
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-10-18 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● What is Vacuum Mold Casting?
● What is Traditional Mold Casting?
>> Vacuum Mold Casting Process
>> Traditional Mold Casting Process (Injection Molding Example)
● Applications for Vacuum Mold Casting
● Applications for Traditional Mold Casting
>> Cost Efficiency Over Volume
● Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
>> 1. What materials are used in vacuum mold casting?
>> 2. How many parts can a silicone mold produce?
>> 3. Can vacuum casting replicate fine surface details?
>> 4. What is the cost difference between vacuum casting and injection molding?
>> 5. Can vacuum casting be used for large parts?
Choosing the right manufacturing process is essential to the success of any project involving molded parts. Vacuum mold casting and traditional mold casting are two prominent methods used in various industries, each with unique benefits and limitations. This article provides a detailed comparison of these two technologies to help you make the best decision whether you are producing prototypes, small runs, or large-scale manufacturing.
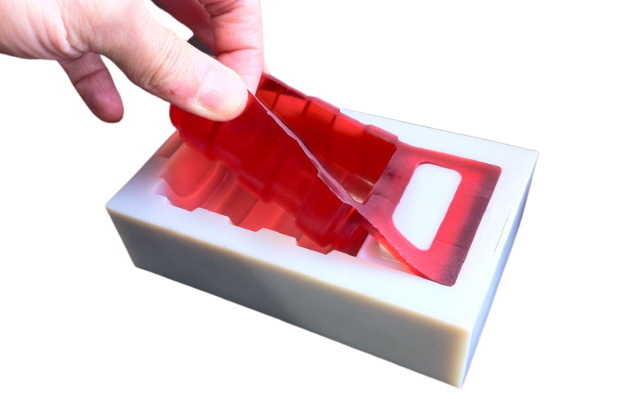
Vacuum mold casting, also called urethane casting, uses silicone molds and vacuum technology to produce parts with intricate details and smooth surface finishes. In this process, a master model—typically made via CNC machining or 3D printing—is used to create a flexible silicone mold. The mold is placed inside a vacuum chamber where liquid polyurethane resin is poured and drawn into the mold, ensuring air bubbles and voids are removed.
Key advantages include:
- Cost-effective for low volumes (commonly under 100 parts)
- Rapid mold production, often ready within a few days
- Excellent replication of fine surface textures and complex geometries
- Silicone molds can produce up to about 20 castings before replacement
- Suitable for prototypes, concept models, and limited production runs
The process combines speed, accuracy, and material flexibility, making it a preferred choice for functional prototypes and specialty components that require aesthetic or performance validation before committing to expensive tooling.
Traditional mold casting encompasses several established techniques such as injection molding, die casting, and sand casting. Injection molding is the most widespread method for producing plastic parts at scale. It involves injecting molten thermoplastic material into a precision-machined metal mold under high pressure.
Characteristics of traditional mold casting:
- Requires costly and time-consuming fabrication of metal molds
- Economical primarily for high-volume production runs (thousands to millions of parts)
- Wide selection of thermoplastic materials including ABS, polycarbonate, polypropylene
- Generally less capable than silicone molds at capturing extremely fine detail or complex undercuts
- Fast cycle times after mold setup, enabling mass production efficiencies
Traditional molding is optimal for when large volumes are required economically, but the initial investment and lead time can be prohibitive for short runs or rapid prototyping.
1. Master Model Creation: Produced via CNC machining or additive manufacturing (e.g., SLA 3D printing).
2. Silicone Mold Fabrication: Master is encased in liquid silicone rubber, which cures into a flexible form capturing all details.
3. Casting: Silicone mold is placed in a vacuum chamber; resin is mixed, degassed, and poured into the mold, vacuum-assisted to eliminate trapped air.
4. Curing and Demolding: Resin cures in an oven, then the mold is opened to retrieve the detailed casting. Molds can be reused several times.
1. Metal Mold Production: Steel or aluminum molds are precision-machined.
2. Material Melting: Thermoplastic pellets are melted in a heated barrel.
3. Injection: Molten plastic is injected into the metal mold under high pressure.
4. Cooling and Ejection: Part cools in the mold and is ejected quickly, ready for finishing if necessary.

| Criteria | Vacuum Mold Casting | Traditional Mold Casting (Injection Molding) |
| Tooling Cost | Low; silicone molds inexpensive and fast to produce | High; metal molds costly and time-consuming |
| Production Volume | Ideal for low volume, prototyping, small batch production | Best for medium to high volume mass production |
| Material Options | Polyurethane resins with various properties | Wide range of thermoplastics with different characteristics |
| Surface Finish & Detail | Superior fine detail, surface texture, and undercuts | Good but limited detail and surface texture replication |
| Lead Time | Short; mold ready in days | Long; mold lead times can be weeks or months |
| Cycle Time | Longer per part due to curing | Very fast cycles allowing mass production |
| Part Size & Complexity | Suited to small-medium, complex and detailed parts | Suited for parts of varying sizes; complexity limited by mold design |
| Reusable Molds | Approx. 20 uses before mold degradation | Thousands to millions of cycles |
| Waste & Environmental Impact | Low waste; silicone molds reusable but less durable | More waste due to scrap and runner systems |
Vacuum casting is commonly employed for:
- Rapid prototypes that closely mimic final injection molded parts
- Functional testing components for design validation
- Small batches of specialized parts for market testing or niche products
- Marketing models and product displays requiring high fidelity
- Parts with complex shapes, thin walls, or intricate textures
The flexibility of silicone molds and range of polyurethane materials used make vacuum casting an excellent choice for projects requiring aesthetic and functional realism at a lower upfront cost.
