3dp.com/blog/examining-and-differentiating-vacuum-casting-3d-printing-and-injection-moulding)
[11](https://xometry.pro/en/articles/vacuum-casting-vs-injection-molding/)
[12](https://www.3erp.com/blog/vacuum-casting-vs-injection-molding/)
[13](https://www.cnkaierwo.com/blogs/vacuum-casting-vs.-cnc-machining-a-technical-analysis-for-low-volume-production.html)
[14](https://firstpart.com/cnc_machining_vs_vacuum_casting_for_rapid_prototyping/)
[15](https://www.3erp.com/blog/vacuum-casting/)
[16](https://www.immould.com/vacuum-casting/)
[17](https://xometry.eu/en/vacuum-casting-technology-overview/)
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal