
Views: 222 Author: Amanda Publish Time: 2025-10-03 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Process Differences Explained
● Material and Product Considerations
● Advantages and Limitations Summarized
>> Injection Molding Advantages:
>> Injection Molding Limitations:
● Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
>> 1. What types of products are best manufactured with injection molding?
>> 2. Can blow molding produce parts with complex shapes?
>> 3. How do injection molding and blow molding differ in material use?
>> 4. Which molding process has lower mold costs?
>> 5. Is post-processing necessary for parts from these processes?
Injection molding and blow molding are two of the most widely used plastic manufacturing processes globally, each serving unique purposes and producing distinct types of products. Understanding their key differences is critical for manufacturers, brand owners, wholesalers, and producers seeking efficient OEM service partners. This article explores the technical distinctions, applications, advantages, process details, and challenges of both injection molding and blow molding, helping industry professionals make informed decisions.
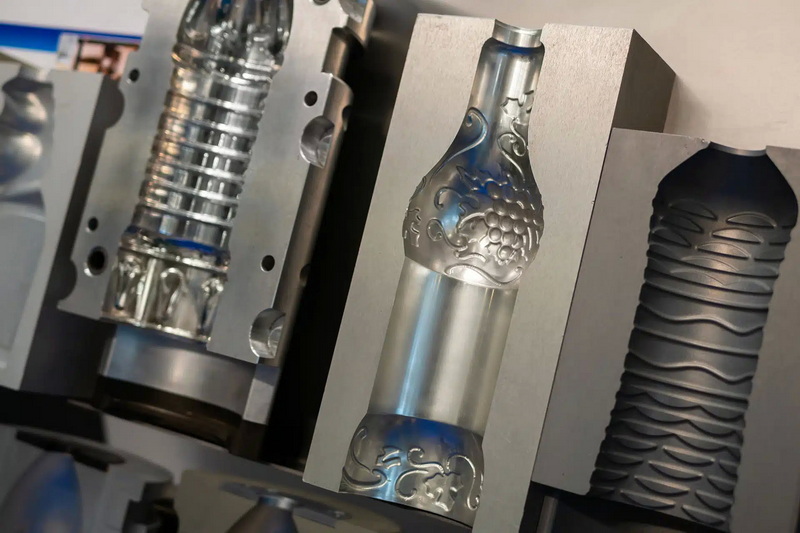

Injection molding is a precision manufacturing process where molten plastic is injected under high pressure into a meticulously designed mold cavity. The plastic then cools and solidifies to form a solid, durable part with intricate shapes and smooth finishes.
The process uses a specialized injection molding machine that melts plastic pellets and forces the molten plastic through a nozzle into the mold. This mold is typically made of hardened steel or aluminum, designed with extreme precision using CNC machining to guarantee tight tolerances and repeatability. Injection molding can produce complex geometries with detailed features that often require no additional finishing after molding.
Because of its accuracy and speed, injection molding is ideal for high-volume production runs. It is widely used to manufacture a variety of products including automotive components, electronic housings, kitchenware, medical devices, and industrial tools.
Injection molding offers several advantages:
- High dimensional accuracy and consistency across large quantities.
- Capability to mold complex and delicate designs.
- Fast cycle times allowing rapid production.
- Broad material compatibility including thermoplastics, thermosets, and reinforced plastics.
- Minimal post-processing required, reducing finishing costs.
Injection molds are costly to produce but offer longevity and can be used repeatedly without loss of quality, making injection molding economically viable for mass production.[1][2][3][11]
Blow molding is a manufacturing process specialized in forming hollow plastic parts by inflating a hot plastic tube (called a parison) inside a mold cavity. The softened parison is captured within the mold and air pressure is applied to blow the plastic outward, conforming to the shape of the mold.
There are several types of blow molding:
- Extrusion Blow Molding: Used mostly for making hollow containers by extruding a molten tube.
- Injection Blow Molding: Involves injecting molten plastic to form the parison, which is then blown into shape.
- Stretch Blow Molding: Adds a stretching phase for molecular orientation and strength, used for higher strength containers like beverage bottles.