Traditional mold casting, especially injection molding, excels in:
- Manufacturing large volumes of plastic parts economically
- Producing durable components for automotive, consumer goods, electronics industries
- Materials selection tailored to strength, flexibility, chemical resistance, and more
- High repeatability and consistent quality for end-use products
The suitability lies in economies of scale and material versatility, making it indispensable for mass production with established designs.
Vacuum mold casting's silicone molds allow for complex geometries including undercuts and variable wall thicknesses without the need for draft angles or complex mold designs required in injection molding. This advantage supports rapid iteration during product development.
Although vacuum casting resins can mimic many plastic properties, they generally lack the full mechanical and thermal performance of injection molded thermoplastics. For functional parts exposed to heat or mechanical stress, traditional molded plastics may be necessary.
Vacuum casting is highly cost effective for volumes up to roughly 100 parts. Injection molding becomes more economical beyond this as the high tooling costs are amortized over many units.
Vacuum casting produces minimal waste with reusable molds but is limited by the mold's durability. Injection molding generates some scrap during start-up and material overflow but benefits from long-lasting metal molds.
Vacuum mold casting offers a compelling solution for low-volume, rapid production projects requiring superb detail and surface finish with minimal upfront cost. It is ideal for prototypes and short batch runs, allowing quick turnaround and design flexibility. Traditional mold casting, particularly injection molding, remains the dominant choice for high-volume manufacturing with superior material options and faster per-part production once the tool is in place.
By aligning your project's volume, budget, timeline, and quality requirements with the strengths of each method, you can select the ideal casting process to bring your designs to life efficiently and economically.
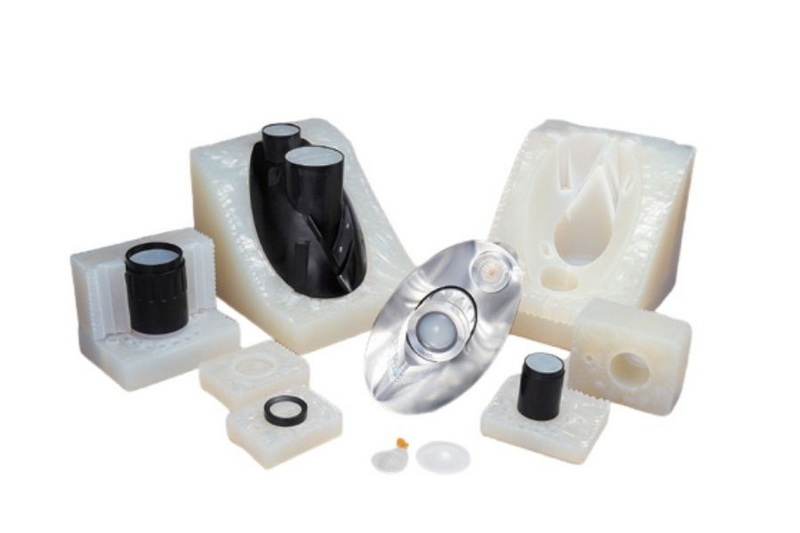

Vacuum mold casting primarily uses polyurethane resins that vary in hardness, color, and mechanical properties. These materials are durable and flexible but do not fully match the performance of traditional thermoplastics.
Typically, a silicone mold can be used to produce about 20 high-quality parts before losing detail or degrading, making it suitable for prototyping and small batch runs.
Yes, vacuum casting excels at capturing intricate textures, undercuts, and fine geometries thanks to the flexible silicone molds and vacuum bubble removal.
Vacuum casting has low tooling and setup costs, making it more affordable for small runs, while injection molding requires significant upfront investment in metal molds, cost-effective only for large volumes.
Vacuum casting is generally limited to small to medium-sized parts due to mold size and vacuum chamber constraints, whereas traditional casting can accommodate larger components depending on mold size.
[1](https://www.plasticmoulds.net/what-is-vacuum-casting-and-when-should-you-choose-it-over-traditional-molding.html)
[2](https://www.zeal3dprinting.com.au/injection-moulding-vs-vacuum-casting-a-comparative-analysis/)
[3](https://quickparts.com/gb/vacuum-casting-or-injection-moulding/)
[4](https://formlabs.com/blog/vacuum-casting-urethane-casting-polyurethane-casting/)
[5](https://www.lsrpf.com/blog/vacuum-casting-vs-centrifugal-casting-pros-cons-costs-and-applications)
[6](https://www.xavier-parts.com/vacuum-casting-process/)
[7](https://jlc3dp.com/blog/examining-and-differentiating-vacuum-casting-3d-printing-and-injection-moulding)
[8](https://www.sc-rapidmanufacturing.com/what-makes-vacuum-casting-different-from-other-casting-methods.html)
content is empty!
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Lithuania
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Norway
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Czech Republic
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Denmark
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Hungary
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Ireland
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Finland
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Greece
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Sweden
Top 5 Axis CNC Machining Manufacturers and Suppliers in Turkey