Blow molding excels at producing thin-walled, hollow products such as bottles, jugs, fuel tanks, and large industrial containers. The mold design in blow molding is less complex than injection molds but requires a blowing port for air inflation.
Advantages of blow molding include:
- Cost-efficient tooling and mold creation compared to injection molding.
- Ability to produce large hollow parts that injection molding cannot make.
- Faster production for hollow shapes.
- Material savings due to thin walls.
However, blow molding is limited in its ability to produce intricate solid details and typically results in more variable wall thickness compared to injection molding. It is best suited for simpler, hollow shapes where uniform thickness is less critical.[2][3][12][1]
The defining difference between injection molding and blow molding lies in how the material takes shape inside the mold.
- In injection molding, plastic is injected as a molten mass under intense pressure into a closed mold cavity that entirely defines the solid part's shape.
- In blow molding, a softened plastic tube is placed inside an open mold and expanded by air pressure, pushing the plastic to the mold walls to form a hollow cavity.
Injection molding requires much higher pressure to force plastic into all mold sections, while blow molding uses air pressure to inflate the molten tube. Injection molds must be machined to very tight dimensions supporting complex part design, whereas blow molds are simpler and accommodate the inflation mechanism.
Injection molding solidifies quickly upon entering the cooler mold, providing fast cycle times. Blow molding requires additional time for inflation and cooling of the hollow structure, making the cycle generally slower.
Injection molding supports a broader range of materials including thermoplastics, thermosets, elastomers, and composites. It allows high-strength polymers to be used in engineering parts requiring durability and precision.
Blow molding is primarily used with thermoplastics that can be softened and formed into hollow shapes. The raw materials need to have sufficient toughness and flexibility to stretch without cracking during the blowing process.
Product design also dictates the choice:
- Injection molding is chosen for solid, complex, and multifeatured parts like gears, handles, and housings.
- Blow molding is best for hollow containers such as bottles, drums, and plastic tanks.
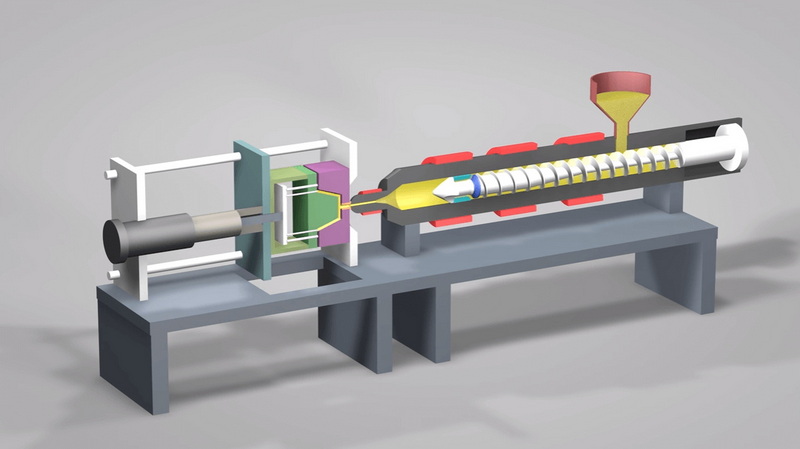
Injection molding molds generally cost more to create due to intricate precision machining and durable materials needed to withstand high pressure and high cycle fatigue. Despite higher initial tooling, injection molding becomes cost-effective for high volumes due to rapid cycles and minimal waste.
Blow molding offers more affordable tooling and is economical for producing large hollow products with lower complexity molds. While it may have slower cycle times, the lower tooling cost and material savings often balance production costs for suitable product types.
Manpower and machine complexity also differentiate these processes. Injection molding machines tend to be more complex and require skilled operators for troubleshooting, while blow molding machinery is often simpler with emphasis on controlling air pressure precisely.
- High precision and repeatability.
- Complex part geometry possible.
- Ability to use diverse materials.
- Fast production cycles.
- Minimal finishing required.
- Higher tooling cost.
- Not suitable for hollow parts.
- Design constraints regarding undercuts and thin walls.
- Ideal for hollow parts and containers.
- Lower initial tooling costs.
- Efficient for large volume hollow parts.
- Material efficient with thin walls.
- Less geometric complexity.
- Wall thickness variation.
- Longer cycle times.
Injection molding powers the production of high-precision plastic parts in medical equipment, electronics, automotive components, consumer products, and industrial machinery. Blow molding is indispensable in the packaging industry for water bottles, detergents, food containers, automotive fuel tanks, and large plastic drums.
By leveraging the strengths of each process—solid precise components via injection molding and lightweight hollow shapes via blow molding—factories like Shangchen can provide comprehensive OEM manufacturing solutions across various sectors.
Understanding the core differences between injection molding and blow molding ensures the right manufacturing choice for plastic products. Injection molding is the go-to for intricate solid components demanding precision and strength, while blow molding effectively produces hollow, thin-walled parts economically. Both processes complement each other in modern manufacturing, and selecting the appropriate method impacts product quality, cost-efficiency, and production speed significantly.
Working with an experienced manufacturer that offers both injection and blow molding capabilities provides the flexibility to meet diverse client needs—from intricate automotive parts to high-volume plastic containers. This strategic approach enables global brands and producers to harness optimal production technologies ensuring competitive excellence.
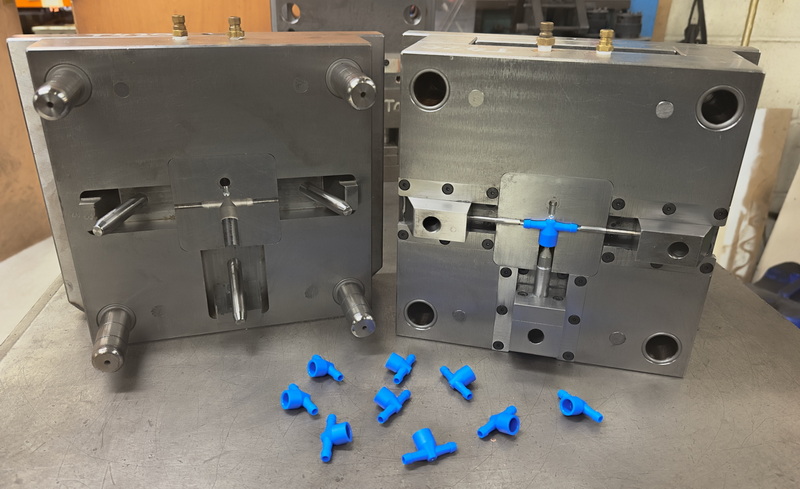
Injection molding is ideal for producing solid plastic parts with complex designs and tight tolerances, such as automotive components, medical devices, electronic housings, and durable consumer goods.[11][2]
Blow molding is generally limited to simpler hollow shapes like bottles and containers. It cannot replicate the fine intricate features achievable with injection molding.[3][5]
Injection molding supports a wider variety of materials including thermoplastics, thermosets, and composites, whereas blow molding primarily uses flexible thermoplastics suitable for hollow parts.[6]
Blow molding molds are typically less expensive to produce since the molds are simpler and require less precision than injection molds.[1][3]
Injection molded parts often require minimal post-processing due to their precision finish, whereas blow molded parts may need trimming or surface finishing depending on the product.[3]
[1](https://www.rapiddirect.com/blog/blow-molding-vs-injection-molding/)
[2](https://www.rcoeng.com/blog/blow-molding-vs-injection-molding)
[3](https://zetarmold.com/injection-molding-blow-molding/)
[4](https://www.madearia.com/blog/blow-molding-vs-injection-molding/)
[5](https://eupegypt.com/blog/blow-molding-vs-injection-molding/)
[6](https://www.xometry.com/resources/injection-molding/blow-molding-vs-injection-molding/)
[7](https://www.cdf1.com/blow-molding-vs-injection-molding-whats-the-difference/)
[8](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XsJzRImP8JY)
[9](https://www.kaysun.com/blog/blow-molding-vs.-injection-molding)
[10](https://www.djmolding.com/injection-molding-vs-blow-molding-a-comprehensive-comparison/)
[11](https://www.yichyi.com/zh/250/defining-custom-plastic-injection-molding/)
[12](https://www.micronsolutions.com/blog/blow-molding-vs-injection-molding)
content is empty!
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Germany
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Russia
Top CNC Machining Parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal